half-cell potentials and the corrosion of steel in concrete
... been steam-cured. For a given cement factor there is a significant increase in the half-cell potential of the steel between the time when it is first measured to be active and the time when a crack in the concrete is first observed. As shown in Figure 5, the average half-cell potential of the steel ...
... been steam-cured. For a given cement factor there is a significant increase in the half-cell potential of the steel between the time when it is first measured to be active and the time when a crack in the concrete is first observed. As shown in Figure 5, the average half-cell potential of the steel ...
Underground Building Works – Requirements on PE(GEO) and AC
... Excavation/ERSS > 6 m deep and not classified as UBW: e.g. non-basement excavation involving hill-slope ...
... Excavation/ERSS > 6 m deep and not classified as UBW: e.g. non-basement excavation involving hill-slope ...
Occurrence of Soil Liquefaction Potential Assessed Over Time
... In effect, this phenomenon repeated in sedimentary soils with soil resistance of static shear stresses occur. Deformation of periodic mental stress due to the increase in static and dynamic earthquake spread. Mental results of periodic broadcast side (Lateral spreading) of soil on lower slopes and f ...
... In effect, this phenomenon repeated in sedimentary soils with soil resistance of static shear stresses occur. Deformation of periodic mental stress due to the increase in static and dynamic earthquake spread. Mental results of periodic broadcast side (Lateral spreading) of soil on lower slopes and f ...
Engineering the World`s Tallest - ctbuh
... Dr. Max Irvine (with Structural Mechanics & Dynamics Consulting Engineers located in Sydney Australia) developed site specific seismic reports for the project including a seismic hazard analysis. The potential for liquefaction was investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined tha ...
... Dr. Max Irvine (with Structural Mechanics & Dynamics Consulting Engineers located in Sydney Australia) developed site specific seismic reports for the project including a seismic hazard analysis. The potential for liquefaction was investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined tha ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE)
... - Crack from settling of new addition. Anew addition has experienced settling as a result of soil consolidation at the new foundation. - Crack formation due to soil related influences. Ground water can cause soil erosion and reduction of soil compressive strength, reduction load bearing capacity of ...
... - Crack from settling of new addition. Anew addition has experienced settling as a result of soil consolidation at the new foundation. - Crack formation due to soil related influences. Ground water can cause soil erosion and reduction of soil compressive strength, reduction load bearing capacity of ...
Engineering the World`s Tallest – Burj Dubai
... potential for liquefaction was investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined that liquefaction is not considered to have any structural implications for the deep seated Tower foundations. Foundations and Site Conditions The Tower foundations consist of a pile supported raft. The ...
... potential for liquefaction was investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined that liquefaction is not considered to have any structural implications for the deep seated Tower foundations. Foundations and Site Conditions The Tower foundations consist of a pile supported raft. The ...
Engineering the World`s Tallest - Burj Dubai
... potential for liquefaction was investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined that liquefaction is not considered to have any structural implications for the deep seated Tower foundations. Foundations and Site Conditions The Tower foundations consist of a pile supported raft. The ...
... potential for liquefaction was investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined that liquefaction is not considered to have any structural implications for the deep seated Tower foundations. Foundations and Site Conditions The Tower foundations consist of a pile supported raft. The ...
Engineering the World`s Tallest – Burj Dubai
... investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined that liquefaction is not considered to have any structural implications for the deep seated Tower foundations. Foundations and Site Conditions The Tower foundations consist of a pile supported raft. The solid reinforced concrete raft ...
... investigated based on several accepted methods; it was determined that liquefaction is not considered to have any structural implications for the deep seated Tower foundations. Foundations and Site Conditions The Tower foundations consist of a pile supported raft. The solid reinforced concrete raft ...
designing structures in expansive clay
... SKIN FRICTION PIERS: Are straight shaft piers ranging in diameter from a minimum of 12" (used on small lightly loaded elements of a building like a porch), up to about 72" (used on high-rise structures). These shafts extend down through the expansive soils layers into a firm bearing strata of limest ...
... SKIN FRICTION PIERS: Are straight shaft piers ranging in diameter from a minimum of 12" (used on small lightly loaded elements of a building like a porch), up to about 72" (used on high-rise structures). These shafts extend down through the expansive soils layers into a firm bearing strata of limest ...
Design and Construction Planning of the Burj
... Figure 9 depicts the construction sequence of the tower and show the auto climbing formwork system (ACS), designed by Doka. The ACS form work is divided into four sections consisting of the center core wall that is followed by the wing wall construction along each of the three tower wings. Figure 9 ...
... Figure 9 depicts the construction sequence of the tower and show the auto climbing formwork system (ACS), designed by Doka. The ACS form work is divided into four sections consisting of the center core wall that is followed by the wing wall construction along each of the three tower wings. Figure 9 ...
History of building foundations in Chicago : a
... On account of the raising of the grade, the upper eight feet of soil indicated in Fig. 2 consist of miscellaneous fill. Beneath the fill is commonly found a gray, lake-bottom silt of variable quality, but usually loose and compressible. It has a thickness of about six feet. Approximately at datum is ...
