Force and Motion Unit Plan
... 7.7A: Contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 7.7C: Demonstrate and illustrate forces that affect motion in everyday life, such as emergence of seedlings, turgor ...
... 7.7A: Contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 7.7C: Demonstrate and illustrate forces that affect motion in everyday life, such as emergence of seedlings, turgor ...
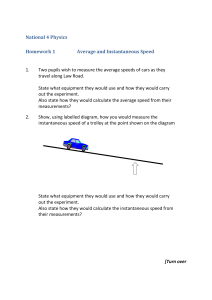
National 4 Physics Homework 1 Average and Instantaneous Speed
... a. A force is defined by the three main effects it may have on an object. Name any two of these. b. A tennis player applies a force on the ball with his racquet. Give one effect on the ball that proves a force has been applied. ...
... a. A force is defined by the three main effects it may have on an object. Name any two of these. b. A tennis player applies a force on the ball with his racquet. Give one effect on the ball that proves a force has been applied. ...
Chapter 2 Lessons 1 - 3 slides
... A particle moves in a straight line from O to A with a constant acceleration of 2ms-2. Its velocity at A is 30ms-1 and it takes 12 seconds to travel from O to A. Find the particle’s velocity at O and the distance OA. A train starts from rest at a station S and moves with constant acceleration. It p ...
... A particle moves in a straight line from O to A with a constant acceleration of 2ms-2. Its velocity at A is 30ms-1 and it takes 12 seconds to travel from O to A. Find the particle’s velocity at O and the distance OA. A train starts from rest at a station S and moves with constant acceleration. It p ...
PHYS 201 General Physics
... Final Exam Review Sheet • The final exam will be comprehensive. Look over your midterm exam review sheet and the midterm exam. • Here are some problems of the type you may expect on the exam. Many of these have been used in previous examinations. 1. A 150-gram arrow is shot straight up with a speed ...
... Final Exam Review Sheet • The final exam will be comprehensive. Look over your midterm exam review sheet and the midterm exam. • Here are some problems of the type you may expect on the exam. Many of these have been used in previous examinations. 1. A 150-gram arrow is shot straight up with a speed ...
graphs and equations of motion
... A basket ball player throws the ball at 600 to the horizontal and scores a basket. The foot of the basket was 12m away. If the ball takes 2s to reach the basket find:(a) The initial speed of the ball. (b) The height of the basket above the initial position of the ball. ...
... A basket ball player throws the ball at 600 to the horizontal and scores a basket. The foot of the basket was 12m away. If the ball takes 2s to reach the basket find:(a) The initial speed of the ball. (b) The height of the basket above the initial position of the ball. ...
Mav Mark 10/17/11 - Madison County Schools
... Well, that depends on its direction of motion. If you’re an air traffic controller, if you just give the speeds of the other planes to the pilots, then they still might crash into each other. The planes’ directions are vitally important. ...
... Well, that depends on its direction of motion. If you’re an air traffic controller, if you just give the speeds of the other planes to the pilots, then they still might crash into each other. The planes’ directions are vitally important. ...
Lecture1_Inertia
... across the lake. If both outboard motors run together at full bore, the speed that they travel together with will be ...
... across the lake. If both outboard motors run together at full bore, the speed that they travel together with will be ...
Lecture Notes for Section 11.3
... For an object’s position vector at time t given by the vector-valued function r t f t , g t , h t , we saw in section 11.2 that the derivative r t f t , g t , h t is a vector that is tangent to the curve and that points in the direction of motion at time t, ...
... For an object’s position vector at time t given by the vector-valued function r t f t , g t , h t , we saw in section 11.2 that the derivative r t f t , g t , h t is a vector that is tangent to the curve and that points in the direction of motion at time t, ...
AP Physics B Content Outline
... i. Static equilibrium (first law – object in motion stays in motion, object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force) ii. Dynamics of a single particle (second law – f = ma) iii. Systems of two or more bodies (third law – equal and opposite forces) Examples: two boxes pushing e ...
... i. Static equilibrium (first law – object in motion stays in motion, object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force) ii. Dynamics of a single particle (second law – f = ma) iii. Systems of two or more bodies (third law – equal and opposite forces) Examples: two boxes pushing e ...
Physics principles
... 52.Polarization occurs when all electric fields in light are in the same plane. 53.Coherent light waves are all in phase. 54.All angles in reflection and refraction are measured with respect to the normal. 55.At the critical angle a wave will be refracted to 90 °. 56.Total internal reflection occurs ...
... 52.Polarization occurs when all electric fields in light are in the same plane. 53.Coherent light waves are all in phase. 54.All angles in reflection and refraction are measured with respect to the normal. 55.At the critical angle a wave will be refracted to 90 °. 56.Total internal reflection occurs ...
r (t) - VT Math
... 4 feet above the ground with an initial speed of 95 feet per second at a launch angle of 42 degrees. How high above the ground will the projectile be when it is 224 feet downrange? ...
... 4 feet above the ground with an initial speed of 95 feet per second at a launch angle of 42 degrees. How high above the ground will the projectile be when it is 224 feet downrange? ...
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... Hint : Recall that the equation of an ellipse of of semi-axes a and b is given by r(θ) = (a cos θ, b sin θ). Part B A 100 kg payload is dropped from a height of 20km above the earth’s surface. The drag force is given by D = k 2 v 2 where k2 = (1/36) kg/m, and v is the velocity. Determine the magnit ...
... Hint : Recall that the equation of an ellipse of of semi-axes a and b is given by r(θ) = (a cos θ, b sin θ). Part B A 100 kg payload is dropped from a height of 20km above the earth’s surface. The drag force is given by D = k 2 v 2 where k2 = (1/36) kg/m, and v is the velocity. Determine the magnit ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it will bend toward the normal (the angle gets smaller). When light enters a medium with lower index (e.g. from water to air) then it will bend away from the normal (the angle gets larger). This creates an interesting possibility – what if ...
... When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it will bend toward the normal (the angle gets smaller). When light enters a medium with lower index (e.g. from water to air) then it will bend away from the normal (the angle gets larger). This creates an interesting possibility – what if ...
All Kinematics Worksheet
... 22. A little boy spits straight downward from the top of a 75 meter tall building. When the gob of spit leaves his mouth, it is traveling 15 m/s downward. a) How long does it take to reach the ground? b) How fast is it moving upon impact? 23. An arrow is fired directly upwards at 15 m/s from ground ...
... 22. A little boy spits straight downward from the top of a 75 meter tall building. When the gob of spit leaves his mouth, it is traveling 15 m/s downward. a) How long does it take to reach the ground? b) How fast is it moving upon impact? 23. An arrow is fired directly upwards at 15 m/s from ground ...
Physics Review Questions for Final
... 31) Suppose the gravitational force between two masses is 10 N. If the distance between the masses were cut in half, what would the force between them be? a) 40 b) 20 c) 5 d) 2.5 N 32) Same question, but distance is doubled. 33) Same question, but each mass is doubled (distance as original). 34) The ...
... 31) Suppose the gravitational force between two masses is 10 N. If the distance between the masses were cut in half, what would the force between them be? a) 40 b) 20 c) 5 d) 2.5 N 32) Same question, but distance is doubled. 33) Same question, but each mass is doubled (distance as original). 34) The ...
2nd Term Exam - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... How fast can this car round a second curve of radius 320 m? (Assume the same coefficient of friction between the car's tires and each road surface.) a) 20 m/s ...
... How fast can this car round a second curve of radius 320 m? (Assume the same coefficient of friction between the car's tires and each road surface.) a) 20 m/s ...