Toxic Food Preservatives : Sulfur Dioxide and Sulfites
... Effects of sulfur dioxide consumption to human health Whilst harmless to healthy persons when used in recommended concentrations, it can induce asthma when inhaled or ingested. According to (World Health Organization, 1999), sulfur dioxide when introduced, it inhibits specific nerve signals, restri ...
... Effects of sulfur dioxide consumption to human health Whilst harmless to healthy persons when used in recommended concentrations, it can induce asthma when inhaled or ingested. According to (World Health Organization, 1999), sulfur dioxide when introduced, it inhibits specific nerve signals, restri ...
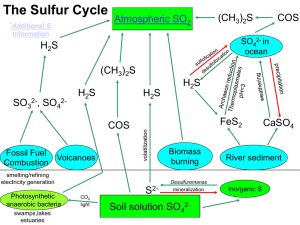
Carbon Cycle
... help return the Sulfur for the next generation of phosphorus in the soil. 4. Some of the phosphorus in soils can be washed away into water ___________. 5. Another source of phosphorus in water comes from man-made _____________. 6. Too much phosphorus in water leads to plant ________________, strangl ...
... help return the Sulfur for the next generation of phosphorus in the soil. 4. Some of the phosphorus in soils can be washed away into water ___________. 5. Another source of phosphorus in water comes from man-made _____________. 6. Too much phosphorus in water leads to plant ________________, strangl ...
The Spark of Life: Sulfur
... Why does the body need sulfur? Sulfur is required for production of DNA, insulin, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, neurotransmitters, amino acids (building blocks of proteins), collagen, connective tissues, and much more. It is also essential for the production of detoxifying compounds and antioxidant ...
... Why does the body need sulfur? Sulfur is required for production of DNA, insulin, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, neurotransmitters, amino acids (building blocks of proteins), collagen, connective tissues, and much more. It is also essential for the production of detoxifying compounds and antioxidant ...
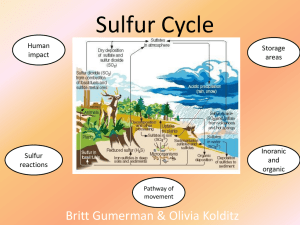
Sulfur - SOIL 5813
... • Sulfur is a pale yellow, non-metallic solid. • Name was derived from the Latin word for brimstone (“burning stone”), since it burns readily in air. • Elemental sulfur has been used since ancient times in religious ceremonies, to fumigate buildings, and for bleaching cloth. Also used agriculturally ...
... • Sulfur is a pale yellow, non-metallic solid. • Name was derived from the Latin word for brimstone (“burning stone”), since it burns readily in air. • Elemental sulfur has been used since ancient times in religious ceremonies, to fumigate buildings, and for bleaching cloth. Also used agriculturally ...
Quiz 2
... 1. The EPA limit for CO is 9 ppm. Express this number as a percentage. A. 90% B. 9% C. 0.09% D. 0.0009% Percent is parts per hundred. One hundred is 10,000 times less than one million. 2. The burning of coal produces sulfur dioxide, SO2, a pollutant that slowly reacts in air to form SO3. Sulfur trio ...
... 1. The EPA limit for CO is 9 ppm. Express this number as a percentage. A. 90% B. 9% C. 0.09% D. 0.0009% Percent is parts per hundred. One hundred is 10,000 times less than one million. 2. The burning of coal produces sulfur dioxide, SO2, a pollutant that slowly reacts in air to form SO3. Sulfur trio ...
Chemistry Review - Woodlawn School Wiki
... 2) A 1.42-g sample of a pure compound, with formula M2SO4 , was dissolved in a water and treated with an excess of aqueous barium chloride, resulting in the precipitation of all the sulfate ions as barium sulfate. The precipitate was collected, dried, and found to weigh 2.33 g. Determine the atomic ...
... 2) A 1.42-g sample of a pure compound, with formula M2SO4 , was dissolved in a water and treated with an excess of aqueous barium chloride, resulting in the precipitation of all the sulfate ions as barium sulfate. The precipitate was collected, dried, and found to weigh 2.33 g. Determine the atomic ...
Sulfur

Sulfur or sulphur (see spelling differences) is a chemical element with symbol S and atomic number 16. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow crystalline solid when at room temperature. Chemically, sulfur can react as either an oxidant or a reducing agent. It oxidizes most metals and several nonmetals, including carbon, which leads to its negative charge in most organosulfur compounds, but it reduces several strong oxidants, such as oxygen and fluorine.Sulfur occurs naturally as the pure element (native sulfur) and as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Elemental sulfur crystals are commonly sought after by mineral collectors for their distinct, brightly colored polyhedron shapes. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China and Egypt. Fumes from burning sulfur were used as fumigants, and sulfur-containing medicinal mixtures were used as balms and antiparasitics. Sulfur is referred to in the Bible as brimstone (burn stone) in English, with this name still used in several nonscientific tomes. It was needed to make the best quality of black gunpowder. In 1777, Antoine Lavoisier helped convince the scientific community that sulfur was a basic element rather than a compound.Elemental sulfur was once extracted from salt domes where it sometimes occurs in nearly pure form, but this method has been obsolete since the late 20th century. Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum. The element's largest commercial use (after mostly being converted to sulfuric acid) is to produce sulfate and phosphate fertilizers, because of the relatively high requirement of plants for sulfur and phosphorus. Sulfuric acid is also a primary industrial chemical outside fertilizer manufacture. Other well-known uses for the element are in matches, insecticides and fungicides. Many sulfur compounds are odoriferous, and the smell of odorized natural gas, skunk scent, grapefruit, and garlic is due to sulfur compounds. Hydrogen sulfide produced by living organisms imparts the characteristic odor to rotting eggs and other biological processes.Sulfur is an essential element for all life, and is widely used in biochemical processes. In metabolic reactions, sulfur compounds serve as both fuels (electron donors) and respiratory (oxygen-alternative) materials (electron acceptors). Sulfur in organic form is present in the vitamins biotin and thiamine, the latter being named for the Greek word for sulfur. Sulfur is an important part of many enzymes and in antioxidant molecules like glutathione and thioredoxin. Organically bonded sulfur is a component of all proteins, as the amino acids cysteine and methionine. Disulfide bonds are largely responsible for the mechanical strength and insolubility of the protein keratin, found in outer skin, hair, and feathers, and the element contributes to their pungent odor when burned.