Review 6 with Answers
... means that the data set is spread out. C) As the amount of data increases, the standard deviation usually increases. D) A data set with many outliers will have a high standard deviation. ...
... means that the data set is spread out. C) As the amount of data increases, the standard deviation usually increases. D) A data set with many outliers will have a high standard deviation. ...
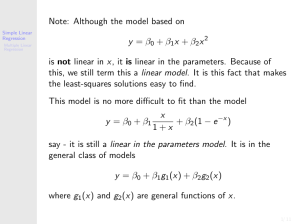
Note: Although the model based on y = β0 + β1x + β2x2 is not linear
... is not linear in x, it is linear in the parameters. Because of this, we still term this a linear model. It is this fact that makes the least-squares solutions easy to find. This model is no more difficult to fit than the model y = β0 + β1 ...
... is not linear in x, it is linear in the parameters. Because of this, we still term this a linear model. It is this fact that makes the least-squares solutions easy to find. This model is no more difficult to fit than the model y = β0 + β1 ...
Module 4: Introduction to the Normal Gamma Model
... Do a teacher’s expectations influence student achievement? Do a teacher’s expectations influence student achievement? In a famous study, Rosenthal and Jacobson (1968) performed an experiment in a California elementary school to try to answer this question. At the beginning of the year, all students ...
... Do a teacher’s expectations influence student achievement? Do a teacher’s expectations influence student achievement? In a famous study, Rosenthal and Jacobson (1968) performed an experiment in a California elementary school to try to answer this question. At the beginning of the year, all students ...
Educational Research - Pearson Higher Education
... that fall at or above a given score Standard scores – a derived score based on how far a raw score is from a reference point in terms of standard deviation units ...
... that fall at or above a given score Standard scores – a derived score based on how far a raw score is from a reference point in terms of standard deviation units ...