Mathematical Template
... randomly selected subjects from the Harrisonburg community. Give your subject a sheet of blank paper. Have the subject close his or her eyes for 10 seconds, then open them and stare at the blank paper, trying not to blink. Time how many seconds elapse before the subject blinks. We call this the subj ...
... randomly selected subjects from the Harrisonburg community. Give your subject a sheet of blank paper. Have the subject close his or her eyes for 10 seconds, then open them and stare at the blank paper, trying not to blink. Time how many seconds elapse before the subject blinks. We call this the subj ...
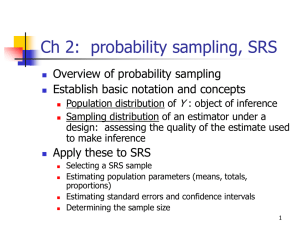
Ch 2: probability sampling, SRS
... Nonzero probability every SU has a positive chance of being included in the sample ...
... Nonzero probability every SU has a positive chance of being included in the sample ...
CHAPTER EIGHT Confidence Intervals, Effect Size, and Statistical
... a medium effect size, and a d of .8 is considered a large effect size. 6. The sign of the effect size does not matter. > Discussion Question 8-4 Imagine you obtain an effect size of –0.3. How would you interpret this number? Your students’ answers should include: If you obtained an effect size of ...
... a medium effect size, and a d of .8 is considered a large effect size. 6. The sign of the effect size does not matter. > Discussion Question 8-4 Imagine you obtain an effect size of –0.3. How would you interpret this number? Your students’ answers should include: If you obtained an effect size of ...
- Sleeping Polar Bear
... For such distributions, when N is sufficiently large, the empirical rule tells us that: (1) Approximately 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean o 68% of scores fall within the following interval: X ± S → [X − S, X + S ] o In other words, 68% of scores have a Z-score between -1 an ...
... For such distributions, when N is sufficiently large, the empirical rule tells us that: (1) Approximately 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean o 68% of scores fall within the following interval: X ± S → [X − S, X + S ] o In other words, 68% of scores have a Z-score between -1 an ...