Human reproductive s.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Explain the function of the following structures of the female reproductive system. (5) a. vagina – organ of sexual intercourse and birth canal b. cervix – opening of the uterus, protects the uterus from bacterial infections c. uterus – houses the developing fetus d. ovaries – produces egg and es ...
... 2. Explain the function of the following structures of the female reproductive system. (5) a. vagina – organ of sexual intercourse and birth canal b. cervix – opening of the uterus, protects the uterus from bacterial infections c. uterus – houses the developing fetus d. ovaries – produces egg and es ...
Egg Production or Oogenesis
... Sperm and eggs are formed in specialized organs Males and females have different reproductive organs Infertility is a problem in some areas of the world ...
... Sperm and eggs are formed in specialized organs Males and females have different reproductive organs Infertility is a problem in some areas of the world ...
Male and Female Reproductive Systems
... human reproductive systems, including the process of egg and sperm production. A. Sex Cells (gametes) 1. Ovum (Ova)-Egg(s) is the female sex cell. 2. Sperm is the male sex cell. 3. The joining of the female and male sex cells is called fertilization. 4. Reproduction is when living things produce new ...
... human reproductive systems, including the process of egg and sperm production. A. Sex Cells (gametes) 1. Ovum (Ova)-Egg(s) is the female sex cell. 2. Sperm is the male sex cell. 3. The joining of the female and male sex cells is called fertilization. 4. Reproduction is when living things produce new ...
Sexual Selection
... Sperm length has been selected (direct benefits, intermale competition, counteradaptations) Constrained by sperm length vs. numbers Sperm motility predicts successful fertilization Speed and duration of “swimming” Non-nucleate sperm enhance ejaculate “bulk” Sperm “train” for faster access ...
... Sperm length has been selected (direct benefits, intermale competition, counteradaptations) Constrained by sperm length vs. numbers Sperm motility predicts successful fertilization Speed and duration of “swimming” Non-nucleate sperm enhance ejaculate “bulk” Sperm “train” for faster access ...
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
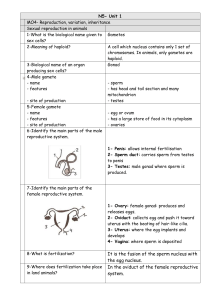
... N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual reproduction in animals 1-What is the biological name given to Gametes sex cells? 2-Meaning of haploid? A cell which nucleus contains only 1 set of chromosomes. In animals, only gametes are haploid. 3-Biological name of an organ Gonad produ ...
... N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual reproduction in animals 1-What is the biological name given to Gametes sex cells? 2-Meaning of haploid? A cell which nucleus contains only 1 set of chromosomes. In animals, only gametes are haploid. 3-Biological name of an organ Gonad produ ...
Earthworm Dissection
... nerves. In the earthworm, there is a pair of ganglia in each segment and a cerebral ganglia acts like a brain ...
... nerves. In the earthworm, there is a pair of ganglia in each segment and a cerebral ganglia acts like a brain ...
Mating of gastropods

The mating of gastropods is a vast and varied topic, because the taxonomic class Gastropoda is very large and diverse, a group comprising sea snails and sea slugs, freshwater snails and land snails and slugs. Gastropods are second only to the class Insecta in terms of total number of species. Some gastropods have separate sexes, others are hermaphroditic. Some hermaphroditic groups have simultaneous hermaphroditism, whereas some sequential hermaphroditism. In addition, numerous very different mating strategies are used within different taxa.This article currently focuses primarily on the mating habits of air-breathing terrestrial slugs. Land slugs can be thought of as land snails that over evolutionary time have either lost the shell completely, have a very reduced external shell, or have retained only internal remnants of a shell. Land slugs are a highly polyphyletic group, which means that many land slug families are not at all closely related to one another.The majority of land slugs are simultaneous hermaphrodites, meaning they possess both male and female reproductive organs that are functional at the same time. Some species regularly self-fertilise. Uniparental reproduction may also occur by apomixis, an asexual process.For the most part, however, land slugs do mate: they find partners, and engage in elaborate courtship rituals before actual sperm transfer takes place. It is common for slugs to mate in a simultaneous reciprocal manner, as occurs in the monophyletic groups Limacoidea and Philomycidae. Limacoidea comprises the family Limacidae (the keelback slugs) and the largest genus of slugs, Deroceras, which contains over 100 known species. Sperm transfer may be external (as in Deroceras) or internal (as in Ariolimax).