Lab 11: Simple genomic data analysis using R 1. UCSC genome
... Click “Genomes” at top left corner. This will bring you to the Human Genome (Homo sapiens) Browser. From here you can select genomes for a number of species; the default species is human. Now from the “Human Assembly” pull down menu, select “Mar. 2006 (NCBI36/hg18).” Some information for this assemb ...
... Click “Genomes” at top left corner. This will bring you to the Human Genome (Homo sapiens) Browser. From here you can select genomes for a number of species; the default species is human. Now from the “Human Assembly” pull down menu, select “Mar. 2006 (NCBI36/hg18).” Some information for this assemb ...
Transposable Elements
... Her first contribution was built on the idea that genes were located on chromosomes. She took the ten linkage groups of maize and connected each with a specific chromosome. Her microscopic observations were so exact that she was able to observe recombination events and show that they corresponded wi ...
... Her first contribution was built on the idea that genes were located on chromosomes. She took the ten linkage groups of maize and connected each with a specific chromosome. Her microscopic observations were so exact that she was able to observe recombination events and show that they corresponded wi ...
src
... Filterable virus: A term that had been coined a decade or so earlier to describe pathogenic agents that were small enough to pass through filters that were impermeable to bacteria. ...
... Filterable virus: A term that had been coined a decade or so earlier to describe pathogenic agents that were small enough to pass through filters that were impermeable to bacteria. ...
Document
... fourth generations (third and fourth rows) have been omitted because the mutant gene was not transmitted to them. ...
... fourth generations (third and fourth rows) have been omitted because the mutant gene was not transmitted to them. ...
electroporation of a - The Steve Clough Lab
... 5. Apply a single 2.5kV electrical pulse (field strength of 12.5 kV/cm) by simultaneously pressing both red buttoms on face of gene pulser. Pulser will beep when finished. Time reading ideally will be above 9.3, but lower values may still be ok. Time will be lower the more salt (remember that DNA is ...
... 5. Apply a single 2.5kV electrical pulse (field strength of 12.5 kV/cm) by simultaneously pressing both red buttoms on face of gene pulser. Pulser will beep when finished. Time reading ideally will be above 9.3, but lower values may still be ok. Time will be lower the more salt (remember that DNA is ...
Mendel and Punnett Square notes
... - carries the dominant trait - represented by uppercase letter - because this gene is dominant, you only need one gene for the trait to show. Example: TT: 2 genes for tall Homozygous: Same genetic trait Tt: 1 gene for tall 1 gene for short. ( tall is dominant, short is recessive) Heterozygous: 2 dif ...
... - carries the dominant trait - represented by uppercase letter - because this gene is dominant, you only need one gene for the trait to show. Example: TT: 2 genes for tall Homozygous: Same genetic trait Tt: 1 gene for tall 1 gene for short. ( tall is dominant, short is recessive) Heterozygous: 2 dif ...
Section 9 – Human therapeutics and forensic uses
... symptoms and there are a number of steps required to establish the definitive genetic cause: 1.Trace the disease through family relationships by carrying out pedigree analysis to determine if the faulty gene is dominant, recessive or X-linked. 2.Once the disease has been identified as a monogenic tr ...
... symptoms and there are a number of steps required to establish the definitive genetic cause: 1.Trace the disease through family relationships by carrying out pedigree analysis to determine if the faulty gene is dominant, recessive or X-linked. 2.Once the disease has been identified as a monogenic tr ...
Answers-to-examination-in-Gene-technology_20121020
... Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of the gene. If the gene product is toxic and harmfu ...
... Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of the gene. If the gene product is toxic and harmfu ...
Fundamentals of Biotechnology
... Homologous recombination-based gene targeting low efficiency and ...
... Homologous recombination-based gene targeting low efficiency and ...
13.4 Gene Expression
... Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA silencing complex is known as RNA interference. ...
... Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA silencing complex is known as RNA interference. ...
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)
... The model coefficient β3 indicates the interaction effect and there is no statistically significant interaction effect. On the other hand, treatment and time have significant effects on several gene sets. For the GSEA we used the values of the β1 and β2 coefficients for all genes. A positive value o ...
... The model coefficient β3 indicates the interaction effect and there is no statistically significant interaction effect. On the other hand, treatment and time have significant effects on several gene sets. For the GSEA we used the values of the β1 and β2 coefficients for all genes. A positive value o ...
Gene Ontology
... independent of any organism. Composed of three independent ontologies: molecular function, biological process, cellular component GO itself does not contain any information on genes or gene products ...
... independent of any organism. Composed of three independent ontologies: molecular function, biological process, cellular component GO itself does not contain any information on genes or gene products ...
Gene regulation
... • It is thought to bind more than 20 different proteins • It is very sensitive to the position of the gene (nucleus) within the developing giant cell • The different concentrations of the different proteins impact on the expression of ‘Eve’ ...
... • It is thought to bind more than 20 different proteins • It is very sensitive to the position of the gene (nucleus) within the developing giant cell • The different concentrations of the different proteins impact on the expression of ‘Eve’ ...
