
test 2 review sheet
... c) E ( x) 3.2 , Var ( x) 3.2 , 1.79 3. a) 0.0668 b) 0.1587 c) 0.7745 ...
... c) E ( x) 3.2 , Var ( x) 3.2 , 1.79 3. a) 0.0668 b) 0.1587 c) 0.7745 ...
Ch9 - OCCC.edu
... 3.745. If you then go up the column you see that this corresponds to a confidence level of 99.9%. So we are at least 0.001 sure that we should NOT find a test stat of 12.5 Since 0.001 < 0.05 ( we are simply comparing our p-value to α ) then we reject Ho and conclude there is enough evidence to sugge ...
... 3.745. If you then go up the column you see that this corresponds to a confidence level of 99.9%. So we are at least 0.001 sure that we should NOT find a test stat of 12.5 Since 0.001 < 0.05 ( we are simply comparing our p-value to α ) then we reject Ho and conclude there is enough evidence to sugge ...
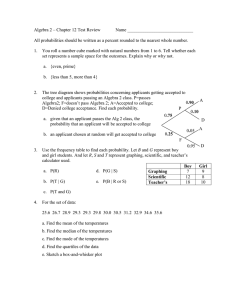
Algebra 2 – Chapter 12 Test Review Name _____________________________
... of 7 ounces and a standard deviation of 0.02 oz. Find the number of candies in a bag of 300 that weigh less than 6.96 ounces. 12. A set of data has a normal distribution with a mean of 6.7 and a standard deviation of 1.1. What percent of the data is between 5.6 and 7.8? What percent is greater than ...
... of 7 ounces and a standard deviation of 0.02 oz. Find the number of candies in a bag of 300 that weigh less than 6.96 ounces. 12. A set of data has a normal distribution with a mean of 6.7 and a standard deviation of 1.1. What percent of the data is between 5.6 and 7.8? What percent is greater than ...
[MSM04]
... • In ANOVA, an estimate of variability between groups is compared with variability within groups. – Between-group variation is the variation among the means of the different treatment conditions due to chance (random sampling error) and treatment effects, if any exist. – Within-group variation is th ...
... • In ANOVA, an estimate of variability between groups is compared with variability within groups. – Between-group variation is the variation among the means of the different treatment conditions due to chance (random sampling error) and treatment effects, if any exist. – Within-group variation is th ...
Exam 1 PS 217, Spring 2006 standard error mean standard
... 0 (If you reject H0 you could be making a Type I error, but you can only make a Type II error when you retain H0.) 14. Under which circumstances would you be able to test a null hypothesis using a z-score? [1 pt] ...
... 0 (If you reject H0 you could be making a Type I error, but you can only make a Type II error when you retain H0.) 14. Under which circumstances would you be able to test a null hypothesis using a z-score? [1 pt] ...
Variability
... FACTORS THAT AFFECT VARIABILITY 1. Extreme Scores i.e. 1, 3, 8, 11, 1,000,000.00 . We can’t use the Range in this situation but we can use the other measures of variability. ...
... FACTORS THAT AFFECT VARIABILITY 1. Extreme Scores i.e. 1, 3, 8, 11, 1,000,000.00 . We can’t use the Range in this situation but we can use the other measures of variability. ...
AP Statistics Chapter 11 - William H. Peacock, LCDR USN
... elementary school. Though there is a 25 MPH SCHOOL ZONE sign nearby, most drivers seem to go much faster than that, even when the warning sign flashes. The students randomly selected 20 flashing zone times during the school year, noted the speeds of the cars passing the school during the flashing zo ...
... elementary school. Though there is a 25 MPH SCHOOL ZONE sign nearby, most drivers seem to go much faster than that, even when the warning sign flashes. The students randomly selected 20 flashing zone times during the school year, noted the speeds of the cars passing the school during the flashing zo ...
Class2
... General process of making inference about a statistic (1) Establish the sampling distribution of the statistic to assess the variability of the statistic. For example, if we are interested in the mean reading score of students in Taipei, we take a sample and compute the sample mean. Because this sa ...
... General process of making inference about a statistic (1) Establish the sampling distribution of the statistic to assess the variability of the statistic. For example, if we are interested in the mean reading score of students in Taipei, we take a sample and compute the sample mean. Because this sa ...







![[MSM04]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008529088_2-3ce1cce4ea32dddeeb96e74b738216a4-300x300.png)














