Variance and Standard Deviation
... – Sample variance is found by dividing by (n – 1) to keep it an unbiased (since we estimate the population mean, μ, by using the sample mean, x‾) estimator of population variance – The larger the standard deviation, the more dispersion the distribution has – Boxplots can be used to check outliers an ...
... – Sample variance is found by dividing by (n – 1) to keep it an unbiased (since we estimate the population mean, μ, by using the sample mean, x‾) estimator of population variance – The larger the standard deviation, the more dispersion the distribution has – Boxplots can be used to check outliers an ...
STA 291 Summer 2010
... If the data is approximately symmetric and bell-shaped then ◦ About 68% of the observations are within one standard deviation from the mean ◦ About 95% of the observations are within two standard deviations from the mean ◦ About 99.7% of the observations are within three standard deviations from the ...
... If the data is approximately symmetric and bell-shaped then ◦ About 68% of the observations are within one standard deviation from the mean ◦ About 95% of the observations are within two standard deviations from the mean ◦ About 99.7% of the observations are within three standard deviations from the ...
normal probability
... The mean of sleep time for 50 IPTS students are 7 hours with standard deviation of 1 hour. The mean of sleep time for 60 IPTA students is 6 hours with standard deviation of 0.7 hour. Find the 99% confidence interval for the difference mean of sleep time between the IPTS and IPTA students. a. Assume ...
... The mean of sleep time for 50 IPTS students are 7 hours with standard deviation of 1 hour. The mean of sleep time for 60 IPTA students is 6 hours with standard deviation of 0.7 hour. Find the 99% confidence interval for the difference mean of sleep time between the IPTS and IPTA students. a. Assume ...
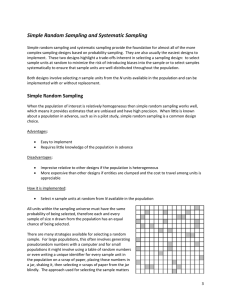
Simple Random Sampling and Systematic Sampling
... Occasionally, selecting sample units at random can introduce logistical challenges that preclude collecting data efficiently. If the chance of introducing a bias is low or if ideal dispersion of sample units in the population is a higher priority that a strictly random sample, then it might be ap ...
... Occasionally, selecting sample units at random can introduce logistical challenges that preclude collecting data efficiently. If the chance of introducing a bias is low or if ideal dispersion of sample units in the population is a higher priority that a strictly random sample, then it might be ap ...
Chapter 5-13. Monte Carlo Simulation andBootstrapping
... example) from the population, compute the mean from each of these samples, and then display these means in a histogram. This histogram represents the “sampling distribution of the mean”. In bootstrapping, we do something very similar. We begin with our sample (of size n=50, for example). Then we tak ...
... example) from the population, compute the mean from each of these samples, and then display these means in a histogram. This histogram represents the “sampling distribution of the mean”. In bootstrapping, we do something very similar. We begin with our sample (of size n=50, for example). Then we tak ...