GMO vs Selective breeding
... GMO (genetically modified organism) is the result of a laboratory process where genes from the DNA of one species are extracted and artificially forced into the genes of an unrelated plant or animal. The foreign genes may come from bacteria, viruses, insects, animals or even humans. ...
... GMO (genetically modified organism) is the result of a laboratory process where genes from the DNA of one species are extracted and artificially forced into the genes of an unrelated plant or animal. The foreign genes may come from bacteria, viruses, insects, animals or even humans. ...
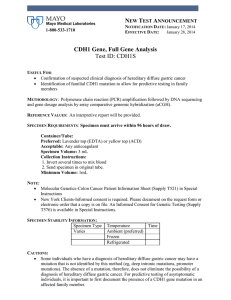
CDH1 Gene, Full Gene Analysis Test ID: CDH1S
... genetic counseling both prior to testing and after results are available. Predictive testing of an asymptomatic child is not recommended. Rare polymorphisms exist that could lead to false-negative or false-positive results. If results obtained do not match the clinical findings, additional testing s ...
... genetic counseling both prior to testing and after results are available. Predictive testing of an asymptomatic child is not recommended. Rare polymorphisms exist that could lead to false-negative or false-positive results. If results obtained do not match the clinical findings, additional testing s ...
Gene Finding
... Gene length: 30kb, coding region: 1-2kb Binding site: ~6bp; ~30bp upstream of TSS Average of 6 exons, 150bp long Huge variance: - dystrophin: 2.4Mb long – Blood coagulation factor: 26 exons, 69bp to 3106bp; intron 22 contains another unrelated gene ...
... Gene length: 30kb, coding region: 1-2kb Binding site: ~6bp; ~30bp upstream of TSS Average of 6 exons, 150bp long Huge variance: - dystrophin: 2.4Mb long – Blood coagulation factor: 26 exons, 69bp to 3106bp; intron 22 contains another unrelated gene ...
2. recombinant gene
... About 10 to 30% of offspring contain injected foreign DNA. Foreign DNA is present in equal amounts in all tissues ...
... About 10 to 30% of offspring contain injected foreign DNA. Foreign DNA is present in equal amounts in all tissues ...
1. dia
... About 10 to 30% of offspring contain injected foreign DNA. Foreign DNA is present in equal amounts in all tissues ...
... About 10 to 30% of offspring contain injected foreign DNA. Foreign DNA is present in equal amounts in all tissues ...
Basics in Genetics
... Thus most mutations recessive!! Null mutation= makes no protein or totally non-functional protein. Weak or Hypomorphic mutation= makes protein that retains some but not all function. Loss of function mutation vs. Gain of function mutation c. One gene has different alleles. Normal allele = wild type. ...
... Thus most mutations recessive!! Null mutation= makes no protein or totally non-functional protein. Weak or Hypomorphic mutation= makes protein that retains some but not all function. Loss of function mutation vs. Gain of function mutation c. One gene has different alleles. Normal allele = wild type. ...
Genetic Variation Worksheet
... Scenario #1 In a population of spiders, there is a protein that is coded in the DNA to make venom. In a particular spider, there was a protein variation due to a change in the genetic code. This protein variation caused the spider’s venom to be stronger to kill its prey. This genetic variation was p ...
... Scenario #1 In a population of spiders, there is a protein that is coded in the DNA to make venom. In a particular spider, there was a protein variation due to a change in the genetic code. This protein variation caused the spider’s venom to be stronger to kill its prey. This genetic variation was p ...
Mutagenesis and Genetic Screens
... that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
... that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
Gene therapy

Gene therapy is the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acid polymers into a patient's cells as a drug to treat disease. Gene therapy could be a way to fix a genetic problem at its source. The polymers are either expressed as proteins, interfere with protein expression, or possibly correct genetic mutations.The most common form uses DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic gene to replace a mutated gene. The polymer molecule is packaged within a ""vector"", which carries the molecule inside cells.Gene therapy was conceptualized in 1972, by authors who urged caution before commencing human gene therapy studies. By the late 1980s the technology had already been extensively used on animals, and the first genetic modification of a living human occurred on a trial basis in May 1989 , and the first gene therapy experiment approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) occurred on September 14, 1990, when Ashanti DeSilva was treated for ADA-SCID. By January 2014, some 2,000 clinical trials had been conducted or approved.Early clinical failures led to dismissals of gene therapy. Clinical successes since 2006 regained researchers' attention, although as of 2014, it was still largely an experimental technique. These include treatment of retinal disease Leber's congenital amaurosis, X-linked SCID, ADA-SCID, adrenoleukodystrophy, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), multiple myeloma, haemophilia and Parkinson's disease. Between 2013 and April 2014, US companies invested over $600 million in the field.The first commercial gene therapy, Gendicine, was approved in China in 2003 for the treatment of certain cancers. In 2011 Neovasculgen was registered in Russia as the first-in-class gene-therapy drug for treatment of peripheral artery disease, including critical limb ischemia.In 2012 Glybera, a treatment for a rare inherited disorder, became the first treatment to be approved for clinical use in either Europe or the United States after its endorsement by the European Commission.