Lumped Electro-Thermal Model of On-chip Interconnects
... Simultaneously the aggressive scaling down of devices dimension and the increase of operating frequency has dramatically magnified the electrical power density leading to a significant temperature increase in the substrate and in the metal interconnects. The increase of temperature determines, among ...
... Simultaneously the aggressive scaling down of devices dimension and the increase of operating frequency has dramatically magnified the electrical power density leading to a significant temperature increase in the substrate and in the metal interconnects. The increase of temperature determines, among ...
Remote Service Sentinel (SS)
... • Single point power connection • Ave. leaving air temperature 92° vrs Trane at 80°!!!!! (see chart) • This application for boilerless electric heat; heating provided is electric only-no compressor operation. • Typically applicable to NC latitude and south ...
... • Single point power connection • Ave. leaving air temperature 92° vrs Trane at 80°!!!!! (see chart) • This application for boilerless electric heat; heating provided is electric only-no compressor operation. • Typically applicable to NC latitude and south ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 11 – Chapter 25 sec. 4-5
... Kirchhoff’s Rules • General problem: – Calculate the currents that flow in an electric circuit composed of voltage sources and resistors connected by wires. – Recall that work done to move a charge from point to point is = − ∙ ℓ – If and are the same point then ...
... Kirchhoff’s Rules • General problem: – Calculate the currents that flow in an electric circuit composed of voltage sources and resistors connected by wires. – Recall that work done to move a charge from point to point is = − ∙ ℓ – If and are the same point then ...
V - Faculty
... from other competing variables. • Accuracy—Difference between true value and measured value divided by the true value. • Precision—Number of distinguishable alternatives from which a given result is selected • Resolution—Smallest increment that can be measured with certainty. • Reproducibility—Same ...
... from other competing variables. • Accuracy—Difference between true value and measured value divided by the true value. • Precision—Number of distinguishable alternatives from which a given result is selected • Resolution—Smallest increment that can be measured with certainty. • Reproducibility—Same ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... b) If a wire was attached between points A and B in circuit 2, would this change effect the brightness of each individual bulb in the circuit? If yes, explain in what way each bulb would be effected. Identify the two bulbs as X and Y (as shown). ...
... b) If a wire was attached between points A and B in circuit 2, would this change effect the brightness of each individual bulb in the circuit? If yes, explain in what way each bulb would be effected. Identify the two bulbs as X and Y (as shown). ...
Ohm`s Law - UStudy.in
... Power in Electrical Circuits Electrical Power, (P) in a circuit is the amount of energy that is ...
... Power in Electrical Circuits Electrical Power, (P) in a circuit is the amount of energy that is ...
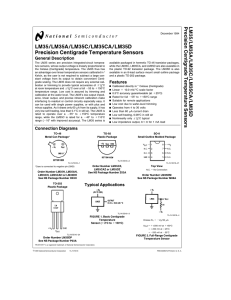
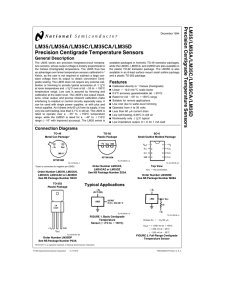
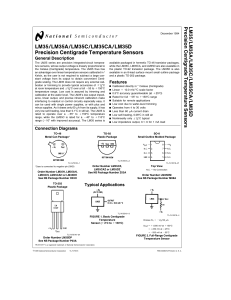
LM35/LM35A/LM35C/LM35CA/LM35D Precision Centigrade Temperature Sensors Precision Centigrade
... metal tube, and can then be dipped into a bath or screwed into a threaded hole in a tank. As with any IC, the LM35 and accompanying wiring and circuits must be kept insulated and dry, to avoid leakage and corrosion. This is especially true if the circuit may operate at cold temperatures where conden ...
... metal tube, and can then be dipped into a bath or screwed into a threaded hole in a tank. As with any IC, the LM35 and accompanying wiring and circuits must be kept insulated and dry, to avoid leakage and corrosion. This is especially true if the circuit may operate at cold temperatures where conden ...
Good Layout
... – Keep loop area small for high frequency, di/dt, signals and away from high impedance circuits (Magnetic coupling) – Keep high dV/dt signal’s area small and away from high impedance circuits (Electric Coupling) ...
... – Keep loop area small for high frequency, di/dt, signals and away from high impedance circuits (Magnetic coupling) – Keep high dV/dt signal’s area small and away from high impedance circuits (Electric Coupling) ...
Chapter 5: Resistors - Mt. San Antonio College
... “The larger the cross-sectional area of the conductor, the more electrons are available to carry the current, so the lower the resistance. The longer the conductor, the more scattering events occur in each electron's path through the material, so the higher the resistance. Different materials also a ...
... “The larger the cross-sectional area of the conductor, the more electrons are available to carry the current, so the lower the resistance. The longer the conductor, the more scattering events occur in each electron's path through the material, so the higher the resistance. Different materials also a ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... 20.4 Resistance Resistance is the measure of how strongly an object resists current flowing through it. The relationship between electric current and resistance can be compared with water flowing from the open end of a bottle. ...
... 20.4 Resistance Resistance is the measure of how strongly an object resists current flowing through it. The relationship between electric current and resistance can be compared with water flowing from the open end of a bottle. ...
Lumped element model
The lumped element model (also called lumped parameter model, or lumped component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc.Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters.