DNA Sequence Analysis Using Boolean Algebra
... believed that there are only about a thousand basic protein folding patterns; it also has been conjectured that genes duplicate themselves sometimes for evolutionary or simply for “selfish: purposes. All these give more concrete support that the DNA sequences should be reasonably compressible. Howev ...
... believed that there are only about a thousand basic protein folding patterns; it also has been conjectured that genes duplicate themselves sometimes for evolutionary or simply for “selfish: purposes. All these give more concrete support that the DNA sequences should be reasonably compressible. Howev ...
DustinHancks_proposal
... GeneTools vers. 2.0 (BioTools Inc.). Genes that have been identified as candidate loci for analysis include: TPI, Surf 3 (Douglas Crawford, pers. comm.), and S7 (Jason Allen, pers. comm.). We will identify additional gene loci to analyze by searching sequenced fish genomes available online via GenBa ...
... GeneTools vers. 2.0 (BioTools Inc.). Genes that have been identified as candidate loci for analysis include: TPI, Surf 3 (Douglas Crawford, pers. comm.), and S7 (Jason Allen, pers. comm.). We will identify additional gene loci to analyze by searching sequenced fish genomes available online via GenBa ...
dna and its structure
... • It directs all the cell’s activities • Instructions in DNA codes for proteins (proteins are responsible for thousands of chemical reactions that take place in our bodies and also codes for our traits) ...
... • It directs all the cell’s activities • Instructions in DNA codes for proteins (proteins are responsible for thousands of chemical reactions that take place in our bodies and also codes for our traits) ...
Lacroix_Insyght navigating amongst abundant - Migale
... Moreover, shared synteny may indicate a relationship between gene products such as protein–protein interaction (9) or functional coupling (10,11). Transcriptional activity has also been correlated to conserved synteny in expression pattern and transcriptional regulation studies (12,13). Several anno ...
... Moreover, shared synteny may indicate a relationship between gene products such as protein–protein interaction (9) or functional coupling (10,11). Transcriptional activity has also been correlated to conserved synteny in expression pattern and transcriptional regulation studies (12,13). Several anno ...
1 BIOL 3200 Spring 2015 DNA Subway and RNA
... Part I: Introduction to the DNA subway (http://dnasubway.iplantcollaborative.org/) DNA subway is part of an NSF funded project to bridge the gap between biology and computer science. You can input a variety of sequence types (DNA/RNA/Protein) from a wide range of organisms, mostly plants and animals ...
... Part I: Introduction to the DNA subway (http://dnasubway.iplantcollaborative.org/) DNA subway is part of an NSF funded project to bridge the gap between biology and computer science. You can input a variety of sequence types (DNA/RNA/Protein) from a wide range of organisms, mostly plants and animals ...
Cis-regulatory mutations in human disease
... diversity of human genetic diseases attributed, in whole or in part, to mutations in non-coding regulatory sequences is on the rise. Improvements in genome-wide methods of associating genetic variation with human disease and predicting DNA with cis-regulatory potential are two of the major reasons f ...
... diversity of human genetic diseases attributed, in whole or in part, to mutations in non-coding regulatory sequences is on the rise. Improvements in genome-wide methods of associating genetic variation with human disease and predicting DNA with cis-regulatory potential are two of the major reasons f ...
Lecture 19 Spring 2011
... thymine forms thymidine dimers, which block DNA replication and activate error-prone DNA repair mechanisms. ...
... thymine forms thymidine dimers, which block DNA replication and activate error-prone DNA repair mechanisms. ...
LETTER The Preferential Retention of Starch Synthesis Genes
... between chromosomes 11 and 12 formed by segmental duplication (fig. 1). We expect the gene number and size of each pair of duplicated chromosomal segments to be the same immediately following the WGD and the current gene number and size to be similar if the gene loss was random during the diploidiza ...
... between chromosomes 11 and 12 formed by segmental duplication (fig. 1). We expect the gene number and size of each pair of duplicated chromosomal segments to be the same immediately following the WGD and the current gene number and size to be similar if the gene loss was random during the diploidiza ...
Creating mosaics in Drosophila
... promoter. These techniques, however, are limited by the availability of cloned and characterized promoters that can direct expression in a desired pattern and by the problems inherent to uniform expression, respectively (see Discussions in Brand and Perrimon, 1993; Brand et al., 1994). To overcome t ...
... promoter. These techniques, however, are limited by the availability of cloned and characterized promoters that can direct expression in a desired pattern and by the problems inherent to uniform expression, respectively (see Discussions in Brand and Perrimon, 1993; Brand et al., 1994). To overcome t ...
Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary
... Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Background Between 1990–2003, scientists working on an international research project known as the Human Genome Project were able to identify and map the 20,000–25,000 genes that define a human being. The project also succes ...
... Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Background Between 1990–2003, scientists working on an international research project known as the Human Genome Project were able to identify and map the 20,000–25,000 genes that define a human being. The project also succes ...
How Genes and Genomes Evolve
... • Most cell types can be cultured but only cells that express telomerase can be immortalized • DNA can be cut reliably and in a repeatable manner using restriction enzymes – Be aware of the details of restriction endonucleases ...
