CSC598BIL675-2016
... 3. Deviating from a standard, usually by only a slight difference. n. Something that differs in form only slightly from something else, as a different spelling or pronunciation of the same word. ...
... 3. Deviating from a standard, usually by only a slight difference. n. Something that differs in form only slightly from something else, as a different spelling or pronunciation of the same word. ...
DNA Duplications and Deletions Help Determine Health
... attach in the wrong place, or duplicate, creating “structural variations” that range in size from 2 to 2 million bases. A piece of a gene, a whole gene, or many genes can get caught up in these rearrangements, which occur as DNA is copied during cell division. Until recently, these submicroscopic ch ...
... attach in the wrong place, or duplicate, creating “structural variations” that range in size from 2 to 2 million bases. A piece of a gene, a whole gene, or many genes can get caught up in these rearrangements, which occur as DNA is copied during cell division. Until recently, these submicroscopic ch ...
Greatest Discoveries With Bill Nye: Genetics
... After students have chosen which trait to use in their square, tell them to think about this trait in both their parents so they can label their own genes for this exercise. If they have curly hair (dominant), do both of their parents? If not, tell them to assume that their genotype is Hh, not HH. I ...
... After students have chosen which trait to use in their square, tell them to think about this trait in both their parents so they can label their own genes for this exercise. If they have curly hair (dominant), do both of their parents? If not, tell them to assume that their genotype is Hh, not HH. I ...
Gene Linkage
... together. – Since both of the DNA molecules were cut with the same restriction enzymes the sticky ends will contain complimentary bases. – DNA ligase can be used to fuse together the DNA fragments. – Beside recombinant DNA, in what other process is DNA ligase used? ...
... together. – Since both of the DNA molecules were cut with the same restriction enzymes the sticky ends will contain complimentary bases. – DNA ligase can be used to fuse together the DNA fragments. – Beside recombinant DNA, in what other process is DNA ligase used? ...
Cancer Genomics - support.illumina.com
... 5. Stephens PJ et al. (2009) Complex landscapes of somatic rearrangement in human breast cancer genomes. Nature 462: 1005–1010. 6. Choi YL et al. (2010) EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 363: 1734–1799. 7. Ding L et al. (2010) Genome remodellin ...
... 5. Stephens PJ et al. (2009) Complex landscapes of somatic rearrangement in human breast cancer genomes. Nature 462: 1005–1010. 6. Choi YL et al. (2010) EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 363: 1734–1799. 7. Ding L et al. (2010) Genome remodellin ...
Answers to Problem Set 3A
... Note that the enzymes (numbers) are placed in locations they are likely to be functioning with respect to the way the DNA molecules are presented (ie, the topology of the DNA). This is a simplified view. For example, you could have placed DNA polymerase III (the circled number 6) at either of the t ...
... Note that the enzymes (numbers) are placed in locations they are likely to be functioning with respect to the way the DNA molecules are presented (ie, the topology of the DNA). This is a simplified view. For example, you could have placed DNA polymerase III (the circled number 6) at either of the t ...
KAN GRUPLARININ MOLEKÜLER YAPISI
... This R.E. leaves TTAA single stranded ends (‘sticky ends’) If you cut DNA of interest and plasmid with same restriction enzyme then you will have fragments with identical sticky ends. ...
... This R.E. leaves TTAA single stranded ends (‘sticky ends’) If you cut DNA of interest and plasmid with same restriction enzyme then you will have fragments with identical sticky ends. ...
ch 13 and genetic disorders
... -there is a chance that half of the zygotes will be 46XX and half will be 46XY -all egg cells carry a single X chromosome -however, half of all sperm cells carry an X chromosome and half carry a Y -human chromosomes contain both protein and a single, double-stranded DNA molecule -many human genes ha ...
... -there is a chance that half of the zygotes will be 46XX and half will be 46XY -all egg cells carry a single X chromosome -however, half of all sperm cells carry an X chromosome and half carry a Y -human chromosomes contain both protein and a single, double-stranded DNA molecule -many human genes ha ...
