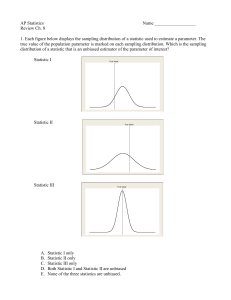
Chapter 8 Review with answers
... needs to be used. The justification is found in checking the conditions needed for a t-interval. The problem stated it was a random sample so we will assume this is sufficient. Since the sample size is slightly under 30, we will still check for the data being roughly normal. Either a boxplot or norm ...
... needs to be used. The justification is found in checking the conditions needed for a t-interval. The problem stated it was a random sample so we will assume this is sufficient. Since the sample size is slightly under 30, we will still check for the data being roughly normal. Either a boxplot or norm ...
Sampling Distribution Models
... A sampling distribution model for how a sample proportion varies from sample to sample allows us to quantify that variation and how likely it is that we’d observe a sample proportion in any particular interval. ...
... A sampling distribution model for how a sample proportion varies from sample to sample allows us to quantify that variation and how likely it is that we’d observe a sample proportion in any particular interval. ...
A Wall Street Journal/NBC News poll asked 2013 adults
... 4-12: [No. diff from 4ed] The Powerball lottery is played twice each week in 28 states, the Virgin Islands, and the District of Colombia. To play Powerball a participant must purchase a ticket and then select five numbers from the digits 1 through 55 and a Powerball number from the digits 1 through ...
... 4-12: [No. diff from 4ed] The Powerball lottery is played twice each week in 28 states, the Virgin Islands, and the District of Colombia. To play Powerball a participant must purchase a ticket and then select five numbers from the digits 1 through 55 and a Powerball number from the digits 1 through ...
Statistics AP Chapter 10 Review: confidence interval
... 13. Find the standard error AND margin of error for the given situations: a) Mrs. Skaff conducts a survey and finds that 82 out of 160 students know where the “F” building is on NPHS campus. She wants to find a 95% confidence interval to predict the true proportion of students who know this informa ...
... 13. Find the standard error AND margin of error for the given situations: a) Mrs. Skaff conducts a survey and finds that 82 out of 160 students know where the “F” building is on NPHS campus. She wants to find a 95% confidence interval to predict the true proportion of students who know this informa ...
Sampling and Descriptive Statistics
... • Two different samples from the same population will vary from each other as well • This phenomenon is known as sampling variation ...
... • Two different samples from the same population will vary from each other as well • This phenomenon is known as sampling variation ...
8.7 Estimation and Sample Size Determination for Finite Populations
... To illustrate the use of the finite population correction factor when developing a confidence interval estimate of the population proportion, consider again the estimate developed for Saxon Home Improvement Company in Section 8.3. For these data, N = 5,000, n = 100, p = 10>100 = 0.10, and, with 95% ...
... To illustrate the use of the finite population correction factor when developing a confidence interval estimate of the population proportion, consider again the estimate developed for Saxon Home Improvement Company in Section 8.3. For these data, N = 5,000, n = 100, p = 10>100 = 0.10, and, with 95% ...
practice homework problems
... 2. 12 choose 5 is 12!/(5!7!)=792. Keep in mind that 5!=5*4*3*2*1. 3. 1+2+5+9+10+20+21=68. Then we take the sum and divide by ”n” which is 7, 69/7=9.714 rounding to the third decimal place. 4. The median leaves at least half of the observations at or below and at least half at or above. With 7 observ ...
... 2. 12 choose 5 is 12!/(5!7!)=792. Keep in mind that 5!=5*4*3*2*1. 3. 1+2+5+9+10+20+21=68. Then we take the sum and divide by ”n” which is 7, 69/7=9.714 rounding to the third decimal place. 4. The median leaves at least half of the observations at or below and at least half at or above. With 7 observ ...