chapter 15 section 3 notes
... No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for identical twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with repeated DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. Here, one sample has 12 repeats between genes A and B, while the se ...
... No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for identical twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with repeated DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. Here, one sample has 12 repeats between genes A and B, while the se ...
XML
... Lymphoma represents a heterogeneous group of neoplastic blood disorders involving monoclonal proliferation of malignant lymphocytes. Historically, lymphomas have been divided in two basic categories: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (DeVita et al., 2015). Different subtypes were ...
... Lymphoma represents a heterogeneous group of neoplastic blood disorders involving monoclonal proliferation of malignant lymphocytes. Historically, lymphomas have been divided in two basic categories: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (DeVita et al., 2015). Different subtypes were ...
Modeling Genetic Engineering Lab
... An understanding of the basis of inheritance has led to a new form of applied genetics called genetic engineering. Genetic engineering is the use of genetics for practical purposes. For example, it can be used to identify genes for specific traits or transfer genes for a specific trait from one orga ...
... An understanding of the basis of inheritance has led to a new form of applied genetics called genetic engineering. Genetic engineering is the use of genetics for practical purposes. For example, it can be used to identify genes for specific traits or transfer genes for a specific trait from one orga ...
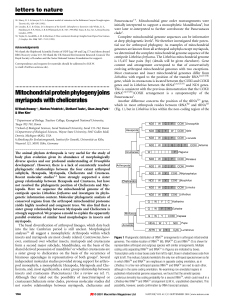
Mitochondrialproteinphylogenyjoins myriapods with chelicerates
... ®nal elongation step at 68 8C. A single 15.5-kb-long PCR fragment was puri®ed and used as a template for secondary PCR reactions. EcoRI or XbaI restriction fragments were cloned and sequenced in both directions on an ABI310 automated sequencer (Perkin Elmer) Overlaps between restriction fragment clo ...
... ®nal elongation step at 68 8C. A single 15.5-kb-long PCR fragment was puri®ed and used as a template for secondary PCR reactions. EcoRI or XbaI restriction fragments were cloned and sequenced in both directions on an ABI310 automated sequencer (Perkin Elmer) Overlaps between restriction fragment clo ...
Chromosomal Rearrangements I
... symbol used. Deletions can be located within a chromosome (interstitial) or can remove the end of a chromosome (terminal). Deletions can be small (intragenic), affecting only one gene, or can span multiple genes (multigenic). Deletions can arise from DNA damage (X-rays or chemical agents that break ...
... symbol used. Deletions can be located within a chromosome (interstitial) or can remove the end of a chromosome (terminal). Deletions can be small (intragenic), affecting only one gene, or can span multiple genes (multigenic). Deletions can arise from DNA damage (X-rays or chemical agents that break ...
a15 GenesFormFunc
... Viruses: Genes in Packages • Properties of Viruses – They exhibit some, but not all, characteristics of living organisms – They are made of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coating. Some also have envelopes outside their protein coat – They are incredibly small (< 1 um) ...
... Viruses: Genes in Packages • Properties of Viruses – They exhibit some, but not all, characteristics of living organisms – They are made of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coating. Some also have envelopes outside their protein coat – They are incredibly small (< 1 um) ...
Will Entrez Find Every Sequence Record?
... • The sequences that you miss are the ones that have not been annotated with the current official gene symbol in the “gene” field • DO NOT use this method if you need to find every sequence for a particular gene ...
... • The sequences that you miss are the ones that have not been annotated with the current official gene symbol in the “gene” field • DO NOT use this method if you need to find every sequence for a particular gene ...
DNA ANALYSIS - Simulating Recombination
... Compare the sequence of base pairs on an enzyme card with the sequences of the plasmid base pairs. If you find the same sequence of pairs on both the enzyme card and the plasmid strip, mark the location on the plasmid with a pencil, and write the enzyme number in the marked area. Repeat this step fo ...
... Compare the sequence of base pairs on an enzyme card with the sequences of the plasmid base pairs. If you find the same sequence of pairs on both the enzyme card and the plasmid strip, mark the location on the plasmid with a pencil, and write the enzyme number in the marked area. Repeat this step fo ...
