1 Formal Languages
... Note: the term ‘symbol’ may be replaced by the term ‘character’, as used in many computer languages, such as Basic, Pascal, and C++. Notice in this connection that the term ‘string’ is also used in many computer languages, usually to mean string of characters. Let us not worry too much about exactly ...
... Note: the term ‘symbol’ may be replaced by the term ‘character’, as used in many computer languages, such as Basic, Pascal, and C++. Notice in this connection that the term ‘string’ is also used in many computer languages, usually to mean string of characters. Let us not worry too much about exactly ...
Noncommutative Uniform Algebras Mati Abel and Krzysztof Jarosz
... Proof of Theorem 1. It is clear that our condition kak ≤ C,C (a) implies that ,C (ab) ≤ γ,C (a) ,C (b) , with γ = C 2 . Since the commutant Cπ is a normed real division algebra ([3] p. 127) it is isomorphic with R, C, or H. Hence by Theorem 2 any irreducible representation of A in an algebra of line ...
... Proof of Theorem 1. It is clear that our condition kak ≤ C,C (a) implies that ,C (ab) ≤ γ,C (a) ,C (b) , with γ = C 2 . Since the commutant Cπ is a normed real division algebra ([3] p. 127) it is isomorphic with R, C, or H. Hence by Theorem 2 any irreducible representation of A in an algebra of line ...
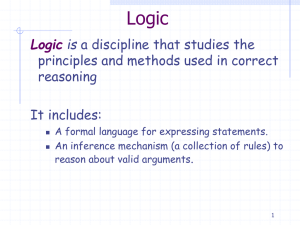
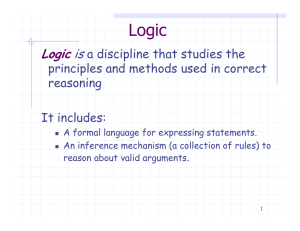
First-Order Logic
... Suppose that F is not valid, i.e., there is an interpretation I such that the above assumption holds. By following the semantic argument steps, one can show that each step preserves satisfiability. (For or-nodes, one new branch will be satisfiable.) This may require updating the current interpretati ...
... Suppose that F is not valid, i.e., there is an interpretation I such that the above assumption holds. By following the semantic argument steps, one can show that each step preserves satisfiability. (For or-nodes, one new branch will be satisfiable.) This may require updating the current interpretati ...
2 - arithmetic exlicit sequence.notebook
... Students write sequences with explicit formula. Students learn the structure of arithmetic sequences. ...
... Students write sequences with explicit formula. Students learn the structure of arithmetic sequences. ...
MATH 225A PROBLEMS OCTOBER 2, 2012 (1)
... (i) Show that T rL/K : L × L → K; (x, y) 7→ T rL/K (xy) is a non-degenerate, symmetric, K-bilinear form on L. (ii) Show that the map T rL/K : L → K; x 7→ T rL/K (x) is surjective. (Hint for both (i) and (ii): Artin’s theorem on linear independence of characters.) (4) Suppose that K is a number field ...
... (i) Show that T rL/K : L × L → K; (x, y) 7→ T rL/K (xy) is a non-degenerate, symmetric, K-bilinear form on L. (ii) Show that the map T rL/K : L → K; x 7→ T rL/K (x) is surjective. (Hint for both (i) and (ii): Artin’s theorem on linear independence of characters.) (4) Suppose that K is a number field ...
Furstenberg`s topological proof of the infinitude of primes
... Recall that if X is a set, a collection B of subsets of X is a basis for a topology on X if (1) every element of X is contained in a basis element, and (2) if x ∈ B1 ∩ B2 for two basis elements Bi , there exists a basis element B3 such that x ∈ B3 ⊆ B1 ∩ B2 . A set S ⊆ X is called open in the topolo ...
... Recall that if X is a set, a collection B of subsets of X is a basis for a topology on X if (1) every element of X is contained in a basis element, and (2) if x ∈ B1 ∩ B2 for two basis elements Bi , there exists a basis element B3 such that x ∈ B3 ⊆ B1 ∩ B2 . A set S ⊆ X is called open in the topolo ...