... On account of the raising of the grade, the upper eight feet of soil indicated in Fig. 2 consist of miscellaneous fill. Beneath the fill is commonly found a gray, lake-bottom silt of variable quality, but usually loose and compressible. It has a thickness of about six feet. Approximately at datum is ...
Subject - IESL e-Learning System
... To demonstrate the ability to determine the relevant strength parameters of soils for foundation design, evaluate the allowable bearing pressure of soil using bearing capacity equations, select an appropriate shallow foundation for a given structure to suit the subsurface condition, estimate the imm ...
... To demonstrate the ability to determine the relevant strength parameters of soils for foundation design, evaluate the allowable bearing pressure of soil using bearing capacity equations, select an appropriate shallow foundation for a given structure to suit the subsurface condition, estimate the imm ...
Tall Buildings and Their Foundations: Three
... The lateral system consists of a core and outrigger system. Large outrigger elements at the mechanical levels tie the concrete core to perimeter columns, thereby engaging the perimeter columns in the building footprint. This increases the building’s lateral stiffness, as well as its resistance to ov ...
... The lateral system consists of a core and outrigger system. Large outrigger elements at the mechanical levels tie the concrete core to perimeter columns, thereby engaging the perimeter columns in the building footprint. This increases the building’s lateral stiffness, as well as its resistance to ov ...
Foundations
... with a uniform distributed load. Beams and plates calculus under linear deformable semi-infinite space (Gorbunov – Posadov method; Simvulidi method; Jemocikin method). Beams and flexible plates under a layer of finite thickness - Boussinesq model Retaining Walls Retaining walls types: gravity retain ...
... with a uniform distributed load. Beams and plates calculus under linear deformable semi-infinite space (Gorbunov – Posadov method; Simvulidi method; Jemocikin method). Beams and flexible plates under a layer of finite thickness - Boussinesq model Retaining Walls Retaining walls types: gravity retain ...
The anchored pile wall optimization using NLP approach
... The intention of the present paper is to present economical differences between a cantilever and anchoring pile wall and the impact of different parameter on costs. The type of a retaining structure as well as the structure configuration (the optimal number and layouts of the structural elements) ma ...
... The intention of the present paper is to present economical differences between a cantilever and anchoring pile wall and the impact of different parameter on costs. The type of a retaining structure as well as the structure configuration (the optimal number and layouts of the structural elements) ma ...
standard penetration test
... for greater depth up to 15 meter. The auger is vertically driven into the ground by roating its handle and is pressed down during the process of rotation. At every 30 cm. depth of penetration, the aiger is drawn out and the samples of soils are collected separately for testing. ...
... for greater depth up to 15 meter. The auger is vertically driven into the ground by roating its handle and is pressed down during the process of rotation. At every 30 cm. depth of penetration, the aiger is drawn out and the samples of soils are collected separately for testing. ...
Department: Electrical and Electronic Engineering
... 3. Evaluation of factors considered in design of shallow foundations. 4. Structural design of shallow foundations. 5. Determination of lateral earth pressures and stability of retaining walls. 6. Determination of load capacity and settlement of deep foundations. ...
... 3. Evaluation of factors considered in design of shallow foundations. 4. Structural design of shallow foundations. 5. Determination of lateral earth pressures and stability of retaining walls. 6. Determination of load capacity and settlement of deep foundations. ...
Foundations powerpoint
... foundations are placed upon them. Clay has a tendency to absorb water and ...
... foundations are placed upon them. Clay has a tendency to absorb water and ...
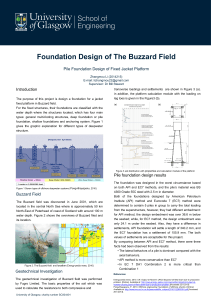
Foundation Design of The Buzzard Field
... The foundation was designed in the worst circumstance based on both API and EC7 methods, and the pile’s material was BS 4360 Grade 55C steel with 2.5 m in diameter. Both of the foundations designed by American Petroleum Institute (API) method and Eurocode 7 (EC7) method were determined to contain 5 ...
... The foundation was designed in the worst circumstance based on both API and EC7 methods, and the pile’s material was BS 4360 Grade 55C steel with 2.5 m in diameter. Both of the foundations designed by American Petroleum Institute (API) method and Eurocode 7 (EC7) method were determined to contain 5 ...
Structure Foundation Considerations
... Where lateral load capacity of shaft is an important design consideration, are p-y (load vs. deflection) curves or soils data provided which will allow the structural engineer to evaluate the lateral load capacity of shafts. ...
... Where lateral load capacity of shaft is an important design consideration, are p-y (load vs. deflection) curves or soils data provided which will allow the structural engineer to evaluate the lateral load capacity of shafts. ...
Deep foundation

A deep foundation is a type of foundation which transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does, to a subsurface layer or a range of depths.A pile is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven deep into the ground at the building site.