Decline and Fall of Roman Empire
... Attempts to Reform the Empire ■ In 284 A.D. Emperor Diocletian came to power & made a series of reforms that temporarily halted Rome’s decline –To fix the military, he doubled the size of the Roman army –To fix the economy, he fixed prices for goods –To fix the lack of loyalty, he presented himself ...
... Attempts to Reform the Empire ■ In 284 A.D. Emperor Diocletian came to power & made a series of reforms that temporarily halted Rome’s decline –To fix the military, he doubled the size of the Roman army –To fix the economy, he fixed prices for goods –To fix the lack of loyalty, he presented himself ...
Freshmen Midterm Review Sheet_2
... Greece Greece is a mountainous peninsula. The Greeks developed city-states (small independent cities) because of the mountains. Minoan civilization was on Crete. Myceneaens fought the Trojan War. The story of the Trojan War is told in the Iliad and the Odyssey orally retold by the blind poet Homer. ...
... Greece Greece is a mountainous peninsula. The Greeks developed city-states (small independent cities) because of the mountains. Minoan civilization was on Crete. Myceneaens fought the Trojan War. The story of the Trojan War is told in the Iliad and the Odyssey orally retold by the blind poet Homer. ...
Freshmen Midterm Review Sheet Know the Basic Ideas of these Religions
... Greece Greece is a mountainous peninsula. The Greeks developed city-states (small independent cities) because of the mountains. Minoan civilization was on Crete. Myceneaens fought the Trojan War. The story of the Trojan War is told in the Iliad and the Odyssey orally retold by the blind poet Homer. ...
... Greece Greece is a mountainous peninsula. The Greeks developed city-states (small independent cities) because of the mountains. Minoan civilization was on Crete. Myceneaens fought the Trojan War. The story of the Trojan War is told in the Iliad and the Odyssey orally retold by the blind poet Homer. ...
The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire
... Attempts to Reform the Empire ■ In 284 A.D. Emperor Diocletian came to power & made a series of reforms that temporarily halted Rome’s decline –To fix the military, he doubled the size of the Roman army –To fix the economy, he fixed prices for goods –To fix the lack of loyalty, he presented himself ...
... Attempts to Reform the Empire ■ In 284 A.D. Emperor Diocletian came to power & made a series of reforms that temporarily halted Rome’s decline –To fix the military, he doubled the size of the Roman army –To fix the economy, he fixed prices for goods –To fix the lack of loyalty, he presented himself ...
Ancient Rome
... Fun Facts About Rome The Romans built thousands of miles of road to connect the entire empire. These roads were used up until about 100 ...
... Fun Facts About Rome The Romans built thousands of miles of road to connect the entire empire. These roads were used up until about 100 ...
ancient rome
... Fun Facts About Rome The Romans built thousands of miles of road to connect the entire empire. These roads were used up until about 100 ...
... Fun Facts About Rome The Romans built thousands of miles of road to connect the entire empire. These roads were used up until about 100 ...
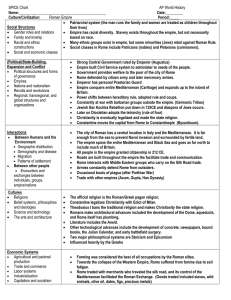
Rome SPICE Chart
... Two major philosophical systems are Stoicism and Epicureism Influenced heavily by the Greeks ...
... Two major philosophical systems are Stoicism and Epicureism Influenced heavily by the Greeks ...
Ancient Rome
... Fun Facts About Rome The Romans built thousands of miles of road to connect the entire empire. These roads were used up until about 100 ...
... Fun Facts About Rome The Romans built thousands of miles of road to connect the entire empire. These roads were used up until about 100 ...
PPTX - Student Handouts
... • Senate – upper house • About 300 patricians • Served for life • Controlled by about 12 families • Assembly – lower house • All free, adult males who could afford weaponry • All acts had to be approved by the Senate ...
... • Senate – upper house • About 300 patricians • Served for life • Controlled by about 12 families • Assembly – lower house • All free, adult males who could afford weaponry • All acts had to be approved by the Senate ...
