Comparison of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Homologies of Six Strains of
... could be separated from one another based upon differences in polynucleotide sequence homologies and to determine whether there are any polynucleotide sequence homologies among the four genera of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria which we examined. In the past, DNA-DNA hybridization studies involving the a ...
... could be separated from one another based upon differences in polynucleotide sequence homologies and to determine whether there are any polynucleotide sequence homologies among the four genera of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria which we examined. In the past, DNA-DNA hybridization studies involving the a ...
AP Biology Chapter 20 Biotechnology Guided Notes
... • In humans, researchers analyze the genomes of many people with a certain genetic condition to try to find nucleotide changes specific to the condition • Genetic markers called SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) occur on average every 100– 300 base pairs • SNPs can be detected by PCR, and any ...
... • In humans, researchers analyze the genomes of many people with a certain genetic condition to try to find nucleotide changes specific to the condition • Genetic markers called SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) occur on average every 100– 300 base pairs • SNPs can be detected by PCR, and any ...
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is
... coenzyme A, FAD, and NAD+. This common structure may reflect a common evolutionary origin as part of ribozymes in an ancient RNAworld. It has been suggested that the AMP part of the molecule can be considered a kind of "handle" by which the enzyme can "grasp" the coenzyme to switch it between differ ...
... coenzyme A, FAD, and NAD+. This common structure may reflect a common evolutionary origin as part of ribozymes in an ancient RNAworld. It has been suggested that the AMP part of the molecule can be considered a kind of "handle" by which the enzyme can "grasp" the coenzyme to switch it between differ ...
eprint_1_29837_493
... Many enzymes require the presence of small non-protein organic molecules for their efficient performances. Only when both enzy-me and co-enzyme are present catalysis will occur. Co-enzymes are low molecular weight, non-protein organic compounds that are heat resistant, function as cosubstances. Usua ...
... Many enzymes require the presence of small non-protein organic molecules for their efficient performances. Only when both enzy-me and co-enzyme are present catalysis will occur. Co-enzymes are low molecular weight, non-protein organic compounds that are heat resistant, function as cosubstances. Usua ...
Lecture3- Molecular Biology-1(2013).
... Two polynucleotide chains wind around a common axis to form a double helix The two strands are anti-parallel (run in opposite direction) Each strand is a right-handed helix The nitrogenous bases are in the center of the double helix and the sugar-phosphate chains are on the sides ...
... Two polynucleotide chains wind around a common axis to form a double helix The two strands are anti-parallel (run in opposite direction) Each strand is a right-handed helix The nitrogenous bases are in the center of the double helix and the sugar-phosphate chains are on the sides ...
Allosteric enzymes
... Some enzymes, mostly digestive enzymes, are originally secreted from the organ of production in a structurally inactive form, called a proenzyme or zymogen. Other enzymes later alter the structure of the zymogen to make active sites available by hydrolyzing specific amino acid residues. This mechani ...
... Some enzymes, mostly digestive enzymes, are originally secreted from the organ of production in a structurally inactive form, called a proenzyme or zymogen. Other enzymes later alter the structure of the zymogen to make active sites available by hydrolyzing specific amino acid residues. This mechani ...
Chromatin: a multi-scale jigsaw puzzle
... determine the destinations of the nucleosomes that they mobilize. Rather, the remodelling complexes may allow nucleosomes to sample and so genomes encode information to bias alternative positions rapidly, explicit resulting in a thermodynamic equilibrium between the nucleosomes and the site-specific ...
... determine the destinations of the nucleosomes that they mobilize. Rather, the remodelling complexes may allow nucleosomes to sample and so genomes encode information to bias alternative positions rapidly, explicit resulting in a thermodynamic equilibrium between the nucleosomes and the site-specific ...
Protein Synthesis
... The single stranded _____ molecule falls on it’s side with it’s nitrogen bases pointing _____ and moves out of the nucleus to find a __________. Each group of 3 nitrogen bases in mRNA is called a __________. AUG is a special codon that is called an ________________. It always codes for the amino aci ...
... The single stranded _____ molecule falls on it’s side with it’s nitrogen bases pointing _____ and moves out of the nucleus to find a __________. Each group of 3 nitrogen bases in mRNA is called a __________. AUG is a special codon that is called an ________________. It always codes for the amino aci ...
Enzymes - Philadelphia University Jordan
... VIII. Enzymes Clinical Diagnosis A. Alteration of plasma enzyme levels in disease states • Many diseases that cause tissue damage result in an increased release of intracellular enzymes into the plasma. • determining the degree of elevation of a particular enzyme activity in the plasma is often use ...
... VIII. Enzymes Clinical Diagnosis A. Alteration of plasma enzyme levels in disease states • Many diseases that cause tissue damage result in an increased release of intracellular enzymes into the plasma. • determining the degree of elevation of a particular enzyme activity in the plasma is often use ...
ENZYMES
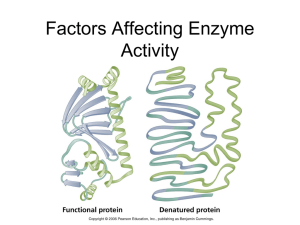
... shape. The overall 3D shape of an enzyme molecule is very important: if it is altered, the enzyme cannot bind to its substrate and so cannot function. Enzyme shape is maintained by hydrogen bonds and ionic forces. Enzymes have several important properties: Enzymes are specific: each enzyme usually ...
... shape. The overall 3D shape of an enzyme molecule is very important: if it is altered, the enzyme cannot bind to its substrate and so cannot function. Enzyme shape is maintained by hydrogen bonds and ionic forces. Enzymes have several important properties: Enzymes are specific: each enzyme usually ...
Sourcing, Storing And Handling Enzymes
... Tel: 01895 251496; Fax: 01895 814372; E-mail: [email protected]; Web site: www.cleapss.org.uk ...
... Tel: 01895 251496; Fax: 01895 814372; E-mail: [email protected]; Web site: www.cleapss.org.uk ...