Lesson Plan
... how information for specifying a trait of an organism is carried in the DNA. 6B(S): SWBAT recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and ...
... how information for specifying a trait of an organism is carried in the DNA. 6B(S): SWBAT recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... a. They tend to be weaker and smaller than diploid plants. b. They tend to be bigger and stronger than diploid plants. c. They tend to be weaker, but bigger than diploid plants. d. They tend to be smaller, but stronger than diploid plants ...
... a. They tend to be weaker and smaller than diploid plants. b. They tend to be bigger and stronger than diploid plants. c. They tend to be weaker, but bigger than diploid plants. d. They tend to be smaller, but stronger than diploid plants ...
Worksheet 15.3 Applications of Genetic Engineering
... Examples include vitamin-rich rice, human proteins made in animals, animal models of human disease (for research), and bacteria that produce human insulin. Gene therapy is the process of changing a gene to treat a disorder. However, gene therapy is still an experimental and high-risk technique. Gene ...
... Examples include vitamin-rich rice, human proteins made in animals, animal models of human disease (for research), and bacteria that produce human insulin. Gene therapy is the process of changing a gene to treat a disorder. However, gene therapy is still an experimental and high-risk technique. Gene ...
Introduction to your genome
... All blue eyes have a single common ancestor with a regulatory change in HERC2 Walsh, et al. 2010 Sturm, et al. 2008 ...
... All blue eyes have a single common ancestor with a regulatory change in HERC2 Walsh, et al. 2010 Sturm, et al. 2008 ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology – summary of mark
... 4.4.10 Discuss the potential benefits and possible harmful effects of one example of genetic modification. ...
... 4.4.10 Discuss the potential benefits and possible harmful effects of one example of genetic modification. ...
AP Biology Review Chapters 13-14 Review Questions Chapter 12
... RNA splicing Repressor proteins Methylation siRNA b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. c) Identify TWO environmental factors that increase the mutation rate in an organism, and discuss their effect ...
... RNA splicing Repressor proteins Methylation siRNA b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. c) Identify TWO environmental factors that increase the mutation rate in an organism, and discuss their effect ...
Evolution process by which species change over time
... • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic make up • DNA strands can ...
... • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic make up • DNA strands can ...
Gene Section CHEK2 (CHK2 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe)) in Oncology and Haematology
... Molecular studies of Chk2 typically do not distinguish between the different isoforms. ...
... Molecular studies of Chk2 typically do not distinguish between the different isoforms. ...
Gene Regulation
... arac muants are rare because the mutation must make AraC active without binding arabinose Inactivation of araC (unlike lacI) produces an ara- phenotype AraC must also be an antiactivator since... araCc mutations should be dominant (but they are not). IV. The trp operon (Negative regulation and trans ...
... arac muants are rare because the mutation must make AraC active without binding arabinose Inactivation of araC (unlike lacI) produces an ara- phenotype AraC must also be an antiactivator since... araCc mutations should be dominant (but they are not). IV. The trp operon (Negative regulation and trans ...
Gene Regulation
... inactivated lacIrare dominant lacc mutations... ...all mapped to lacI inactived LacI protein but it could still form tetramers As a Tool in Molecular Biology lac promoter is inducible. Allowing production of toxic genes IPTG, nonclevable derivative of allolactose Several colorimetric substrates exis ...
... inactivated lacIrare dominant lacc mutations... ...all mapped to lacI inactived LacI protein but it could still form tetramers As a Tool in Molecular Biology lac promoter is inducible. Allowing production of toxic genes IPTG, nonclevable derivative of allolactose Several colorimetric substrates exis ...
A novel CDKN1C variant uncovered in a patient with Beckwith
... for developing tumors when compared to BWS cases that are caused by other mutations within 11p15.5. In cases resulting from molecular anomalies in CDKN1C, it appears that mutations were either inherited from the mother or had emerged de novo on the maternal allele, although this is not always the ca ...
... for developing tumors when compared to BWS cases that are caused by other mutations within 11p15.5. In cases resulting from molecular anomalies in CDKN1C, it appears that mutations were either inherited from the mother or had emerged de novo on the maternal allele, although this is not always the ca ...
