Independent T
... What is the likelihood that two samples we have collected were drawn from populations with the same value for ? ...
... What is the likelihood that two samples we have collected were drawn from populations with the same value for ? ...
SAWE Presentation - International
... – a mathematical method that employs probability theory for inferring the properties of a population from the analysis of a sample taken from that population ...
... – a mathematical method that employs probability theory for inferring the properties of a population from the analysis of a sample taken from that population ...
10.2 review answers
... withdrawal. After a 24-hr smoking abstinence, 20 smokers were asked to estimate how much time had passed during a 45-sec period. These smokers were not a random sample but were considered a representative sample. The mean perceived elapsed time was 59.30 seconds with a standard deviation of 9.84 sec ...
... withdrawal. After a 24-hr smoking abstinence, 20 smokers were asked to estimate how much time had passed during a 45-sec period. These smokers were not a random sample but were considered a representative sample. The mean perceived elapsed time was 59.30 seconds with a standard deviation of 9.84 sec ...
Exam III 2008 solutions
... (iii) At the U.S. pharmacy, what percent of drugs cost more than $200 per 100 pills? Solution: This requires a confidence interval: 1) proportions, 2) one sample, and 3) z-interval. (iv) Is the percent of drugs that cost more than $200 per 100 pills the same at the two pharmacies? Solution: This req ...
... (iii) At the U.S. pharmacy, what percent of drugs cost more than $200 per 100 pills? Solution: This requires a confidence interval: 1) proportions, 2) one sample, and 3) z-interval. (iv) Is the percent of drugs that cost more than $200 per 100 pills the same at the two pharmacies? Solution: This req ...
chp12_section1_seta_answers
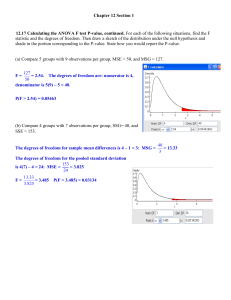
... As the means change in difference then the F –value starts to increase, which means that we are increasing the amount of evidence to support the alternative hypothesis that at least one of the means is different. We are trying to find if there is a difference in the means. If we continue to change t ...
... As the means change in difference then the F –value starts to increase, which means that we are increasing the amount of evidence to support the alternative hypothesis that at least one of the means is different. We are trying to find if there is a difference in the means. If we continue to change t ...
c5_hypo1
... laminated materials. Twelve pieces of material 1 were tested, by exposing each piece to a machine measuring wear. Ten pieces of material 2 were similarly tested. In each case, the depth of wear was observed. The samples of material 1 gave an average (coded) wear of 85 units with a standard deviation ...
... laminated materials. Twelve pieces of material 1 were tested, by exposing each piece to a machine measuring wear. Ten pieces of material 2 were similarly tested. In each case, the depth of wear was observed. The samples of material 1 gave an average (coded) wear of 85 units with a standard deviation ...