What`s Stat - DrJimMirabella.com
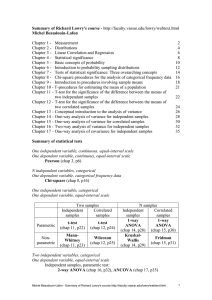
... not be used for a lower level, but can be used for a higher level. An implication of this guideline is that data obtained from using a Likert-type scale (a scale in which people set their preferences from say 1= totally agree to 10 = totally disagree) should, generally, not be used in parametric tes ...
... not be used for a lower level, but can be used for a higher level. An implication of this guideline is that data obtained from using a Likert-type scale (a scale in which people set their preferences from say 1= totally agree to 10 = totally disagree) should, generally, not be used in parametric tes ...
homeworke_ch3
... D) negatively skewed 71. A disadvantage of using an arithmetic mean to summarize a set of data is A) The arithmetic mean sometimes has two values B) It can be used for interval and ratio data C) It is always different from the median D) It can be biased by one or two extremely small or large values ...
... D) negatively skewed 71. A disadvantage of using an arithmetic mean to summarize a set of data is A) The arithmetic mean sometimes has two values B) It can be used for interval and ratio data C) It is always different from the median D) It can be biased by one or two extremely small or large values ...
Exposure Assessment: Tolerance Limits, Confidence Intervals and
... with probability (power) .90, when the true 95th percentile is 20ppm. On the basis of past data or based on data from a similar workplace, suppose the value of the geometric SD exp(σ) is guessed to be 2.015ppm. Then δ ∗ = (ξp0 − ξp )/σ = (ln(50) − ln(20))/ ln(2.015) = 1.308. Since we are computing t ...
... with probability (power) .90, when the true 95th percentile is 20ppm. On the basis of past data or based on data from a similar workplace, suppose the value of the geometric SD exp(σ) is guessed to be 2.015ppm. Then δ ∗ = (ξp0 − ξp )/σ = (ln(50) − ln(20))/ ln(2.015) = 1.308. Since we are computing t ...
Notes2
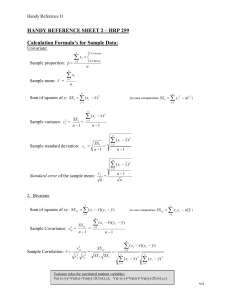
... Confidence Interval for 1 - 2; 21 22 and Unknown. Ifx1 and s21, andx2 and s22, are the means and variances of small independent samples of size n1 and n2, respectively, from approximate normal distributions with unknown and unequal variances, an approximate (1 - )100% confidence interval f ...
... Confidence Interval for 1 - 2; 21 22 and Unknown. Ifx1 and s21, andx2 and s22, are the means and variances of small independent samples of size n1 and n2, respectively, from approximate normal distributions with unknown and unequal variances, an approximate (1 - )100% confidence interval f ...
252oneal
... A Confidence Interval for a Median. In a situation where the population distribution is not normal, it is often more appropriate to find the median than the mean. The process of finding a confidence interval for a median is based on one simple fact: the probability that a single number picked at ran ...
... A Confidence Interval for a Median. In a situation where the population distribution is not normal, it is often more appropriate to find the median than the mean. The process of finding a confidence interval for a median is based on one simple fact: the probability that a single number picked at ran ...
Lecture 3 - Bauer College of Business
... A customer who bought within the last 11 days is treated exactly similar to a customer who bought within the last 11 months. ...
... A customer who bought within the last 11 days is treated exactly similar to a customer who bought within the last 11 months. ...