Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation
... To understand how energy is trapped or generated and how ATP functions as an energy currency, some knowledge of the basic principles of thermodynamics is required. The science of thermodynamics analyzes energy changes in a collection of matter (e.g., a cell or a plant) called a system. All other mat ...
... To understand how energy is trapped or generated and how ATP functions as an energy currency, some knowledge of the basic principles of thermodynamics is required. The science of thermodynamics analyzes energy changes in a collection of matter (e.g., a cell or a plant) called a system. All other mat ...
Molecular cloning and characterization of cm3 gene, from t
... Southern blotting of wheat genomic DNA was used to investigate the organization and copy number of gene(s) encoding the T. durum CM3 protein and T. aestivum CM3 protein. High molecular weight DNA from cv. PDW279 and UP2425 was digested to completion with EcoR1 (Fig. 3). Single fragment of approximat ...
... Southern blotting of wheat genomic DNA was used to investigate the organization and copy number of gene(s) encoding the T. durum CM3 protein and T. aestivum CM3 protein. High molecular weight DNA from cv. PDW279 and UP2425 was digested to completion with EcoR1 (Fig. 3). Single fragment of approximat ...
PREDICTION OF THE INTERACTION OF HIV
... traditional medicinal plants, are a novel class of integrase inhibitors. These compounds are potent inhibitors of HIV-1 replication in cultured cell lines and catalytic activities of integrase in vitro. They are therefore promising compounds for developing new anti-AIDS drugs. To understand how the ...
... traditional medicinal plants, are a novel class of integrase inhibitors. These compounds are potent inhibitors of HIV-1 replication in cultured cell lines and catalytic activities of integrase in vitro. They are therefore promising compounds for developing new anti-AIDS drugs. To understand how the ...
Development of Biocatalysts for Production of Fine Chemicals
... that can be used in the synthesis of optically active alcoIn recent years efficient production with little impact ...
... that can be used in the synthesis of optically active alcoIn recent years efficient production with little impact ...
Effect of non-ionic detergents on apparent enzyme mechanism
... sigmoidal in this case and essentially the same with that of wild type. This suggests that the cooperative phenomenon of V121A is dependent on non-ionic detergents. V121 is in a hydrophobic loop which is located near the active site. The loop covers the active site as shown in Figure 1. As the side ...
... sigmoidal in this case and essentially the same with that of wild type. This suggests that the cooperative phenomenon of V121A is dependent on non-ionic detergents. V121 is in a hydrophobic loop which is located near the active site. The loop covers the active site as shown in Figure 1. As the side ...
Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism
... addition, Asp-283 faces the active site so that there is electrostatic repulsion between this residue and the substrate inorganic phosphate. In the R-state, the active site is exposed to the solvent facilitating substrate binding. In addition, Asp-283 is displaced from the active site and replaced b ...
... addition, Asp-283 faces the active site so that there is electrostatic repulsion between this residue and the substrate inorganic phosphate. In the R-state, the active site is exposed to the solvent facilitating substrate binding. In addition, Asp-283 is displaced from the active site and replaced b ...
Sequence, expression, and characterization of the first archaeal ATP
... Enzyme assays and determination of kinetic parameters Since the enzyme activity was not sensitive to oxygen, all assays were performed under oxic conditions. The ATP-dependent PFK activity (F-6-P+ATP→F-1,6-BP+ADP) was determined in the direction of F-1,6-BP formation. The reaction was measured by co ...
... Enzyme assays and determination of kinetic parameters Since the enzyme activity was not sensitive to oxygen, all assays were performed under oxic conditions. The ATP-dependent PFK activity (F-6-P+ATP→F-1,6-BP+ADP) was determined in the direction of F-1,6-BP formation. The reaction was measured by co ...
Physiological and Chemical Properties of a
... mg. bacterial protein/ml. ; y lactate = 2.32 g.]mole). Effluent of this culture was used for experiments and also to inoculate 20 1. batch cultures of similar medium with the trace element solution omitted but with the addition of (per litre): NH,CI, 1.5 g.; FeS0,.7H20, 3 mg.; and yeast extract, 1.0 ...
... mg. bacterial protein/ml. ; y lactate = 2.32 g.]mole). Effluent of this culture was used for experiments and also to inoculate 20 1. batch cultures of similar medium with the trace element solution omitted but with the addition of (per litre): NH,CI, 1.5 g.; FeS0,.7H20, 3 mg.; and yeast extract, 1.0 ...
The Affect of Enzymes on a Chemical Reaction
... Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. They have active sites where substrates attach to the enzyme and a chemical reaction occurs in which a product is produced. Although a chemical reaction occurs, the enzyme remains unchanged. Salt concentration, pH, temperature, and competitive a ...
... Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. They have active sites where substrates attach to the enzyme and a chemical reaction occurs in which a product is produced. Although a chemical reaction occurs, the enzyme remains unchanged. Salt concentration, pH, temperature, and competitive a ...
Lesson 8. Enzymes
... each enzyme. Enzymes are also classified on the basis of their composition. Enzymes composed wholly of protein are known as simple enzymes in contrast to complex enzymes, which are composed of protein plus a relatively small organic molecule. Complex enzymes are also known as holo-enzymes. The nonpr ...
... each enzyme. Enzymes are also classified on the basis of their composition. Enzymes composed wholly of protein are known as simple enzymes in contrast to complex enzymes, which are composed of protein plus a relatively small organic molecule. Complex enzymes are also known as holo-enzymes. The nonpr ...
2014
... As a result, all of the subunits are either in the low- or high-affinity conformation. In the sequential model, each subunit is changed individually to the high affinity conformation. As a result, there are many possible combinations of low- and high-affinity subunits. ...
... As a result, all of the subunits are either in the low- or high-affinity conformation. In the sequential model, each subunit is changed individually to the high affinity conformation. As a result, there are many possible combinations of low- and high-affinity subunits. ...
Lecture 25 Cofactors and Coenzymes
... two groups- organic cofactors and inorganic cofactors. Coenzymes are organic cofactors which are again divided into two groups- cosubstrates and prosthetic groups. Cofactors which bound loosely to an enzyme are termed as coenzymes and cofactors which bound tightly to an enzyme are termed as prosthet ...
... two groups- organic cofactors and inorganic cofactors. Coenzymes are organic cofactors which are again divided into two groups- cosubstrates and prosthetic groups. Cofactors which bound loosely to an enzyme are termed as coenzymes and cofactors which bound tightly to an enzyme are termed as prosthet ...
Metabolic Reactions Responsible for Glucose
... Waters, 1976). Similar observations were made with cells grown in LP glycerol (data not shown), but the inhibitors had no effect when cells were grown in LP (Fig. 2b). Thus it seemed reasonable to conclude that the metabolic reactions of the glycolytic pathway from glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 2-ph ...
... Waters, 1976). Similar observations were made with cells grown in LP glycerol (data not shown), but the inhibitors had no effect when cells were grown in LP (Fig. 2b). Thus it seemed reasonable to conclude that the metabolic reactions of the glycolytic pathway from glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 2-ph ...
Metabolic networks: enzyme function and metabolite structure
... Palsson and co-workers have also demonstrated the importance of charge (electron and proton) balance in the constraints-based network analysis of metabolism. In a constraints-based model of Escherichia coli, they have shown that the predicted properties of the system, such as growth rate, depend on ...
... Palsson and co-workers have also demonstrated the importance of charge (electron and proton) balance in the constraints-based network analysis of metabolism. In a constraints-based model of Escherichia coli, they have shown that the predicted properties of the system, such as growth rate, depend on ...
Characterizing the complexity of enzymes on the basis of their
... enzymes with an identical EC number (and therefore overall reaction) occasionally have significantly different mechanisms. A good example of this phenomenon is provided by the haloperoxidases (EC 1.11.1.10). There are three different types of this enzyme that have been identified so far, all of which ...
... enzymes with an identical EC number (and therefore overall reaction) occasionally have significantly different mechanisms. A good example of this phenomenon is provided by the haloperoxidases (EC 1.11.1.10). There are three different types of this enzyme that have been identified so far, all of which ...
Generalities Main amino acid reactions
... Proteins are the polypeptides formed by sequences of amino acids General formula of the a-amino acids NH2-CH-COOH R The amino acids occupy a central position in the metabolism of nitrogenous compounds ...
... Proteins are the polypeptides formed by sequences of amino acids General formula of the a-amino acids NH2-CH-COOH R The amino acids occupy a central position in the metabolism of nitrogenous compounds ...
Uncommon pathways of metabolism among lactic acid bacteria
... some amino acids. Synthetically, they possess the potential to manufacture a host of complex carbohydrates (expressed as cell wall antigens or loosely associated slime matrices) and, in at least one instance, some rare amino acids. Past contributions to this series of symposia have dealt with the ge ...
... some amino acids. Synthetically, they possess the potential to manufacture a host of complex carbohydrates (expressed as cell wall antigens or loosely associated slime matrices) and, in at least one instance, some rare amino acids. Past contributions to this series of symposia have dealt with the ge ...
Name: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ Student ID: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ
... __) (1pt) The strongest, angle-independent force of attraction between the side-chains of aspartate and arginine within a protein is likely to be (circle one) H-bonding / hydrophobic interaction / van der Waals / a peptide bond / electrostatic ...
... __) (1pt) The strongest, angle-independent force of attraction between the side-chains of aspartate and arginine within a protein is likely to be (circle one) H-bonding / hydrophobic interaction / van der Waals / a peptide bond / electrostatic ...
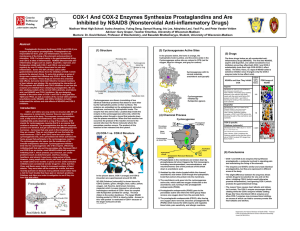
COX-1 And COX-2 Enzymes Synthesize Prostaglandins and Are
... stands for cyclooxygenase meaning that it is an enzyme that oxidizes a substrate. The prostaglandins that the two enzymes produce are identical, but get converted into different paracrine hormones - hormones that only work in the immediate area they are created. They are not shipped all over the bod ...
... stands for cyclooxygenase meaning that it is an enzyme that oxidizes a substrate. The prostaglandins that the two enzymes produce are identical, but get converted into different paracrine hormones - hormones that only work in the immediate area they are created. They are not shipped all over the bod ...
Enzymologychapter13 - Panama College of Cell Science
... enzyme, analysis of the enzymatic rate under different reaction conditions yields insights regarding the enzyme’s mechanism of catalytic action. Such information is essential to an overall understanding of metabolism. Significantly, this information can be exploited to control and manipulate the cou ...
... enzyme, analysis of the enzymatic rate under different reaction conditions yields insights regarding the enzyme’s mechanism of catalytic action. Such information is essential to an overall understanding of metabolism. Significantly, this information can be exploited to control and manipulate the cou ...
LECT35 trans1
... Q: So, what’s the big deal? A: There are 20 amino acids; the code is degenerate There could be 4 “isoaccepting tRNAs” competing for one Q: I still don’t see a problem ...
... Q: So, what’s the big deal? A: There are 20 amino acids; the code is degenerate There could be 4 “isoaccepting tRNAs” competing for one Q: I still don’t see a problem ...
Engineering carbonic anhydrase for highly selective ester hydrolysis Gunnar Höst
... the interconversion between CO2 and HCO3- in the body, also has the ability to hydrolyze ester bonds. In one project, the specificity of HCAII towards a panel of para-nitrophenyl ester substrates, with acyl chain lengths ranging from one to five carbon atoms, was changed by enlarging the substrate b ...
... the interconversion between CO2 and HCO3- in the body, also has the ability to hydrolyze ester bonds. In one project, the specificity of HCAII towards a panel of para-nitrophenyl ester substrates, with acyl chain lengths ranging from one to five carbon atoms, was changed by enlarging the substrate b ...
Anti-trypanosomal Activity of Potential Inhibitors of Trypanosoma
... microbes to identify essential functions that might serve as starting points for the search for novel inhibitors. This exercise has been aided greatly by the presence of a complete and annotated genome of T. brucei. Additionally, a number of molecular biology techniques are also available to evaluat ...
... microbes to identify essential functions that might serve as starting points for the search for novel inhibitors. This exercise has been aided greatly by the presence of a complete and annotated genome of T. brucei. Additionally, a number of molecular biology techniques are also available to evaluat ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.