Comparison of Genomes using High-Performance - FACOM
... global changes, material sciences, medicine and health, and more recently, the important area of bioinformatics. With recent advances of DNA sequencing technology, whole genomes of bacteria, archaea and eukaryota, including humans, have been sequenced, with the announcements of new sequencing result ...
... global changes, material sciences, medicine and health, and more recently, the important area of bioinformatics. With recent advances of DNA sequencing technology, whole genomes of bacteria, archaea and eukaryota, including humans, have been sequenced, with the announcements of new sequencing result ...
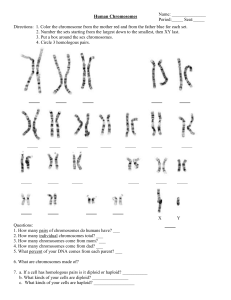
Human Chromosomes
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
Promoter Analysis for Intestinally
... a. The sequences of all hits were extracted and flipped to the strand that maximized As and Gs. b. The sequences were then run through ClustalW. Alignments can be seen in the following file: i. C. elegans : Cele_all_hits_aligned.txt ii. C. briggsae: Cbri_all_hits_aligned.txt iii. C. remanei : Crem_a ...
... a. The sequences of all hits were extracted and flipped to the strand that maximized As and Gs. b. The sequences were then run through ClustalW. Alignments can be seen in the following file: i. C. elegans : Cele_all_hits_aligned.txt ii. C. briggsae: Cbri_all_hits_aligned.txt iii. C. remanei : Crem_a ...
Analysis of a piwi-related Gene Implicates Small RNAs in
... 1. The next 2 slides illustrate the organization of 8 piwi-like (TWI) genes in the Tetrahymena genome and the expression of one of them. 2. Piwi genes are PPD proteins, widely distributed in eukaryotes and found to be associated with RNAi processes. 3. Only the TWI1 gene will be discussed in this p ...
... 1. The next 2 slides illustrate the organization of 8 piwi-like (TWI) genes in the Tetrahymena genome and the expression of one of them. 2. Piwi genes are PPD proteins, widely distributed in eukaryotes and found to be associated with RNAi processes. 3. Only the TWI1 gene will be discussed in this p ...
BLAST_and_Genome_Browser_tutorial
... Genome browser is a dynamic graphical display of several features identified from rice as well as from maize, sorghum, barley and wheat that were mapped on the rice genome. Some of these features are sequenced genetic markers, ESTs, cDNAs, CDSs, genes, insertion and repeat elements. The browser is a ...
... Genome browser is a dynamic graphical display of several features identified from rice as well as from maize, sorghum, barley and wheat that were mapped on the rice genome. Some of these features are sequenced genetic markers, ESTs, cDNAs, CDSs, genes, insertion and repeat elements. The browser is a ...
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 7 Questions
... in RNA splicing and occasional mistakes made during transcription (the wrong bases can get incorporated by an RNA polymerase). Splicing accidents may be quite common, and may, for example lead to retention of an intron sequence that will almost inevitably result in in-frame premature termination cod ...
... in RNA splicing and occasional mistakes made during transcription (the wrong bases can get incorporated by an RNA polymerase). Splicing accidents may be quite common, and may, for example lead to retention of an intron sequence that will almost inevitably result in in-frame premature termination cod ...
chapter 15 chromosomal basis of inheritance
... Chromosome theory of inheritance took form ~1902. Thomas Morgan Hunt, at Columbia University,1st to associate a specific gene with a specific chromosome, early 1900’s. He studied Drosophila melanogaster and found the eye color of fruit flies is located on the X chromosome. Wild type – most common ph ...
... Chromosome theory of inheritance took form ~1902. Thomas Morgan Hunt, at Columbia University,1st to associate a specific gene with a specific chromosome, early 1900’s. He studied Drosophila melanogaster and found the eye color of fruit flies is located on the X chromosome. Wild type – most common ph ...
