Psychiatric illness following traumatic brain injury in
... considered to be for a psychiatric indication only if the prescription was filled within 60 days of a depression diagnosis. Anxiolytics were considered to be for a psychiatric indication if the prescription was filled within 60 days of an anxiety diagnosis. Psychostimulants were excluded if there wa ...
... considered to be for a psychiatric indication only if the prescription was filled within 60 days of a depression diagnosis. Anxiolytics were considered to be for a psychiatric indication if the prescription was filled within 60 days of an anxiety diagnosis. Psychostimulants were excluded if there wa ...
I. The MID Dissociation Scales Graph
... job, how to drive a car, one’s own name, etc. Unlike the other 10 consciouslyexperienced intrusions (which are positive symptoms), temporary loss of skills or knowledge is a negative symptom. That is, what should be there (e.g., skill, knowledge of one’s own name) is suddenly absent. Research has sh ...
... job, how to drive a car, one’s own name, etc. Unlike the other 10 consciouslyexperienced intrusions (which are positive symptoms), temporary loss of skills or knowledge is a negative symptom. That is, what should be there (e.g., skill, knowledge of one’s own name) is suddenly absent. Research has sh ...
Acute Dissociative Responses in Law Enforcement Officers Involved
... ASD was conceptualized as an acute form of PTSD that occurs within four weeks of a traumatic experience. In contrast to PTSD, a diagnosis of ASD requires that an individual experience three of the following five acute traumatic or peritraumatic dissociative symptoms during or after the traumatic eve ...
... ASD was conceptualized as an acute form of PTSD that occurs within four weeks of a traumatic experience. In contrast to PTSD, a diagnosis of ASD requires that an individual experience three of the following five acute traumatic or peritraumatic dissociative symptoms during or after the traumatic eve ...
Assessment of validity and response bias in neuropsychiatric
... the Symptom Combination approach, in which dissimulators report combinations of symptoms that are either unlikely or inconsistent with common mood and psychotic disorders. This approach is utilized by two structured interview approaches, the Miller Forensic Assessment of Symptoms Test (M-FAST; Mille ...
... the Symptom Combination approach, in which dissimulators report combinations of symptoms that are either unlikely or inconsistent with common mood and psychotic disorders. This approach is utilized by two structured interview approaches, the Miller Forensic Assessment of Symptoms Test (M-FAST; Mille ...
Different types of “dissociation” have different psychological
... involved in each case. This idea is embodied in the concept of the so-called dissociative continuum (figure 2) and forms the basis for the Dissociative Experiences Scale (DES; Bernstein & Putnam, 1986), which is commonly used to estimate individual differences in “trait” dissociation. The model is a ...
... involved in each case. This idea is embodied in the concept of the so-called dissociative continuum (figure 2) and forms the basis for the Dissociative Experiences Scale (DES; Bernstein & Putnam, 1986), which is commonly used to estimate individual differences in “trait” dissociation. The model is a ...
Impact of Traumatic Brain Injury Among Recently Returned
... Turning Down a Consult for Neuropsychological Assessment ...
... Turning Down a Consult for Neuropsychological Assessment ...
Traumatic Brain Injury Evaluation and Management of Soldiers
... to extreme stress, whereas TBI is caused by blast exposure or other head injury—they are closely related. People with TBI are more prone to PTSD, and many people with PTSD may have comorbid undiagnosed mild TBI. ...
... to extreme stress, whereas TBI is caused by blast exposure or other head injury—they are closely related. People with TBI are more prone to PTSD, and many people with PTSD may have comorbid undiagnosed mild TBI. ...
Generalized dissociative amnesia
... command memories from both personalities. Analysis In this patient, all forms of memory obtruded into the amnesic personality, unrecognized by him as prior knowledge. Thus, his awareness of these memories was noetic in nature. In DID, some dissociative personalities have access to episodic memory/kn ...
... command memories from both personalities. Analysis In this patient, all forms of memory obtruded into the amnesic personality, unrecognized by him as prior knowledge. Thus, his awareness of these memories was noetic in nature. In DID, some dissociative personalities have access to episodic memory/kn ...
Document
... rear-ended at 50mph. He described severe pain in his neck and back and headaches that originated at the base of his skull and spread to his left eye. His pain was so severe that it prevented him from sleeping, so he suffered from severe fatigue. To maintain some level of function during the day, he ...
... rear-ended at 50mph. He described severe pain in his neck and back and headaches that originated at the base of his skull and spread to his left eye. His pain was so severe that it prevented him from sleeping, so he suffered from severe fatigue. To maintain some level of function during the day, he ...
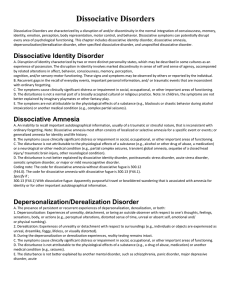
Dissociative Disorders
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, beh ...
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, beh ...
Dissociative Memory Disorders and Immigration
... contribution of psychological factors to its emergence and the absence of structural brain changes as identified via standard structural brain imaging techniques. Amnesic disturbances of psychogenic nature occur not only in dissociative amnesia, but also in other dissociative disorders, such as diss ...
... contribution of psychological factors to its emergence and the absence of structural brain changes as identified via standard structural brain imaging techniques. Amnesic disturbances of psychogenic nature occur not only in dissociative amnesia, but also in other dissociative disorders, such as diss ...
rehabilitation following a mild traumatic brain injury: a team approach
... The neurobehavioral sequelae of mild traumatic brain injury push neuropsychological technology to its limits. The accuracy of neuropsychological tests alone to discriminate between normal variation and neurologic disorders is generally around 70 to 80 percent when comparing normal controls to a we ...
