Marx`s anti-quantity theory of money: A critical evaluation Pichit
... bills are created and circulated only to facilitate capitalist transactions (Marx, 1894: 540). Thus, the quantity of paper money and bills of exchange required in circulation depends on the price-sum of commodities and the velocity. All these independent factors are summed up in the terms “the needs ...
... bills are created and circulated only to facilitate capitalist transactions (Marx, 1894: 540). Thus, the quantity of paper money and bills of exchange required in circulation depends on the price-sum of commodities and the velocity. All these independent factors are summed up in the terms “the needs ...
For a Critique of the Political Economy of the Sign
... community of peers and an aristocratic measure of value. Let us not be mistaken: it is this, and not the satisfaction of needs, that occasionally turns consumption into a passion, a fascinating game, something other than functional economic behavior: it becomes the competitive field of the destructi ...
... community of peers and an aristocratic measure of value. Let us not be mistaken: it is this, and not the satisfaction of needs, that occasionally turns consumption into a passion, a fascinating game, something other than functional economic behavior: it becomes the competitive field of the destructi ...
The Beneficiation Strategy for the Minerals Industry of South Africa
... “Mining and minerals products contribute three-quarters of our exports and the industry employs three-quarters of a million workers, but this could be much higher if our raw materials were processed into intermediate and finished products before export. Our RDP must attempt to increase the level of ...
... “Mining and minerals products contribute three-quarters of our exports and the industry employs three-quarters of a million workers, but this could be much higher if our raw materials were processed into intermediate and finished products before export. Our RDP must attempt to increase the level of ...
Long roots of the crisis - Michael Roberts Blog
... profit for now. Further destruction of capital will be necessary through another significant slump in global capitalism to raise profitability. 14 There is still a long way down to go for US and global capitalism before it reaches the bottom of the current down phase. Section 2. The Keynesian diagno ...
... profit for now. Further destruction of capital will be necessary through another significant slump in global capitalism to raise profitability. 14 There is still a long way down to go for US and global capitalism before it reaches the bottom of the current down phase. Section 2. The Keynesian diagno ...
The Case of Greece (1960-1989), by E. Ioakimoglou and
... accumulation. Without such an approximation to the development of the (Greek) capitalist economy, any general statement about "structural problems of capitalism" becomes meaningless. We believe that the Marxian concept of over-accumulation of capital, developed mainly in Volume 3 of Capital, enlight ...
... accumulation. Without such an approximation to the development of the (Greek) capitalist economy, any general statement about "structural problems of capitalism" becomes meaningless. We believe that the Marxian concept of over-accumulation of capital, developed mainly in Volume 3 of Capital, enlight ...
marx`s economic theory and contemporary capitalism
... thereby increases surplus labor; i.e. increases the profit produced per worker. This positive effect of technological change and higher productivity on the profit produced per worker is also reinforced by other ways to increase the profit per worker, such as wages cuts and increases in the intensity ...
... thereby increases surplus labor; i.e. increases the profit produced per worker. This positive effect of technological change and higher productivity on the profit produced per worker is also reinforced by other ways to increase the profit per worker, such as wages cuts and increases in the intensity ...
12. Nudge Nudge, Wink Wink, Say No More
... There are two aspects to the ‘of greater value’ proposition in the above. The first is the physical surplus: a growing market economy produces more than is needed to keep its inhabitants alive and replace depreciated physical capital. The second is that this physical surplus has to be converted into ...
... There are two aspects to the ‘of greater value’ proposition in the above. The first is the physical surplus: a growing market economy produces more than is needed to keep its inhabitants alive and replace depreciated physical capital. The second is that this physical surplus has to be converted into ...
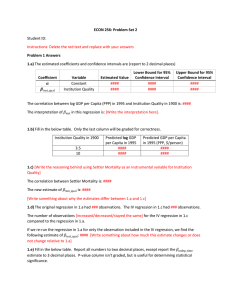
Tabular Approach
... Tabular Approach – Provides scope for good international comparability – But care still needed in interpretation – e.g. since 2006 self employed are included in the BR, prior to that they were in an AR and so N5. – And so focus of comparability should not be on total N1 to N7. – N1+N6 not really af ...
... Tabular Approach – Provides scope for good international comparability – But care still needed in interpretation – e.g. since 2006 self employed are included in the BR, prior to that they were in an AR and so N5. – And so focus of comparability should not be on total N1 to N7. – N1+N6 not really af ...