... • Most cell types can be cultured but only cells that express telomerase can be immortalized • DNA can be cut reliably and in a repeatable manner using restriction enzymes – Be aware of the details of restriction endonucleases ...
Sequence Alignment - Faculty of Science at Bilkent University
... part of this mRNA is translated into proteins involved in the integration complex, which binds to the 3' end of the mRNA transcript. The target site (blue) is cleaved followed by reverse transcription, with the 3' end of the target site as the primer. Newly synthesized cDNA is shown in pale green. L ...
... part of this mRNA is translated into proteins involved in the integration complex, which binds to the 3' end of the mRNA transcript. The target site (blue) is cleaved followed by reverse transcription, with the 3' end of the target site as the primer. Newly synthesized cDNA is shown in pale green. L ...
McElwain, Mark: A Critical Review of Gene Prediction Software
... more features may just interfere with predictions. It is a difficult task to think about the differences between gene prediction algorithms. One problem in directly comparing them is that each group often has a different goal for their program, and they are often trained on sequences from different ...
... more features may just interfere with predictions. It is a difficult task to think about the differences between gene prediction algorithms. One problem in directly comparing them is that each group often has a different goal for their program, and they are often trained on sequences from different ...
click here
... 2. The disease is X-linked and being passed through the dad. The son must therefore receive both the X and Y chromosome from the dad. They would normally segregate from one another during 1st meiotic prophase; so nondisjunction occurs in the father during the first division cycle. Ans: (a) 3. Anhydr ...
... 2. The disease is X-linked and being passed through the dad. The son must therefore receive both the X and Y chromosome from the dad. They would normally segregate from one another during 1st meiotic prophase; so nondisjunction occurs in the father during the first division cycle. Ans: (a) 3. Anhydr ...
Mutations - Miss Garry`s Biology Class Website!
... What is the effect of a mutation? Mutations are a natural process that can lead to: a. No effect nothing happens to the phenotype b. Beneficial effect phenotype is affected. The organism is better adapted to its environment c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adap ...
... What is the effect of a mutation? Mutations are a natural process that can lead to: a. No effect nothing happens to the phenotype b. Beneficial effect phenotype is affected. The organism is better adapted to its environment c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adap ...
Asbury Park School District
... then construct a model protein. They then analyze the effects of a mutation on their model protein. Each student or group of students will research a disorder caused by a genetic mutation and present their research in a multimedia presentation. Testing UV-protective fabrics UV protective clothing is ...
... then construct a model protein. They then analyze the effects of a mutation on their model protein. Each student or group of students will research a disorder caused by a genetic mutation and present their research in a multimedia presentation. Testing UV-protective fabrics UV protective clothing is ...
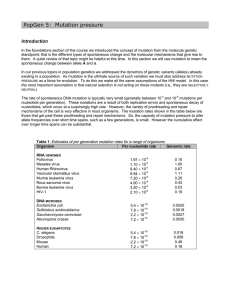
PopGen 5: Mutation pressure
... In the foundations section of this course we introduced the concept of mutation from the molecule genetic standpoint; that is the different types of spontaneous change and the molecular mechanisms that give rise to them. A quick review of that topic might be helpful at this time. In this section we ...
... In the foundations section of this course we introduced the concept of mutation from the molecule genetic standpoint; that is the different types of spontaneous change and the molecular mechanisms that give rise to them. A quick review of that topic might be helpful at this time. In this section we ...
chromosome 17
... Comparative Genomics • Human and chimpanzee genomes – Diverged 35 MYA – 1.06% of the two genomes have fixed differences in single nucleotides – 1.5% difference in insertions and deletions – 53 of human-specific indels lead to lossof-function changes ...
... Comparative Genomics • Human and chimpanzee genomes – Diverged 35 MYA – 1.06% of the two genomes have fixed differences in single nucleotides – 1.5% difference in insertions and deletions – 53 of human-specific indels lead to lossof-function changes ...
REPORTING CATEGORY 1: CELL STRUCTURE AND
... The hydrogen bonds between the two base pairs will break. Each strand of DNA will serve as a template for the new DNA to be created. ...
... The hydrogen bonds between the two base pairs will break. Each strand of DNA will serve as a template for the new DNA to be created. ...
PGLO - jvbiologyk
... 33. What advantage would there be for an organism to be able to turn on or off particular genes in response to certain conditions? 34. The following is a segment of DNA that contains, within it, the gene for production of human insulin. Below that is a plasmid from the E. coli bacteria. Below that ...
... 33. What advantage would there be for an organism to be able to turn on or off particular genes in response to certain conditions? 34. The following is a segment of DNA that contains, within it, the gene for production of human insulin. Below that is a plasmid from the E. coli bacteria. Below that ...
Chapter 6A
... widely used in forensics, paternity analysis, and for research purposes. In the method, minisatellite DNA from a genomic DNA specimen is amplified by PCR using primers that bind to unique sequences flanking minisatellite repeat units. Bands corresponding to each minisatellite locus then are separate ...
... widely used in forensics, paternity analysis, and for research purposes. In the method, minisatellite DNA from a genomic DNA specimen is amplified by PCR using primers that bind to unique sequences flanking minisatellite repeat units. Bands corresponding to each minisatellite locus then are separate ...