The Roman Army
... Among the four main types that had evolved by the early Empire was the heavily armed Samnite, later called a hoplomachus or secutor. (The Romans may have recognized these three as separate and distinct types, but any such distinctions are now unclear; all employed basically the same weapons and tact ...
... Among the four main types that had evolved by the early Empire was the heavily armed Samnite, later called a hoplomachus or secutor. (The Romans may have recognized these three as separate and distinct types, but any such distinctions are now unclear; all employed basically the same weapons and tact ...
CHAPTER 6 ANCIENT ROME and THE RISE OF
... Hannibal, Carthaginian general, led his army including dozens of war elephants, on an epic march across the Pyrenees, through France, and over the Alps into Italy. Carthage gave up all its lands except those in Africa. ...
... Hannibal, Carthaginian general, led his army including dozens of war elephants, on an epic march across the Pyrenees, through France, and over the Alps into Italy. Carthage gave up all its lands except those in Africa. ...
Geography and the Early Development of Rome
... Both the Etruscans and the Romans admired Greek pottery, painting, and sculpture. The Romans got some Greek ideas from Etruscan art. They borrowed others directly from the Greeks. Greek pottery was valued throughout the Mediterranean world for its usefulness and beauty. Greek potters created large c ...
... Both the Etruscans and the Romans admired Greek pottery, painting, and sculpture. The Romans got some Greek ideas from Etruscan art. They borrowed others directly from the Greeks. Greek pottery was valued throughout the Mediterranean world for its usefulness and beauty. Greek potters created large c ...
Name - Madison Public Schools
... judges. The gov’t also had two ____________, elected leaders who shared command of the ____________. The Senate advised these men but the Senate made the laws. 15. Plebeians rebel in 494 B.C.E. because the ____________ held all power in the gov’t. Pats changed ____________ since they were not writte ...
... judges. The gov’t also had two ____________, elected leaders who shared command of the ____________. The Senate advised these men but the Senate made the laws. 15. Plebeians rebel in 494 B.C.E. because the ____________ held all power in the gov’t. Pats changed ____________ since they were not writte ...
Social 8 - Ancient Times - Teacher Copy - 2014
... Again, you will remember that Jesus had a trial before his execution. Rome was a vast empire with many races and nations within. For over a half millennium they ruled this empire with laws. These laws managed to keep the empire relatively peaceful and allowed to trade between the provinces. This law ...
... Again, you will remember that Jesus had a trial before his execution. Rome was a vast empire with many races and nations within. For over a half millennium they ruled this empire with laws. These laws managed to keep the empire relatively peaceful and allowed to trade between the provinces. This law ...
Republic of Rome
... 1. Senate2. Plebeians could vote but were kept by law from holding Senate positions 3. Plebian Assembly- elected Tribunes who could D. Twelve Tables- 451 B.C. Insured that ALL free citizens had a right to protection by law E. Balanced Government1. monarchy- 2 Consuls term one year every 10 years 2. ...
... 1. Senate2. Plebeians could vote but were kept by law from holding Senate positions 3. Plebian Assembly- elected Tribunes who could D. Twelve Tables- 451 B.C. Insured that ALL free citizens had a right to protection by law E. Balanced Government1. monarchy- 2 Consuls term one year every 10 years 2. ...
1 st written law code of Republic
... WARM UP: Describe some important reasons for why Rome was able to have the success shown on this map. ...
... WARM UP: Describe some important reasons for why Rome was able to have the success shown on this map. ...
Works Cited
... numbers so two Roman capable political large that the emperors, one in foreigners structure, late Latin word Rome and one in coming from characterized for "soldier" Constantinople— all ends of the by an came to be continued to Empire had oppressive demand that the kept Rome on burden of barbarus ("b ...
... numbers so two Roman capable political large that the emperors, one in foreigners structure, late Latin word Rome and one in coming from characterized for "soldier" Constantinople— all ends of the by an came to be continued to Empire had oppressive demand that the kept Rome on burden of barbarus ("b ...
Roman History
... 37. What elderly Roman statesman was fond of ending all of his later speeches with the phrase, “ceterum censeo Carthaginem esse delendam”? A. Cato the Elder C. Caesar Augustus B. Marcus Cicero D. Cornelius Scipio 38. In 216 BC, where did the Romans suffer what some historians refer to as “the worst ...