The profit cycle and economic recession
... employed in production. His famous formula followed: P = s/c+v, where P is the rate of profit; s is surplus value; c is constant capital (means of production) and v is the cost of the labour power. Marx is clear that the ROP applies to the whole economy. It is a general rate of profit derived fr ...
... employed in production. His famous formula followed: P = s/c+v, where P is the rate of profit; s is surplus value; c is constant capital (means of production) and v is the cost of the labour power. Marx is clear that the ROP applies to the whole economy. It is a general rate of profit derived fr ...
Capitalism and Post-Keynesian Economics: Some Critical
... system can get out of it. Like strategists we could map out all sorts of scenarios and to do that we would need concrete knowledge about politics, classes and history, something which to day is alien to economists of virtually all persuasions but we cannot claim to have a reliable theory of long ter ...
... system can get out of it. Like strategists we could map out all sorts of scenarios and to do that we would need concrete knowledge about politics, classes and history, something which to day is alien to economists of virtually all persuasions but we cannot claim to have a reliable theory of long ter ...
David Ricardo
... capital is simply equal to the amount of labor that was used to produce that capital good. For example, if a machine has 10 hours of labor imbedded in it, and if it has a useful life of 5 years, then each year 2 units of labor will be expended as machine is used up. Therefore, capital is simply conv ...
... capital is simply equal to the amount of labor that was used to produce that capital good. For example, if a machine has 10 hours of labor imbedded in it, and if it has a useful life of 5 years, then each year 2 units of labor will be expended as machine is used up. Therefore, capital is simply conv ...
Crisis and `law of motion` in economics: a critique of positivist Marxism
... argue, to mainstream political economy and also to Marxism, which is, with great irony, cast as the originator of the opposed notion of mechanical or fatalistic determination. This is the result of two substitutions for Marx’s own ideas. As TSSI scholars (Freeman 2010, Kliman 2007) have establish ...
... argue, to mainstream political economy and also to Marxism, which is, with great irony, cast as the originator of the opposed notion of mechanical or fatalistic determination. This is the result of two substitutions for Marx’s own ideas. As TSSI scholars (Freeman 2010, Kliman 2007) have establish ...
P 1
... Land is divided into “Farms” of different soil qualities, ranging from “Best Farm” to “Worst Farm” Farms produce corn which is used to pay the next season’s workers (the “wages fund”) or to provide seed for planting (“circulating capital”) or to keep as rent Corn can be sold at national price (farms ...
... Land is divided into “Farms” of different soil qualities, ranging from “Best Farm” to “Worst Farm” Farms produce corn which is used to pay the next season’s workers (the “wages fund”) or to provide seed for planting (“circulating capital”) or to keep as rent Corn can be sold at national price (farms ...
Document
... • The firm’s demand for capital services is its marginal value product of capital curve. • In the short run, the supply of capital services is fixed. In the long run, it can be adjusted by producing new capital goods or allowing the existing capital stock to depreciate. • The required rental is the ...
... • The firm’s demand for capital services is its marginal value product of capital curve. • In the short run, the supply of capital services is fixed. In the long run, it can be adjusted by producing new capital goods or allowing the existing capital stock to depreciate. • The required rental is the ...
Capital as a Social Relation - Social Movements and Political Power
... The fourth point follows directly from the third. As noted above, under capitalist relations of production individual labour processes are undertaken in the hope of private gain, with no prior consideration of a social division of labour. But any ensemble of such labours can survive only if they hap ...
... The fourth point follows directly from the third. As noted above, under capitalist relations of production individual labour processes are undertaken in the hope of private gain, with no prior consideration of a social division of labour. But any ensemble of such labours can survive only if they hap ...
Marxism, Crisis Theory and the Crisis of the Early 21st Century
... a crisis, using "cause" here to mean trigger, since it is the deeper structure of capitalist contradiction which is the ultimate cause. In 1850 he and Engels write in the Neue Reinische Zeitungabout the importance of the discovery of gold in California as "a fact of even more importance than the Feb ...
