The Human Body Quiz 1
... As part of an extended field investigation, Steve made the table above to summarize facts about the muscular system. Based on the information in the table, it can be concluded that A there are three types of muscle B tendons act voluntarily C only skeletal muscle can act involuntarily D not here The ...
... As part of an extended field investigation, Steve made the table above to summarize facts about the muscular system. Based on the information in the table, it can be concluded that A there are three types of muscle B tendons act voluntarily C only skeletal muscle can act involuntarily D not here The ...
Article in PDF
... ligament condition shows autosomal dominant inheritance, can be surgically corrected. Ours is the first such report of costocoracoid ligament in cadaver, since it is seen only in right limb so suggesting acquired (probable traumatic) cause. ...
... ligament condition shows autosomal dominant inheritance, can be surgically corrected. Ours is the first such report of costocoracoid ligament in cadaver, since it is seen only in right limb so suggesting acquired (probable traumatic) cause. ...
PPT slides - gserianne.com
... Auditory Tube • Eustachian, auditory, or pharyngotympanic tube • connects middle ear to throat • helps maintain equal pressure on both sides of tympanic membrane • usually closed by valve-like flaps in throat When pressure in tympanic cavity is higher than in nasopharynx, tube opens automatically. ...
... Auditory Tube • Eustachian, auditory, or pharyngotympanic tube • connects middle ear to throat • helps maintain equal pressure on both sides of tympanic membrane • usually closed by valve-like flaps in throat When pressure in tympanic cavity is higher than in nasopharynx, tube opens automatically. ...
Earthworm Dissection Lab draft
... 2. Annelids have the first true closed circulatory system, meaning all of their blood is contained in vessels – including the heart. Explain why this is more efficient than an open circulatory system – a system where the blood vessels open into a large cavity so that the blood is not always containe ...
... 2. Annelids have the first true closed circulatory system, meaning all of their blood is contained in vessels – including the heart. Explain why this is more efficient than an open circulatory system – a system where the blood vessels open into a large cavity so that the blood is not always containe ...
Human Body Quiz
... What human body feature allows the respiratory system to take in oxygen? A. muscles pull the lungs open to draw in air B. the heart is divided into four chambers C. the excretory system carries waste products to the lungs D. the stomach muscles are able to churn and mix food ...
... What human body feature allows the respiratory system to take in oxygen? A. muscles pull the lungs open to draw in air B. the heart is divided into four chambers C. the excretory system carries waste products to the lungs D. the stomach muscles are able to churn and mix food ...
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Parasitic Helminths
... found in separate individuals. Monoecious (Hermaphroditic): One animal has both ...
... found in separate individuals. Monoecious (Hermaphroditic): One animal has both ...
THE GALLBLADDER
... rectus abdominis and costal margin 3. At level of elbow 4. Most anterior visceral structure ...
... rectus abdominis and costal margin 3. At level of elbow 4. Most anterior visceral structure ...
Arthopoda - El Camino College
... Its blood is harvested for a test to ensure medical products are not contaminated. 45 minutes of exposure to the crab's blood is enough to reveal bacteria contamination which otherwise avoid detection It is sensitive enough to isolate a threat the equivalent size of a grain of sand in a swimming poo ...
... Its blood is harvested for a test to ensure medical products are not contaminated. 45 minutes of exposure to the crab's blood is enough to reveal bacteria contamination which otherwise avoid detection It is sensitive enough to isolate a threat the equivalent size of a grain of sand in a swimming poo ...
Weekly Schedule of Blood, Inflammation and Immunity
... Recognize the congenital anomalies of limbs by knowing their development. Identify various nerve injuries in the arm at different levels Recognize the importance of brachial artery Identify the clinical manifestations of Colles’fracture in correlation to the knowledge of structures of forearm. Recog ...
... Recognize the congenital anomalies of limbs by knowing their development. Identify various nerve injuries in the arm at different levels Recognize the importance of brachial artery Identify the clinical manifestations of Colles’fracture in correlation to the knowledge of structures of forearm. Recog ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Quiz on Shoulder and Spine
... Quiz on Shoulder and Spine Directions: Please answer the questions shown in the following slides. When you have answered incorrectly, you will be taken back to the previous slide. If you answer correctly you will proceed to the next slide. Please feel free to take this quiz as many times as you wish ...
... Quiz on Shoulder and Spine Directions: Please answer the questions shown in the following slides. When you have answered incorrectly, you will be taken back to the previous slide. If you answer correctly you will proceed to the next slide. Please feel free to take this quiz as many times as you wish ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Introduction to
... None of the systems functions in isolation. The passive skeletal and articular systems and the active muscular system collectively constitute a supersystem, the locomotor system, because they must work together to produce locomotion of the body. Although the structures directly responsible for locom ...
... None of the systems functions in isolation. The passive skeletal and articular systems and the active muscular system collectively constitute a supersystem, the locomotor system, because they must work together to produce locomotion of the body. Although the structures directly responsible for locom ...
Words and the anatomical position
... When you stand in the anatomical position, your head is superior to your chest. In everyday language you say that your head is above your chest. Strict anatomists frown at colloquialisms like this, but they are in common use. In this book I switch between correct and colloquial terms as seems most n ...