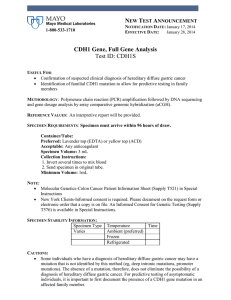
CDH1 Gene, Full Gene Analysis Test ID: CDH1S
... mutation that is not identified by this method (eg, deep intronic mutations, promoter mutations). The absence of a mutation, therefore, does not eliminate the possibility of a diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. For predictive testing of asymptomatic individuals, it is important to first ...
... mutation that is not identified by this method (eg, deep intronic mutations, promoter mutations). The absence of a mutation, therefore, does not eliminate the possibility of a diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. For predictive testing of asymptomatic individuals, it is important to first ...
Chapter One
... – Introns are removed during transcription – Exons are the parts of the sequence that become mRNA ...
... – Introns are removed during transcription – Exons are the parts of the sequence that become mRNA ...
DNA -- The Double Helix
... of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become apparent that a cell has the ab ...
... of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become apparent that a cell has the ab ...
History of Genetics
... 5. The two factors for a particular trait assort independently of factors controlling other traits (Mendel’s second law, the Principle of Independent Assortment). 6. An example is seed color in peas: i. True-breeding plants with yellow seeds (YY) are crossed ...
... 5. The two factors for a particular trait assort independently of factors controlling other traits (Mendel’s second law, the Principle of Independent Assortment). 6. An example is seed color in peas: i. True-breeding plants with yellow seeds (YY) are crossed ...
Topic 5 2010 Positional Gene Cloning
... It is easy to get lost in the details of linkage mapping to identify human disease genes and to forget that the (relatively) simple ideas here only apply to situations where disease is determined principally by mutation of a single gene. Most diseases and behaviors are not likely to be so simple, so ...
... It is easy to get lost in the details of linkage mapping to identify human disease genes and to forget that the (relatively) simple ideas here only apply to situations where disease is determined principally by mutation of a single gene. Most diseases and behaviors are not likely to be so simple, so ...
Open File
... 3. cloning – process of making genetically identical cells or organisms 4. deletion – type of chromosome mutation that occurs when a piece of a chromosome is lost 5. dihybrid – the crossing of two different factors 6. diploid – a nucleus having 2 sets of chromosomes, 2N 7. dominant allele – allele t ...
... 3. cloning – process of making genetically identical cells or organisms 4. deletion – type of chromosome mutation that occurs when a piece of a chromosome is lost 5. dihybrid – the crossing of two different factors 6. diploid – a nucleus having 2 sets of chromosomes, 2N 7. dominant allele – allele t ...
EOC Practice Quiz (5) - Duplin County Schools
... 61. One of Darwin’s finches evolved adaptations more similar to those of woodpeckers that other finches. This is probably explained by a. coevolution b. convergent evolution c. gradualism d. stabilizing selection. 62. The process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms is cal ...
... 61. One of Darwin’s finches evolved adaptations more similar to those of woodpeckers that other finches. This is probably explained by a. coevolution b. convergent evolution c. gradualism d. stabilizing selection. 62. The process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms is cal ...
Get the PDF version of this article
... genes is called an allele. One allele actively produces protein and is dominant. The other allele is dormant and is recessive. An entire semester of genetics compressed into two paragraphs. Keep reading. When a gene nucleotide mutates or is damaged, protein production may be compromised in different ...
... genes is called an allele. One allele actively produces protein and is dominant. The other allele is dormant and is recessive. An entire semester of genetics compressed into two paragraphs. Keep reading. When a gene nucleotide mutates or is damaged, protein production may be compromised in different ...
Genetic Vulnerability Factors - Early Psychosis Intervention
... Genes can have mistakes in them. This is quite common and everyone will have at least some genes with mistakes in them. However, in some people, these mistakes can sometimes cause health problems. We call these genetic mistakes mutations. Mutations can cause health problems because they can change t ...
... Genes can have mistakes in them. This is quite common and everyone will have at least some genes with mistakes in them. However, in some people, these mistakes can sometimes cause health problems. We call these genetic mistakes mutations. Mutations can cause health problems because they can change t ...
Chapters 8-10
... have difficulty adapting to changing environments. E) Sexual reproduction produces 2n gametes. 8. Which of the following statements regarding genotypes and phenotypes is FALSE? A) The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype. B) An organism with two different alleles for a single trait ...
... have difficulty adapting to changing environments. E) Sexual reproduction produces 2n gametes. 8. Which of the following statements regarding genotypes and phenotypes is FALSE? A) The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype. B) An organism with two different alleles for a single trait ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.