... a crisis, using "cause" here to mean trigger, since it is the deeper structure of capitalist contradiction which is the ultimate cause. In 1850 he and Engels write in the Neue Reinische Zeitungabout the importance of the discovery of gold in California as "a fact of even more importance than the Feb ...
quaderni del dipartimento di economia politica e statistica
... Indeed, the necessities must also cover the expenses to raise the next generation of workers (to complete the assimilation of workers to machinery, necessities must perhaps also include the costs of scrapping older workers, that is pensions). Whenever a wage rise is persistent, consumption of new an ...
... Indeed, the necessities must also cover the expenses to raise the next generation of workers (to complete the assimilation of workers to machinery, necessities must perhaps also include the costs of scrapping older workers, that is pensions). Whenever a wage rise is persistent, consumption of new an ...
Capital Accumulation, Technological Change, and the Distribution of
... • Lewis proposed a two sector model—many problems. – Zero marginal product of labour in agriculture? – Agriculture was only 35% of British economy in 1800. – I retain the assumption that savings come out of profits. ...
... • Lewis proposed a two sector model—many problems. – Zero marginal product of labour in agriculture? – Agriculture was only 35% of British economy in 1800. – I retain the assumption that savings come out of profits. ...
Understanding Value Networks By Verna Allee
... The goal of a value network is to generate economic success or other value (benefits) for its participants. People participate in a value network by converting their expertise and knowledge into tangible and intangible deliverables that have value for other members of the network. In a successful va ...
... The goal of a value network is to generate economic success or other value (benefits) for its participants. People participate in a value network by converting their expertise and knowledge into tangible and intangible deliverables that have value for other members of the network. In a successful va ...
Some forerunners
... debt or taxes, the effect on total level of demand in an economy being the same. Extra government spending through deficits will suggest to taxpayers higher taxes in the future and they would put aside savings accordingly. The effect on aggregate demand would be the same as if the government had cho ...
... debt or taxes, the effect on total level of demand in an economy being the same. Extra government spending through deficits will suggest to taxpayers higher taxes in the future and they would put aside savings accordingly. The effect on aggregate demand would be the same as if the government had cho ...
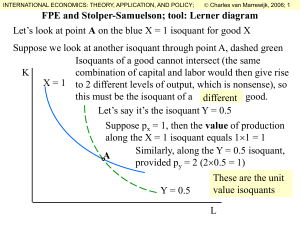
Factor Price Equalization and Stolper
... FPE and Stolper-Samuelson; tool: Lerner diagram Let’s look at point A on the blue X = 1 isoquant for good X Suppose we look at another isoquant through point A, dashed green Isoquants of a good cannot intersect (the same combination of capital and labor would then give rise K X = 1 to 2 different le ...
... FPE and Stolper-Samuelson; tool: Lerner diagram Let’s look at point A on the blue X = 1 isoquant for good X Suppose we look at another isoquant through point A, dashed green Isoquants of a good cannot intersect (the same combination of capital and labor would then give rise K X = 1 to 2 different le ...
Marxian Political Economy: Legacy and Renewal
... 2) A petty bourgeoisie. A more sophisticated option is to seek an overall coherence within the various components (value, surplus-value, and so on) of Marx’s analytical framework in Capital. Marx’s theory of productive and unproductive labor is crucial. On the one hand, the personnel under investiga ...
... 2) A petty bourgeoisie. A more sophisticated option is to seek an overall coherence within the various components (value, surplus-value, and so on) of Marx’s analytical framework in Capital. Marx’s theory of productive and unproductive labor is crucial. On the one hand, the personnel under investiga ...
Fall 2012
... chooses both employment (fraction of people who work), n , and hours worked per person, h . If 0 , it is costly to hire or fire workers. A. Write down the Bellman’s equation associated with this planner’s problem. B. Derive set of equations that characterize a sequence ct , ht , nt , kt ...
... chooses both employment (fraction of people who work), n , and hours worked per person, h . If 0 , it is costly to hire or fire workers. A. Write down the Bellman’s equation associated with this planner’s problem. B. Derive set of equations that characterize a sequence ct , ht , nt , kt ...
Lecture 8
... – They employ themselves and then hire extra labour / sell their extra labour if they want to – They own some capital K, and hire extra capital / lease extra capital if they want to – Initially assume that the supply of L and K is perfectly inelastic: all labour and machines are used all of the time ...
... – They employ themselves and then hire extra labour / sell their extra labour if they want to – They own some capital K, and hire extra capital / lease extra capital if they want to – Initially assume that the supply of L and K is perfectly inelastic: all labour and machines are used all of the time ...