Editorial - Clinical Chemistry
... on this alternative genome and on development of the scientific tools needed to study this remarkable genetic pathway (1, 2 ). In this issue, Chen et al. (3 ) describe the application of temporal temperature gradient gel electrophoresis to the detection of mtDNA mutations and show that this techniqu ...
... on this alternative genome and on development of the scientific tools needed to study this remarkable genetic pathway (1, 2 ). In this issue, Chen et al. (3 ) describe the application of temporal temperature gradient gel electrophoresis to the detection of mtDNA mutations and show that this techniqu ...
Barcode - Statistical Center for HIV/AIDS Research and Prevention
... • Test how depletion impacts phenotype with simple in vitro functional assay. • Unbiased whole genome screens bring new targets into the “pipeline”. ...
... • Test how depletion impacts phenotype with simple in vitro functional assay. • Unbiased whole genome screens bring new targets into the “pipeline”. ...
principles of genetics
... 1- Molecular Genetics (or Molecular Biology), which is • the study of heredity at the molecular level, and so is mainly concerned with the molecule DNA. It also includes genetic engineering and cloning, and is very trendy. This unit is mostly about molecular genetics. 2- Classical or Mendelian Genet ...
... 1- Molecular Genetics (or Molecular Biology), which is • the study of heredity at the molecular level, and so is mainly concerned with the molecule DNA. It also includes genetic engineering and cloning, and is very trendy. This unit is mostly about molecular genetics. 2- Classical or Mendelian Genet ...
Supplemental Appendix A: ClueGene Algorithm and Time
... to be directly compared, since C(g) would then reflect an average co-clustering index per dataset. In our case, we found that dividing by Mg had little effect on the search results. This has to do with the fact that the yeast expression database contains very little missing data: for every dataset, ...
... to be directly compared, since C(g) would then reflect an average co-clustering index per dataset. In our case, we found that dividing by Mg had little effect on the search results. This has to do with the fact that the yeast expression database contains very little missing data: for every dataset, ...
DNA fingerprinting and the 16S
... In this hypothetical case, 18 different bands (differing by 12 bp) are possible (3 to 20 tandem repeats), thus, nearly 200 (171) different patterns are possible for one individual. [On occasion a single band may result because both parents have donated the same VNTR allele.] In human DNA fingerprint ...
... In this hypothetical case, 18 different bands (differing by 12 bp) are possible (3 to 20 tandem repeats), thus, nearly 200 (171) different patterns are possible for one individual. [On occasion a single band may result because both parents have donated the same VNTR allele.] In human DNA fingerprint ...
BioMart: The linked dataset
... Data mining in Ensembl with BioMart Worked Example – Demonstrating the Linked Dataset BioMart can federate (join together) databases, in this example we will join two different datasets, Ensembl genes and RGD (the Rat Genome Database) to identify all Ensembl genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism ...
... Data mining in Ensembl with BioMart Worked Example – Demonstrating the Linked Dataset BioMart can federate (join together) databases, in this example we will join two different datasets, Ensembl genes and RGD (the Rat Genome Database) to identify all Ensembl genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism ...
Genetics of Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
... represents a primary deficiency of intrinsic immunity against certain papillomaviruses[57]. Although most EV patients studied (75.6%, according to collaborative efforts reported in the review by [57]) have been found to have homozygous mutations in EVER1 or EVER2, this still leaves a significant num ...
... represents a primary deficiency of intrinsic immunity against certain papillomaviruses[57]. Although most EV patients studied (75.6%, according to collaborative efforts reported in the review by [57]) have been found to have homozygous mutations in EVER1 or EVER2, this still leaves a significant num ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Notes
... Hint: You should end up with two complete DNA strands when you are done. ...
... Hint: You should end up with two complete DNA strands when you are done. ...
(2) in ppt - NYU Computer Science
... to break the DNA at specific sites. Since DNA molecules are under slight tension, the cut fragments of DNA relax like entropic springs, leaving small visible gaps corresponding to the positions of the restriction site (Fig 4). 1. A restriction enzyme is a highly specific molecular scissor that recog ...
... to break the DNA at specific sites. Since DNA molecules are under slight tension, the cut fragments of DNA relax like entropic springs, leaving small visible gaps corresponding to the positions of the restriction site (Fig 4). 1. A restriction enzyme is a highly specific molecular scissor that recog ...