DNA Libraries - Rose
... If very little information is known, it is sometimes still possible to find a protein coding sequence using the brute force method of sequencing all of the DNA molecules in the library. This sounds inefficient, but advances in sequencing technology have meant that this method is used more and more f ...
... If very little information is known, it is sometimes still possible to find a protein coding sequence using the brute force method of sequencing all of the DNA molecules in the library. This sounds inefficient, but advances in sequencing technology have meant that this method is used more and more f ...
How Does Replication-Associated Mutational Pressure Influence
... translation, is superimposed on other levels of gene control. We have observed different codon usage in proximal and distal regions in relatively large genomes of B. subtilis and E. coli (Fig. 6e), but we have not found such differences in the smaller genomes of Treponema or Borrelia (as observed pr ...
... translation, is superimposed on other levels of gene control. We have observed different codon usage in proximal and distal regions in relatively large genomes of B. subtilis and E. coli (Fig. 6e), but we have not found such differences in the smaller genomes of Treponema or Borrelia (as observed pr ...
Advanced Genetics Unit 1: All about chromosomes Quiz Bowl 1
... 31. Metacentric chromosomes tend to be …. [larger in size] 32. Of the 2 classes of chromatin, this one tends to be associated with DNA that is highly active and produces lots of RNA molecules. [euchromatin] 33. This class of chromatin tends to produce light bands along the chromosome when stained. [ ...
... 31. Metacentric chromosomes tend to be …. [larger in size] 32. Of the 2 classes of chromatin, this one tends to be associated with DNA that is highly active and produces lots of RNA molecules. [euchromatin] 33. This class of chromatin tends to produce light bands along the chromosome when stained. [ ...
251 Lab 2 Chrisine
... Also with behavioral and psychiatric manifestations Q17: From the Table of Contents, select “Allelic Variants”, read this section, and answer the following question: What is the molecular genetic basis for the disease? Explain how repeat sequence variation is responsible for this disease. The nucleo ...
... Also with behavioral and psychiatric manifestations Q17: From the Table of Contents, select “Allelic Variants”, read this section, and answer the following question: What is the molecular genetic basis for the disease? Explain how repeat sequence variation is responsible for this disease. The nucleo ...
Short Communication A Null Allele Impairs Function of CYP2C76
... monkeys. To describe genetic variants, the CYP2C76 cDNA sequence (DQ074807) originally identified (Uno et al., 2006) was regarded as a reference sequence in this study due to the unavailability of a consensus wild-type sequence for CYP2C76. Because we were interested in the null or defective alleles ...
... monkeys. To describe genetic variants, the CYP2C76 cDNA sequence (DQ074807) originally identified (Uno et al., 2006) was regarded as a reference sequence in this study due to the unavailability of a consensus wild-type sequence for CYP2C76. Because we were interested in the null or defective alleles ...
Tool 1
... When performing PFGE, the circular bacterial DNA is treated with a particular restriction enzyme. These are protein structures that bind to particular sequences of normally 6 DNA letters (eg TCTAGA, but nowhere else in the DNA) and cut the DNA in two at these sites. The particular 6-letter sequences ...
... When performing PFGE, the circular bacterial DNA is treated with a particular restriction enzyme. These are protein structures that bind to particular sequences of normally 6 DNA letters (eg TCTAGA, but nowhere else in the DNA) and cut the DNA in two at these sites. The particular 6-letter sequences ...
Final exam review 4
... 4. Explain the significance of these ratios: 3:1 and 9:3:3:1 5. Know all bold terms page 167 to 169. 6. Know how to do a punnet square and describe the outcomes. Example: What are the probably genotype and phenotype ratios for a homozygous blue eyed parent that mates with a parent that is heterozygo ...
... 4. Explain the significance of these ratios: 3:1 and 9:3:3:1 5. Know all bold terms page 167 to 169. 6. Know how to do a punnet square and describe the outcomes. Example: What are the probably genotype and phenotype ratios for a homozygous blue eyed parent that mates with a parent that is heterozygo ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.