- ESAIM: Proceedings
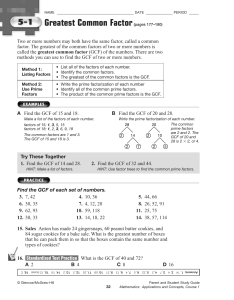
... tree, where each vertex has a fixed number (say m, with m > 1) of offspring. For example, here is a rooted binary tree: Let Zn denote the number of vertices (also called particles or individuals) in the n-th generation, then Zn = mn , ∀n ≥ 0. In probability theory, we often encounter trees where the ...
... tree, where each vertex has a fixed number (say m, with m > 1) of offspring. For example, here is a rooted binary tree: Let Zn denote the number of vertices (also called particles or individuals) in the n-th generation, then Zn = mn , ∀n ≥ 0. In probability theory, we often encounter trees where the ...