Distinct Contributions of Replication and Transcription to Mutation
... distinct influences on human genes, such as significantly increased mutation rates in TS genes but a weaker effect on HK genes. Third, mutation pressure from transcription-associated processes contributes more to the mutation rate of HK genes but exhibits weaker effect on TS genes. Our results furth ...
... distinct influences on human genes, such as significantly increased mutation rates in TS genes but a weaker effect on HK genes. Third, mutation pressure from transcription-associated processes contributes more to the mutation rate of HK genes but exhibits weaker effect on TS genes. Our results furth ...
PTC Lab Instructions/Information
... 2. Using what you know about genetics, SNPs, and the PTC gene, explain why it is possible for a person to be a “weak taster.” 3. Some studies have shown that PTC “tasters” are less likely to become smokers. Why do you think scientists are seeing this correlation? 4. How can the techniques described ...
... 2. Using what you know about genetics, SNPs, and the PTC gene, explain why it is possible for a person to be a “weak taster.” 3. Some studies have shown that PTC “tasters” are less likely to become smokers. Why do you think scientists are seeing this correlation? 4. How can the techniques described ...
2.5.2 Heredity and Gene Expression
... DNA profiling is a method of making a unique pattern of bands from the DNA of a person, which can then be used to distinguish that DNA from other DNA DNA profiling is also called genetic or DNA fingerprinting. Stages involved in DNA profiling 1. DNA isolation Cells are broken down to release DNA 2. ...
... DNA profiling is a method of making a unique pattern of bands from the DNA of a person, which can then be used to distinguish that DNA from other DNA DNA profiling is also called genetic or DNA fingerprinting. Stages involved in DNA profiling 1. DNA isolation Cells are broken down to release DNA 2. ...
Pairwise Alignments 1
... Difficulty of determining ancestral relationships among sequences; Based on a small set of closely related proteins; ...
... Difficulty of determining ancestral relationships among sequences; Based on a small set of closely related proteins; ...
Bioinformatics in the post
... repertoires across different genomes. When two genes are present or absent in a correlated manner among many organisms, there may be a functional link between these genes. A prerequisite to such an analysis is to establish orthologous relationshipsthat is, functionally identical genes that have des ...
... repertoires across different genomes. When two genes are present or absent in a correlated manner among many organisms, there may be a functional link between these genes. A prerequisite to such an analysis is to establish orthologous relationshipsthat is, functionally identical genes that have des ...
Human genome

The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequence for humans (Homo sapiens), encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and sperm gamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNA base pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences among the genomes of human individuals (on the order of 0.1%), these are considerably smaller than the differences between humans and their closest living relatives, the chimpanzees (approximately 4%) and bonobos. Humans share 50% of their DNA with bananas.The Human Genome Project produced the first complete sequences of individual human genomes, with the first draft sequence and initial analysis being published on February 12, 2001. The human genome was the first of all vertebrates to be completely sequenced. As of 2012, thousands of human genomes have been completely sequenced, and many more have been mapped at lower levels of resolution. The resulting data are used worldwide in biomedical science, anthropology, forensics and other branches of science. There is a widely held expectation that genomic studies will lead to advances in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, and to new insights in many fields of biology, including human evolution.Although the sequence of the human genome has been (almost) completely determined by DNA sequencing, it is not yet fully understood. Most (though probably not all) genes have been identified by a combination of high throughput experimental and bioinformatics approaches, yet much work still needs to be done to further elucidate the biological functions of their protein and RNA products. Recent results suggest that most of the vast quantities of noncoding DNA within the genome have associated biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome architecture, and signals controlling epigenetic inheritance.There are an estimated 20,000-25,000 human protein-coding genes. The estimate of the number of human genes has been repeatedly revised down from initial predictions of 100,000 or more as genome sequence quality and gene finding methods have improved, and could continue to drop further. Protein-coding sequences account for only a very small fraction of the genome (approximately 1.5%), and the rest is associated with non-coding RNA molecules, regulatory DNA sequences, LINEs, SINEs, introns, and sequences for which as yet no function has been elucidated.