... The neurobehavioral sequelae of mild traumatic brain injury push neuropsychological technology to its limits. The accuracy of neuropsychological tests alone to discriminate between normal variation and neurologic disorders is generally around 70 to 80 percent when comparing normal controls to a we ...
Definition, Diagnosis, and Forensic Implications of
... specialty of the physician who examines the patient (neurology, psychiatry, pain management, etc.), the clinical setting in which the patient is seen (emergency room, hospital, forensic evaluation), and whether or not more rigorous research criteria are applied.6 Studies suggest that postconcussiona ...
... specialty of the physician who examines the patient (neurology, psychiatry, pain management, etc.), the clinical setting in which the patient is seen (emergency room, hospital, forensic evaluation), and whether or not more rigorous research criteria are applied.6 Studies suggest that postconcussiona ...
Neuropsychological Assessment of Effort and Motivation
... Returning from Iraq Although the relationship is associative and not necessarily causal…… …“after adjustment for PTSD and depression, mild traumatic brain injury was no longer significantly associated with these physical health outcomes or symptoms, except for headaches.” Consistent with Dikmen’ ...
... Returning from Iraq Although the relationship is associative and not necessarily causal…… …“after adjustment for PTSD and depression, mild traumatic brain injury was no longer significantly associated with these physical health outcomes or symptoms, except for headaches.” Consistent with Dikmen’ ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... ones customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past. Confusion about personal identity or assumes new identity (partial or complete) Not due to another dissociative disorder or direct effects of substances or GMC Causes significant distress or impairment in imp areas of functioni ...
... ones customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past. Confusion about personal identity or assumes new identity (partial or complete) Not due to another dissociative disorder or direct effects of substances or GMC Causes significant distress or impairment in imp areas of functioni ...
Road Traffic Accidents - Faculty of Health, Education and Life
... SUV causing $800 damage to his vehicle but no damage to the rear vehicle. The struck driver claimed to have suffered a lasting shoulder injury as a result of the impact. Based on bumper basher test data and other evidence, we demonstrated that the closing speed must have been 4-6 mph, resulting in p ...
... SUV causing $800 damage to his vehicle but no damage to the rear vehicle. The struck driver claimed to have suffered a lasting shoulder injury as a result of the impact. Based on bumper basher test data and other evidence, we demonstrated that the closing speed must have been 4-6 mph, resulting in p ...
DISSOCIATIVE DISORDER
... predisposing factors and seen in MSE Amnesia may provide a primary or secondary ...
... predisposing factors and seen in MSE Amnesia may provide a primary or secondary ...
What Is Amnesia? What Causes Amnesia? When people lose their
... Anterograde amnesia - the patient cannot remember new information. Things that happened recently, information that should be stored into short-term memory disappear. This is usually caused by brain trauma (brain damage from a blow to the head, for example). However, a patient with anterograde amnesi ...
... Anterograde amnesia - the patient cannot remember new information. Things that happened recently, information that should be stored into short-term memory disappear. This is usually caused by brain trauma (brain damage from a blow to the head, for example). However, a patient with anterograde amnesi ...
Traumatic_Brain_Injury
... Sxs persisting beyond the expected recovery are often attributable to non-injury related factors ...
... Sxs persisting beyond the expected recovery are often attributable to non-injury related factors ...
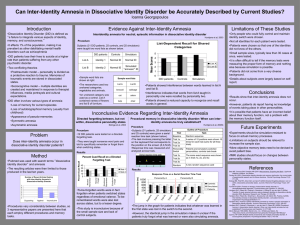
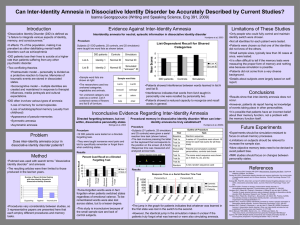
Can Inter-Identity Amnesia in Dissociative Identity
... did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patients did not come from a very diverse background. •Det ...
... did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patients did not come from a very diverse background. •Det ...
Conflicting Views on Inter-Identity Amnesia in Patients
... did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patients did not come from a very diverse background. •Det ...
... did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patients did not come from a very diverse background. •Det ...
DISSOCIATIVE AMNESIA
... G3. There must be amnesia, either partial or complete, for recent events or problems that were or still are traumatic or stressful. G4. The amnesia is too extensive and persistent to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness (although its depth and extent may vary from one assessment to the next) or by ...
... G3. There must be amnesia, either partial or complete, for recent events or problems that were or still are traumatic or stressful. G4. The amnesia is too extensive and persistent to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness (although its depth and extent may vary from one assessment to the next) or by ...
Dissociative and Personality Disorder
... • Fugue comes from the word fugitive • An individual in a fugue state is unaware of or confused about his identity, and in some cases will assume a new identity (although this is the exception). • Can involve unplanned traveling or wandering ...
... • Fugue comes from the word fugitive • An individual in a fugue state is unaware of or confused about his identity, and in some cases will assume a new identity (although this is the exception). • Can involve unplanned traveling or wandering ...
BHS 499-07 Memory and Amnesia
... External cuing devices must provide the reminder as close as possible to the time something is to be done. It should specify what is to be done. ...
... External cuing devices must provide the reminder as close as possible to the time something is to be done. It should specify what is to be done. ...