Simple Panel Data Models
... • Strict exogeneity in the original model has to be assumed • The R2 of the demeaned equation is inappropriate measure of R2 • The effect of time-invariant variables cannot be estimated • The effect of interactions with time-invariant variables can be estimated (e.g. the interaction of education wit ...
... • Strict exogeneity in the original model has to be assumed • The R2 of the demeaned equation is inappropriate measure of R2 • The effect of time-invariant variables cannot be estimated • The effect of interactions with time-invariant variables can be estimated (e.g. the interaction of education wit ...
experiment
... Improve Randomization • Can also use W at stage of assigning treatment • Can guarantee that in your sample X and W are independent instead of it being just probabiliistic • This is what Bertrand/Mullainathan do when assigning names to CVs ...
... Improve Randomization • Can also use W at stage of assigning treatment • Can guarantee that in your sample X and W are independent instead of it being just probabiliistic • This is what Bertrand/Mullainathan do when assigning names to CVs ...
IN THE NAME OF GOD
... In a time-series study , the effect is measured at various points in time before and after the purported cause has been introduced If changes in the purported cause are followed by changes in the purported effect,the associations is less likely to be spurious. An advantage of a time_series anal ...
... In a time-series study , the effect is measured at various points in time before and after the purported cause has been introduced If changes in the purported cause are followed by changes in the purported effect,the associations is less likely to be spurious. An advantage of a time_series anal ...
Slideshow - Sportscience
... The spreadsheet estimates the chances that the true value is greater than this smallest important value. It also shows the chances in a qualitative form (unlikely, possible, almost certain…). The default smallest value for the Cohen effect size is 0.2. Try 0.6, 1.2, or 2.0 to estimate the ch ...
... The spreadsheet estimates the chances that the true value is greater than this smallest important value. It also shows the chances in a qualitative form (unlikely, possible, almost certain…). The default smallest value for the Cohen effect size is 0.2. Try 0.6, 1.2, or 2.0 to estimate the ch ...
A SAS Macro for Assessing Differential Drug Effect
... A common method for assessing the effect of a drug or other treatment on a measurement is to compare baseline with postdrug, using each patient or subject as its own control. If there is an overall increase between pre- and postdrug, then the effect may be less important if the increase is less for ...
... A common method for assessing the effect of a drug or other treatment on a measurement is to compare baseline with postdrug, using each patient or subject as its own control. If there is an overall increase between pre- and postdrug, then the effect may be less important if the increase is less for ...
document
... How long will it take for the resampling procedures (bootstrapping etc.) to be an easy tool in our standard ...
... How long will it take for the resampling procedures (bootstrapping etc.) to be an easy tool in our standard ...
Causal Search Using Graphical Causal Models
... of unconditional and conditional independence based on these basic forms. · Key idea: Reichenbach’s (1956) Principle of the Common Cause: if any two variables, A and B, are truly correlated, then either A causes B (A ® B) or B causes A or (A ¬ B) or the have a common cause. · Generalization: ...
... of unconditional and conditional independence based on these basic forms. · Key idea: Reichenbach’s (1956) Principle of the Common Cause: if any two variables, A and B, are truly correlated, then either A causes B (A ® B) or B causes A or (A ¬ B) or the have a common cause. · Generalization: ...
Document
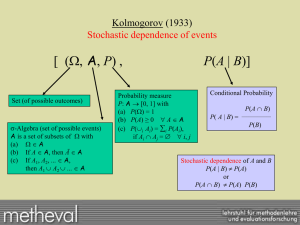
... Kolmogorov´s framework is fine for causal and noncausal dependencies, but it does not distinguish between the two. Prototypical examples for noncausal dependencies: 1. Experiment with treatment and control where the more seriously ill people tend to select themselves into the treatment condition. 2 ...
... Kolmogorov´s framework is fine for causal and noncausal dependencies, but it does not distinguish between the two. Prototypical examples for noncausal dependencies: 1. Experiment with treatment and control where the more seriously ill people tend to select themselves into the treatment condition. 2 ...
Comment on “Causal inference, probability theory, and graphical
... continuous, no such condition exists. That is, for any causal model in which Z is an instrument there exists another model, indistinguishable from the first, in which Z is not an instrument.3 Baker’s Fig. 1(d), for example, where Z is in an instrument, cannot be distinguished (by measuring X, Y , an ...
... continuous, no such condition exists. That is, for any causal model in which Z is an instrument there exists another model, indistinguishable from the first, in which Z is not an instrument.3 Baker’s Fig. 1(d), for example, where Z is in an instrument, cannot be distinguished (by measuring X, Y , an ...
Cause Effect Marco Polo told of rich Asian empires. Prince Henry
... Amerigo Vespucci by putting his name on a new land. 5. Spanish explorers came to America looking for gold and silver. 6. European explorers brought many diseases with them. 7. Vasco Da Gama rounded the southern tip of Africa. 8. The Catholic church of Spain acted to spread Catholicism. 9. Europeans ...
... Amerigo Vespucci by putting his name on a new land. 5. Spanish explorers came to America looking for gold and silver. 6. European explorers brought many diseases with them. 7. Vasco Da Gama rounded the southern tip of Africa. 8. The Catholic church of Spain acted to spread Catholicism. 9. Europeans ...
causation.PH
... Note: Sometimes there are good reasons why study results differ. For example, one study may have looked at low level exposures while another looked at high level exposures. ...
... Note: Sometimes there are good reasons why study results differ. For example, one study may have looked at low level exposures while another looked at high level exposures. ...