Quiz 3 Thursday 4-5 Answer Key
... context of performing genetic screens. Classical genetic screens start with a pathway/process, identify the genes involved, and then try to understand how they work together. (Function to genes) Reverse Genetic screens involve the disruption of known genes by targeted disruption then characterizes t ...
... context of performing genetic screens. Classical genetic screens start with a pathway/process, identify the genes involved, and then try to understand how they work together. (Function to genes) Reverse Genetic screens involve the disruption of known genes by targeted disruption then characterizes t ...
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Mendel and His Peas Lesson 2
... • The 46 human chromosomes contain between 20,000 and 25,000 genes that are copied during replication. ...
... • The 46 human chromosomes contain between 20,000 and 25,000 genes that are copied during replication. ...
vit C effects on yeast mutagenesis Chekan PJAS 2010
... Ames Test Created by Bruce Ames Biological assay used to assess the mutagenic potential of a chemical Reversion rate of –His to +His used to assess mutagenesis. Positive test indicates chemical carcinogen ...
... Ames Test Created by Bruce Ames Biological assay used to assess the mutagenic potential of a chemical Reversion rate of –His to +His used to assess mutagenesis. Positive test indicates chemical carcinogen ...
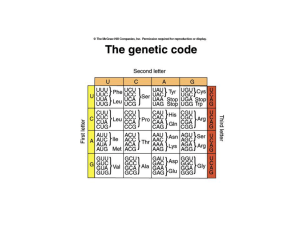
Features of the genetic code
... • Splicesome is needed to identify and catalyze the sequence of events leading to removal of the intron and rejoining of the two successive exons. The splicesome consists of snRNP (snRNA 100300 nucleotides long + proteins). Each splicesome is composed of four snRNPs together and each snRNP is five s ...
... • Splicesome is needed to identify and catalyze the sequence of events leading to removal of the intron and rejoining of the two successive exons. The splicesome consists of snRNP (snRNA 100300 nucleotides long + proteins). Each splicesome is composed of four snRNPs together and each snRNP is five s ...
DNA Replication Notes
... End result is two identical copies of DNA Use for cell division (one copy will end up in each cell) ...
... End result is two identical copies of DNA Use for cell division (one copy will end up in each cell) ...
Unit 6: Biotechnology
... 1. Plasmids or viruses are then used as a vector, a genetic vehicle that carries foreign DNA into a host cell. Usually, the host cell is a ____Bacterium___. 2. The recombinant DNA inside the host cell reproduces new cells that contain copies of the inserted gene. F. Screening – extracting copied gen ...
... 1. Plasmids or viruses are then used as a vector, a genetic vehicle that carries foreign DNA into a host cell. Usually, the host cell is a ____Bacterium___. 2. The recombinant DNA inside the host cell reproduces new cells that contain copies of the inserted gene. F. Screening – extracting copied gen ...
Patterns of Inheritance 10 Grade - Delaware Department of Education
... Patterns of Inheritance 10th Grade The Goldstein family is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and recently experienced the tragic death of their youngest child, Sarah, who was diagnosed with Tay Sachs disorder. Tay Sachs is a genetic disorder resulting from a mutation on chromosome 15. This mutation causes ...
... Patterns of Inheritance 10th Grade The Goldstein family is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and recently experienced the tragic death of their youngest child, Sarah, who was diagnosed with Tay Sachs disorder. Tay Sachs is a genetic disorder resulting from a mutation on chromosome 15. This mutation causes ...
The Goldstein family is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent
... Patterns of Inheritance 10th Grade The Goldstein family is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and recently experienced the tragic death of their youngest child, Sarah, who was diagnosed with Tay Sachs disorder. Tay Sachs is a genetic disorder resulting from a mutation on chromosome 15. This mutation causes ...
... Patterns of Inheritance 10th Grade The Goldstein family is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and recently experienced the tragic death of their youngest child, Sarah, who was diagnosed with Tay Sachs disorder. Tay Sachs is a genetic disorder resulting from a mutation on chromosome 15. This mutation causes ...
CHAPTER 8 Applications of Recombinant DNA Technology
... detects loss or addition of a restriction site in the region of a gene. a. The restriction map is independent of gene function, so RFLPs may occur without changing the phenotype. ...
... detects loss or addition of a restriction site in the region of a gene. a. The restriction map is independent of gene function, so RFLPs may occur without changing the phenotype. ...
MICR 130 Chapter 8
... Mutation: Change in the Genetic Material Type of mutations § Base substitution (point mutation) – one base is replaced by a different base § May cause change in one amino acid, stop codon § Frameshift mutation – one or a few bases are deleted of inserted (not in multiples of three) § Shifts ...
... Mutation: Change in the Genetic Material Type of mutations § Base substitution (point mutation) – one base is replaced by a different base § May cause change in one amino acid, stop codon § Frameshift mutation – one or a few bases are deleted of inserted (not in multiples of three) § Shifts ...
