Slides - Georgia Tech ISyE
... -‐ test for mean with known variance (z-‐test) -‐ test for mean with unknown variance (t-‐test) -‐ test for sample proporTon parameter 6. Use ...
... -‐ test for mean with known variance (z-‐test) -‐ test for mean with unknown variance (t-‐test) -‐ test for sample proporTon parameter 6. Use ...
Unit 1 - Extra Practice MC
... Generally, bars should be square so that both the height and width equal the class count The scale of the vertical axis should be that of the variable whose distribution you are displaying ...
... Generally, bars should be square so that both the height and width equal the class count The scale of the vertical axis should be that of the variable whose distribution you are displaying ...
Chapter 8 Review with answers
... problem stated it was a random sample so we will assume this is sufficient. Since the sample size is slightly under 30, we will still check for the data being roughly normal. Either a boxplot or normal probability plot would suffice. In both cases there is no reason to doubt the sample data are roug ...
... problem stated it was a random sample so we will assume this is sufficient. Since the sample size is slightly under 30, we will still check for the data being roughly normal. Either a boxplot or normal probability plot would suffice. In both cases there is no reason to doubt the sample data are roug ...
Probability Distributions
... In both cases we have the event rate is not constant (in the first it decreases with time, in the second with distance) and therefore the Poisson distribution cannot be applied. The Poisson p.d.f. requires that the events be independent. Consider the case of a counter with a dead time of 1 µsec. Thi ...
... In both cases we have the event rate is not constant (in the first it decreases with time, in the second with distance) and therefore the Poisson distribution cannot be applied. The Poisson p.d.f. requires that the events be independent. Consider the case of a counter with a dead time of 1 µsec. Thi ...
Document
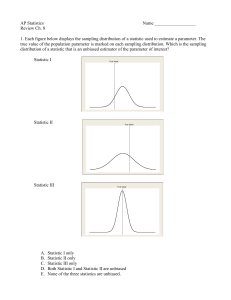
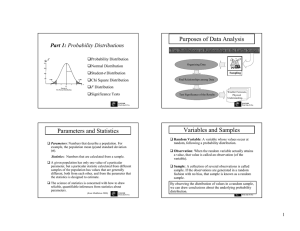
... parameter is called the sampling error. Sampling error is the result of using a subset of the population (the sample), and not the entire population to develop estimates. The sampling errors are: | x | for sample mean |s - | for sample standard deviation | p p | for sample proportion ...
... parameter is called the sampling error. Sampling error is the result of using a subset of the population (the sample), and not the entire population to develop estimates. The sampling errors are: | x | for sample mean |s - | for sample standard deviation | p p | for sample proportion ...
here
... An analysis of a sample is less cumbersome and more practical than an analysis of the entire population. ...
... An analysis of a sample is less cumbersome and more practical than an analysis of the entire population. ...