Compartmentalisation of metabolic pathways
... • Enzyme concentration is much lower than the substrate concentration • The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is directly dependent upon the enzyme concentration • Induction by substrate or repression by product (on the level of transcription) – xenobiotics → induction of cyt P450 – heme → repres ...
... • Enzyme concentration is much lower than the substrate concentration • The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is directly dependent upon the enzyme concentration • Induction by substrate or repression by product (on the level of transcription) – xenobiotics → induction of cyt P450 – heme → repres ...
Slide 1
... populations more than others. For example, the development of lactose-free milk available in Europe and North America would have greater benefit in Africa/ Asia where lactose intolerance is more prevalent. The development of techniques requires financial investment. Should knowledge be shared when t ...
... populations more than others. For example, the development of lactose-free milk available in Europe and North America would have greater benefit in Africa/ Asia where lactose intolerance is more prevalent. The development of techniques requires financial investment. Should knowledge be shared when t ...
Midterm for Bio98B A1 (1) Enzymes accelerate reactions by
... F1 (2) You want to make a pH = 7 phosphate buffer. You have 0.1M KH2PO4. What concentration of K2HPO4 do you need? HPO4-2 + H+ ...
... F1 (2) You want to make a pH = 7 phosphate buffer. You have 0.1M KH2PO4. What concentration of K2HPO4 do you need? HPO4-2 + H+ ...
Chapter 8-Intro to Metabolism
... two or more subunits, a substrate causing induced fit in one subunit can trigger the same favorable conformational change in all the other subunits of the enzyme, amplifies the response of enzymes to substrates, one substrate molecule primes an enzyme to accept additional substrate molecules more ra ...
... two or more subunits, a substrate causing induced fit in one subunit can trigger the same favorable conformational change in all the other subunits of the enzyme, amplifies the response of enzymes to substrates, one substrate molecule primes an enzyme to accept additional substrate molecules more ra ...
Chapter 8-Intro to Metabolism - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... two or more subunits, a substrate causing induced fit in one subunit can trigger the same favorable conformational change in all the other subunits of the enzyme, amplifies the response of enzymes to substrates, one substrate molecule primes an enzyme to accept additional substrate molecules more ra ...
... two or more subunits, a substrate causing induced fit in one subunit can trigger the same favorable conformational change in all the other subunits of the enzyme, amplifies the response of enzymes to substrates, one substrate molecule primes an enzyme to accept additional substrate molecules more ra ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry
... • Each enzyme is specific to a substrate (chemical(s) in the reaction). • They fit each other like a “lock and key”. ...
... • Each enzyme is specific to a substrate (chemical(s) in the reaction). • They fit each other like a “lock and key”. ...
Enzyme Catalysis Lab
... chains in or near the active site to change its shape or block it. Many well known poisons such as potassium-cyanide and curare are enzyme inhibitors that interfere with the active site of critical enzymes. The enzyme used in this lab, catalase, has four polypeptide chains, each composed of more tha ...
... chains in or near the active site to change its shape or block it. Many well known poisons such as potassium-cyanide and curare are enzyme inhibitors that interfere with the active site of critical enzymes. The enzyme used in this lab, catalase, has four polypeptide chains, each composed of more tha ...
Sources of enzyme
... They contain a number of enzymes with different catalytic functions and are not used with either a pure substrate or a completely defined ...
... They contain a number of enzymes with different catalytic functions and are not used with either a pure substrate or a completely defined ...
Enzymes upload
... blocks enzyme bacteria use to build cell walls ◦ disulfiram (Antabuse) treats chronic alcoholism blocks enzyme that breaks down alcohol severe hangover & vomiting 5-10 minutes after drinking ...
... blocks enzyme bacteria use to build cell walls ◦ disulfiram (Antabuse) treats chronic alcoholism blocks enzyme that breaks down alcohol severe hangover & vomiting 5-10 minutes after drinking ...
Classification of Enzymes
... Enzyme activity is decreased by inhibitors.This is the basis of many pharmaceutical agents. Many substances can inhibit enzyme activity. ...
... Enzyme activity is decreased by inhibitors.This is the basis of many pharmaceutical agents. Many substances can inhibit enzyme activity. ...
Fuel for the Future
... the MnO2 itself is broken down to form the oxygen ). Enzymes as catalysts are capable of increasing the reaction rate by as much as 1020. They are able to do this in many ways: reduce the activation energy, reduce energy of transition state, temporarily react with the chemical creating a compound fo ...
... the MnO2 itself is broken down to form the oxygen ). Enzymes as catalysts are capable of increasing the reaction rate by as much as 1020. They are able to do this in many ways: reduce the activation energy, reduce energy of transition state, temporarily react with the chemical creating a compound fo ...
Proteins Act As Catalysts
... • Such organophosphorous inhibitors are used as insecticides or for enzyme research • These inhibitors are toxic because they inhibit acetylcholinesterase (a serine protease that hydrolyzes the neurotransmitter acetylcholine) ...
... • Such organophosphorous inhibitors are used as insecticides or for enzyme research • These inhibitors are toxic because they inhibit acetylcholinesterase (a serine protease that hydrolyzes the neurotransmitter acetylcholine) ...