... When you stand in the anatomical position, your head is superior to your chest. In everyday language you say that your head is above your chest. Strict anatomists frown at colloquialisms like this, but they are in common use. In this book I switch between correct and colloquial terms as seems most n ...
12.3 Notes on Amphibians
... Metamorphosis to grow lungs/lose gills and add to circulatory system Diversity of Amphibians 2 majors groups: o salamanders- have a tail o frogs/toads- no tail difference is the ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... Metamorphosis to grow lungs/lose gills and add to circulatory system Diversity of Amphibians 2 majors groups: o salamanders- have a tail o frogs/toads- no tail difference is the ______________________________________________________________________ ...
Anatomy Terms
... Coronal or Frontal Plane: For quadrupeds a coronal plane is horizontal and a transverse plane is vertical. Sagittal Plane: Perpendicular to the coronal plane, which separates left from right. Mid-Sagittal Plane: The specific sagittal that is exactly in the middle of the body. Oblique Plane: Oblique ...
... Coronal or Frontal Plane: For quadrupeds a coronal plane is horizontal and a transverse plane is vertical. Sagittal Plane: Perpendicular to the coronal plane, which separates left from right. Mid-Sagittal Plane: The specific sagittal that is exactly in the middle of the body. Oblique Plane: Oblique ...
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of
... the larynx to the lungs by dividing into the bronchi. The trachea contains an epithelial lining that secretes mucus, which traps any dust. It is then swept upwards by the cilia towards the larynx away from the lungs. The bronchi are supported by cartilage and are formed when the trachea forks into t ...
... the larynx to the lungs by dividing into the bronchi. The trachea contains an epithelial lining that secretes mucus, which traps any dust. It is then swept upwards by the cilia towards the larynx away from the lungs. The bronchi are supported by cartilage and are formed when the trachea forks into t ...
Trigeminal (Gasserian) Ganglion Block
... radiofrequency at 42°C for a 120-second cycle times two to three cycles. • Standard radiofrequency neurolysis can also be performed at 67°C for 90 seconds. associated with a risk of sensory loss in the trigeminal nerve distribution. ...
... radiofrequency at 42°C for a 120-second cycle times two to three cycles. • Standard radiofrequency neurolysis can also be performed at 67°C for 90 seconds. associated with a risk of sensory loss in the trigeminal nerve distribution. ...
Dissection of the Rat
... The rat is a vertebrate, which means that many aspects of its structural organization are common with all other vertebrates, including humans. The similarity of structures among related organisms shows evidence of common ancestry. In a way, studying the rat is like studying a human. As the leading t ...
... The rat is a vertebrate, which means that many aspects of its structural organization are common with all other vertebrates, including humans. The similarity of structures among related organisms shows evidence of common ancestry. In a way, studying the rat is like studying a human. As the leading t ...
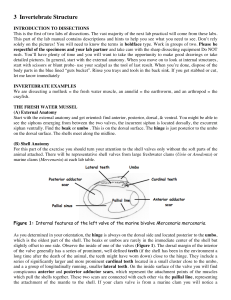
3 Invertebrate Structure
... removed carapace. Flanking the posterior ones is a pair of powerful muscles that extend ventrally to insert on the mandibles. To reveal the extent of the stomach, remove the muscles attached to it and separate the lobes of the digestive glands anterior to the heart. Observe the larger, cardiac stoma ...
... removed carapace. Flanking the posterior ones is a pair of powerful muscles that extend ventrally to insert on the mandibles. To reveal the extent of the stomach, remove the muscles attached to it and separate the lobes of the digestive glands anterior to the heart. Observe the larger, cardiac stoma ...
Shoulder Anatomy and Injuries - PA
... Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint • Synovial Joint double gliding joint • side to side & front to back ...
... Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint • Synovial Joint double gliding joint • side to side & front to back ...
INTRODUCTION
... _____ 2. Homeostasis describes the stable environment that the human body maintains, enabling the body to function properly. When an outside stimulus threatens to disrupt homeostasis, body systems work to bring things back into balance. Which of the following directly describes systems working toget ...
... _____ 2. Homeostasis describes the stable environment that the human body maintains, enabling the body to function properly. When an outside stimulus threatens to disrupt homeostasis, body systems work to bring things back into balance. Which of the following directly describes systems working toget ...
What Does The Heart Do? Lesson Idea Grades 3-5
... a muscle that works all the time; it is a kind of pump; the heart beats faster after exercise.) What does the heart pump? (Blood) Where does the heart pump blood? (To every part of the body) ...
... a muscle that works all the time; it is a kind of pump; the heart beats faster after exercise.) What does the heart pump? (Blood) Where does the heart pump blood? (To every part of the body) ...
Human Anatomy and Histology course Lecturer: Anna Barlasov PhD
... Location: Within blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins) and within the chambers of the heart. Function: Red blood cells transport oxygen and some carbon dioxide; white blood cells carry on phagocytosis and are involved in allergic reactions and immune system responses; ...
... Location: Within blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins) and within the chambers of the heart. Function: Red blood cells transport oxygen and some carbon dioxide; white blood cells carry on phagocytosis and are involved in allergic reactions and immune system responses; ...
History of anatomy

The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern scientists. It has been characterized, over time, by a continually developing understanding of the functions of organs and structures in the body. Human anatomy was the most prominent of the biological sciences of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Methods have also improved dramatically.