... 37. What elderly Roman statesman was fond of ending all of his later speeches with the phrase, “ceterum censeo Carthaginem esse delendam”? A. Cato the Elder C. Caesar Augustus B. Marcus Cicero D. Cornelius Scipio 38. In 216 BC, where did the Romans suffer what some historians refer to as “the worst ...
Roman Republic and Roman Empire
... Eventually he marched his army into Rome and defeated the other ...
... Eventually he marched his army into Rome and defeated the other ...
CP World History Notes 2nd Quarter
... • Cities he founded like Alexandria Egypt, became centers of the ancient world and beyond. • Hellenistic Age: Greek, Egyptian, and Indian influences. • New Philosophy: Stoicism “accept life and have moral standards.” ...
... • Cities he founded like Alexandria Egypt, became centers of the ancient world and beyond. • Hellenistic Age: Greek, Egyptian, and Indian influences. • New Philosophy: Stoicism “accept life and have moral standards.” ...
Chapter 5 Study Guides
... In about the A.D. 200s, the Roman empire began to weaken. The golden age of the Pax Romana had ended. Rome faced political and economic problems. A decline in traditional values and frequent invasions were threatening the empire. Corrupt government added to Rome’s troubles. Political violence grew. ...
... In about the A.D. 200s, the Roman empire began to weaken. The golden age of the Pax Romana had ended. Rome faced political and economic problems. A decline in traditional values and frequent invasions were threatening the empire. Corrupt government added to Rome’s troubles. Political violence grew. ...
Ancian Greece and its Legacy - Fairfield
... stayed home to prepare to be strong mothers who would tell their sons “come home from ...
... stayed home to prepare to be strong mothers who would tell their sons “come home from ...
Roman Architecture - My E-town
... Ceres, Diana, Venus, Mars, Mercurius, Neptunus, Volcanus, and Apollo. They saw these gods as responsible for earthly events that occurred, sometimes being depicted as fooling around or causing the disasters that happened on earth out of anger. The Pantheon was built in The Romans were the first to ...
... Ceres, Diana, Venus, Mars, Mercurius, Neptunus, Volcanus, and Apollo. They saw these gods as responsible for earthly events that occurred, sometimes being depicted as fooling around or causing the disasters that happened on earth out of anger. The Pantheon was built in The Romans were the first to ...
Structure of the Repub.Ppt
... Rome because they didn’t really need to work. They had plenty of money already. Each plebeian family was led by the “Pater Familias,” which means “Father of the Family.” Plebeians often had slaves. They spoke the Latin language, and worshipped the Roman gods and goddesses. ...
... Rome because they didn’t really need to work. They had plenty of money already. Each plebeian family was led by the “Pater Familias,” which means “Father of the Family.” Plebeians often had slaves. They spoke the Latin language, and worshipped the Roman gods and goddesses. ...
View/Open
... The papers by Anne Marie-Carsten and Jørgen Christian Meyer both conceptualise cultural interaction as a process between cultural traditions that are themselves developing and changing. Both authors deal with the cultural diversity and readiness of the dominant population to accept and even adopt th ...
... The papers by Anne Marie-Carsten and Jørgen Christian Meyer both conceptualise cultural interaction as a process between cultural traditions that are themselves developing and changing. Both authors deal with the cultural diversity and readiness of the dominant population to accept and even adopt th ...
Education in ancient Rome

Education in Ancient Rome progressed from an informal, familial system of education in the early Republic to a tuition-based system during the late Republic and the Empire. The Roman education system was based on the Greek system – and many of the private tutors in the Roman system were Greek slaves or freedmen. Due to the extent of Rome's power, the methodology and curriculum used in Rome was copied in its provinces, and thereby proved the basis for education systems throughout later Western civilization. Organized education remained relatively rare, and there are few primary sources or accounts of the Roman educational process until the 2nd century AD. Due to the extensive power wielded by the paterfamilias over Roman families, the level and quality of education provided to Roman children varied drastically from family to family; nevertheless, Roman popular morality came eventually to expect fathers to have their children educated to some extent, and a complete advanced education was expected of any Roman who wished to enter politics.