General Biochemistry Exam – 2002 Excess Acetyl
... replaced with T in humans, the enzyme improved its ability, and when T was replaced with S in the frog, its affinity decreased. On the other hand, when a mutation occurred and S or T was replaced with valine (V) the enzyme lost catalytic activity. Mark the correct answer: a. The S and the T are foun ...
... replaced with T in humans, the enzyme improved its ability, and when T was replaced with S in the frog, its affinity decreased. On the other hand, when a mutation occurred and S or T was replaced with valine (V) the enzyme lost catalytic activity. Mark the correct answer: a. The S and the T are foun ...
Topic guide 1.2: Enzymes
... concentration, the rate will also increase. Remember that if there is not an abundant supply of substrate, increasing the concentration of enzyme will have no effect on the rate of reaction. ...
... concentration, the rate will also increase. Remember that if there is not an abundant supply of substrate, increasing the concentration of enzyme will have no effect on the rate of reaction. ...
Example of Research Proposal
... transition state inhibitor, CCApPmn. This molecule will make it possible to determine how the binding affinity and geometry of the active site are affected by the additional 2'-OH group. The second target is a transition state inhibitor with a chiral phosphate. Using the general scheme outlined in t ...
... transition state inhibitor, CCApPmn. This molecule will make it possible to determine how the binding affinity and geometry of the active site are affected by the additional 2'-OH group. The second target is a transition state inhibitor with a chiral phosphate. Using the general scheme outlined in t ...
Enzyme inhibitor
... zyme has reached equilibrium, which may be a very slow [I] + Ki process for inhibitors with sub-nanomolar dissociation constants. In these cases, it is usually more practical to [I] + Ki − [I] treat the tight-binding inhibitor as an irreversible inhibitor Dividing by [I]+Kᵢ (see below); however, it ...
... zyme has reached equilibrium, which may be a very slow [I] + Ki process for inhibitors with sub-nanomolar dissociation constants. In these cases, it is usually more practical to [I] + Ki − [I] treat the tight-binding inhibitor as an irreversible inhibitor Dividing by [I]+Kᵢ (see below); however, it ...
Enzymes - دانشکده پزشکی
... According to Holum, the non-protein portion may be: • A coenzyme - a non-protein organic substance which is loosely attached to the protein part. • A prosthetic group - an organic substance which is firmly attached to the protein or apoenzyme portion. • A cofactor - these include K+, Fe++, Fe+++, Cu ...
... According to Holum, the non-protein portion may be: • A coenzyme - a non-protein organic substance which is loosely attached to the protein part. • A prosthetic group - an organic substance which is firmly attached to the protein or apoenzyme portion. • A cofactor - these include K+, Fe++, Fe+++, Cu ...
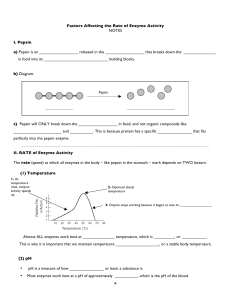
8 Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity NOTES I. Pepsin a
... I. How does TEMPERATURE affect the RATE at which pepsin works? The effect of temperature on the action of pepsin, a protein-digesting enzyme present in stomach fluid, was tested. In this investigation, 20 milliliters of stomach fluid and 10 grams of protein were placed in each of five test tubes. T ...
... I. How does TEMPERATURE affect the RATE at which pepsin works? The effect of temperature on the action of pepsin, a protein-digesting enzyme present in stomach fluid, was tested. In this investigation, 20 milliliters of stomach fluid and 10 grams of protein were placed in each of five test tubes. T ...
ch3b_SP13x
... – Pyruvate enters TCA cycle – NAD+ regenerated by electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation) ...
... – Pyruvate enters TCA cycle – NAD+ regenerated by electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation) ...
Chem 306 Ch 19 Enzymes Spring 2007
... A 3D rendition of the protease pepsin and its zymogen form pepsinogen. ...
... A 3D rendition of the protease pepsin and its zymogen form pepsinogen. ...
Enzymes_Group A
... Once substrate correctly positioned, result in a strained enzyme-substrate complex. This strain help to bring the enzyme-substrate complex into the transition state In general, the more tightly the active site can bind the substrate while it is in the transition state, the greater the reaction ...
... Once substrate correctly positioned, result in a strained enzyme-substrate complex. This strain help to bring the enzyme-substrate complex into the transition state In general, the more tightly the active site can bind the substrate while it is in the transition state, the greater the reaction ...
4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures
... In feedback control, the end product binds to a regulatory site on the allosteric (first) enzyme in the reaction sequence, which prevents the formation of all intermediate compounds needed in the synthesis of the end product. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen ...
... In feedback control, the end product binds to a regulatory site on the allosteric (first) enzyme in the reaction sequence, which prevents the formation of all intermediate compounds needed in the synthesis of the end product. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen ...
PAGES 1-41 INCL. 1. Overview (a) discovery of enzymes (b
... - specificity relates to binding of substrate to enzyme - group specific enzymes can use a variety of substrates, each containing a certain functional group which is modified - absolute specificity utilize only one substrate (or specific pair) in one reaction 2.(a) What is a catalyst? - any molecule ...
... - specificity relates to binding of substrate to enzyme - group specific enzymes can use a variety of substrates, each containing a certain functional group which is modified - absolute specificity utilize only one substrate (or specific pair) in one reaction 2.(a) What is a catalyst? - any molecule ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.