Does premature aging of the mtDNA mutator mouse prove that
... to expand clonally above the threshold within about 70 years in an aged person compared to 6 months in mutator mouse. Thus, we believe that the rapid generation of mtDNA mutations in a relatively small number of progenitor cells beginning at the earliest stages of mouse embryonic development has a d ...
... to expand clonally above the threshold within about 70 years in an aged person compared to 6 months in mutator mouse. Thus, we believe that the rapid generation of mtDNA mutations in a relatively small number of progenitor cells beginning at the earliest stages of mouse embryonic development has a d ...
Report Template for Positive Diagnosis Result
... Chromosome 18 The single nucleotide substitution described above results in the substitution of a valine for an isoleucine at amino acid position 525 of the SMAD4 (SMAD family member 4) protein. This individual is heterozygous for the p.Ile525Val variant in the SMAD4 gene. To our knowledge, this seq ...
... Chromosome 18 The single nucleotide substitution described above results in the substitution of a valine for an isoleucine at amino acid position 525 of the SMAD4 (SMAD family member 4) protein. This individual is heterozygous for the p.Ile525Val variant in the SMAD4 gene. To our knowledge, this seq ...
THE GENOME AND THE ORIGIN OF MAN
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
SPIS TREŚCI
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
Screening for the Lynch Syndrome
... Rt sided colorectal cancer with undifferentiated pattern on histology (<50yr) ...
... Rt sided colorectal cancer with undifferentiated pattern on histology (<50yr) ...
Complex Germline Architecture: Two Genes
... sometimes called nanochromosomes (Doak et al. 2003) because of their size and because they typically contain just one gene each. These together comprise the gene-dense somatic genome. The process of deletion of up to 98% of the germline DNA removes internal eliminated segments (IES) that interrupt g ...
... sometimes called nanochromosomes (Doak et al. 2003) because of their size and because they typically contain just one gene each. These together comprise the gene-dense somatic genome. The process of deletion of up to 98% of the germline DNA removes internal eliminated segments (IES) that interrupt g ...
Work Day 2
... Ciprofloxacin blocks DNA synthesis. Downstream steps of gene expression do not occur. Treatment of ciprofloxacin-sensitive bacteria with the antibiotic results in cell death. ...
... Ciprofloxacin blocks DNA synthesis. Downstream steps of gene expression do not occur. Treatment of ciprofloxacin-sensitive bacteria with the antibiotic results in cell death. ...
A-level Biology B Question paper Unit 2 - Genes and Genetic
... (i) Write the letter Y on the diagram to show where serine would attach. (1 mark) (ii) Write the letter Z on the diagram to show where the anticodon would be. (1 mark) ...
... (i) Write the letter Y on the diagram to show where serine would attach. (1 mark) (ii) Write the letter Z on the diagram to show where the anticodon would be. (1 mark) ...
File
... Taq DNA polymerase is a temperature resistant enzyme which builds DNA strands. Taq was isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which normally lives in hot springs in temperatures around 100° C. Taq is stable under the extreme temperature conditions of PCR. ...
... Taq DNA polymerase is a temperature resistant enzyme which builds DNA strands. Taq was isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which normally lives in hot springs in temperatures around 100° C. Taq is stable under the extreme temperature conditions of PCR. ...
2 cp u9 inheritance notes
... daughters will have it, but ______ of them are likely to be carriers. ...
... daughters will have it, but ______ of them are likely to be carriers. ...
NoLimits 1000bp DNA Fragment
... The NoLimits™ DNA Fragment is a chromatographypurified, exceptionally pure individual DNA fragment. It is produced using specifically designed plasmid DNA purified by a proprietary patent-pending technology. ...
... The NoLimits™ DNA Fragment is a chromatographypurified, exceptionally pure individual DNA fragment. It is produced using specifically designed plasmid DNA purified by a proprietary patent-pending technology. ...
CRISPR/Cas9.
... CRISPR/Cas9 can also be used to induce mutations in cells and to track these lineages throughout development. In 2015, LoTurco et al. [6] used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to introduce somatic mutations into neural progenitor cells. sgRNAs were designed to target tumour suppressor genes that have been lin ...
... CRISPR/Cas9 can also be used to induce mutations in cells and to track these lineages throughout development. In 2015, LoTurco et al. [6] used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to introduce somatic mutations into neural progenitor cells. sgRNAs were designed to target tumour suppressor genes that have been lin ...
Power Point
... How are yeast mutants isolated? Mutants are isolated in genetic screens in which investigators look for particular phenotypes that occur at low frequencies ...
... How are yeast mutants isolated? Mutants are isolated in genetic screens in which investigators look for particular phenotypes that occur at low frequencies ...
Homologous chromosome
... SOURCE: BIOLOGY: CONCEPTS AND CONNECTIONS BY CAMPBELL, REECE, MITCHELL, TAYLOR ...
... SOURCE: BIOLOGY: CONCEPTS AND CONNECTIONS BY CAMPBELL, REECE, MITCHELL, TAYLOR ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.