Electronic Circuits and Devices: ELEE 3455
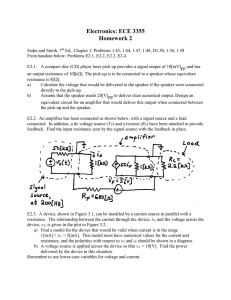
... Assume that the speaker needs 20[V]pp to deliver clear acoustical output. Design an equivalent circuit for an amplifier that would deliver this output when connected between the pick-up and the speaker. E2.2. An amplifier has been connected as shown below, with a signal source and a load connected. ...
... Assume that the speaker needs 20[V]pp to deliver clear acoustical output. Design an equivalent circuit for an amplifier that would deliver this output when connected between the pick-up and the speaker. E2.2. An amplifier has been connected as shown below, with a signal source and a load connected. ...
experiment 2 ohm`s law
... across any two points by touching the points with the two leads of the voltmeter. 2. Manual experiment: Measure the current for 10 different voltages, with the increment of 1V. Record the current and voltage in your data table. Record the instrumental error in your measurements. The instrumental err ...
... across any two points by touching the points with the two leads of the voltmeter. 2. Manual experiment: Measure the current for 10 different voltages, with the increment of 1V. Record the current and voltage in your data table. Record the instrumental error in your measurements. The instrumental err ...
Experiment 1-6
... In many experiments, one needs to either monitor a signal over a long period of time or measure a quantity, such as voltage and current, which may vary with time very fast. In these cases, one may use a computer to control the experiment and take data. Many experimental instruments are now equipped ...
... In many experiments, one needs to either monitor a signal over a long period of time or measure a quantity, such as voltage and current, which may vary with time very fast. In these cases, one may use a computer to control the experiment and take data. Many experimental instruments are now equipped ...
DCAC_Circuits-Voltmeter_Design_Testing-Student_Guide
... The spiral spring holds the coil and the pointer attached to it against a stop on the left when the movement is not in use. The armature around which the coil is wound is made of a magnetic material of very low retentivity so that when there is no current in the coil there is no magnetic field from ...
... The spiral spring holds the coil and the pointer attached to it against a stop on the left when the movement is not in use. The armature around which the coil is wound is made of a magnetic material of very low retentivity so that when there is no current in the coil there is no magnetic field from ...
Purpose:
... The goals of this laboratory exercise are to learn how to: A. use some basic pieces of laboratory equipment, including 1. a circuit breadboard, 2. a dc power supply, and 3. a digital multimeter; (DMM) B. use a breadboard to construct circuits from a circuit schematic and measure electrical quantitie ...
... The goals of this laboratory exercise are to learn how to: A. use some basic pieces of laboratory equipment, including 1. a circuit breadboard, 2. a dc power supply, and 3. a digital multimeter; (DMM) B. use a breadboard to construct circuits from a circuit schematic and measure electrical quantitie ...
The Greek word for “amber” is “elektron” Electricity is the movement
... current alternates direction. AC is better suited for transmission through long distance power lines. Household (wall plug) current in North America delivers 110-115 volts, alternating at 60 times a second (60 Hz). A wire carrying AC will induce a current in nearby wire. - “Wall current” (110-115 VA ...
... current alternates direction. AC is better suited for transmission through long distance power lines. Household (wall plug) current in North America delivers 110-115 volts, alternating at 60 times a second (60 Hz). A wire carrying AC will induce a current in nearby wire. - “Wall current” (110-115 VA ...
Bates
... Fig. 8-10: How meter movement M can be used as an ohmmeter with a 1.5-V battery. (a) Equivalent closed circuit with R1 and the battery when ohmmeter leads are short-circuited for zero ohms of external R. (b) Internal ohmmeter circuit with test leads open, ready to measure an external resistance. Cop ...
... Fig. 8-10: How meter movement M can be used as an ohmmeter with a 1.5-V battery. (a) Equivalent closed circuit with R1 and the battery when ohmmeter leads are short-circuited for zero ohms of external R. (b) Internal ohmmeter circuit with test leads open, ready to measure an external resistance. Cop ...
Lab #7 – Inductors/Capacitors
... • Activities #1 and #2 requires the use of the RLC meter, so the North half of the lab should start with activities #3 and #4 while the South half does Activities #1 and #2 • You will need to be creative and Google some information to find the width of a sheet of paper, its dielectric and other para ...
... • Activities #1 and #2 requires the use of the RLC meter, so the North half of the lab should start with activities #3 and #4 while the South half does Activities #1 and #2 • You will need to be creative and Google some information to find the width of a sheet of paper, its dielectric and other para ...
195 Series Models: 1952 1953 1954
... UL Recognized Interchangeable with other manufactures meters Surface or Window mount Wide selection of ranges Customized scales available Mirrored scales available Frequency models available ...
... UL Recognized Interchangeable with other manufactures meters Surface or Window mount Wide selection of ranges Customized scales available Mirrored scales available Frequency models available ...
Review Sheet Chemistry Electrons and Bonding “Tuiz”
... What is an electric current? (definition) What is a battery? (definition) What is an electric circuit? (definition) What is current measured in? ________ What is resistance measured in? ________ What is power measured in? __________ What is the potential difference measured in? ________ 5. What is a ...
... What is an electric current? (definition) What is a battery? (definition) What is an electric circuit? (definition) What is current measured in? ________ What is resistance measured in? ________ What is power measured in? __________ What is the potential difference measured in? ________ 5. What is a ...
Soln0548 051017
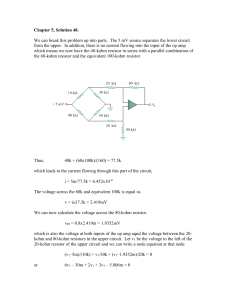
... Chapter 5, Solution 48. We can break this problem up into parts. The 5 mV source separates the lower circuit from the upper. In addition, there is no current flowing into the input of the op amp which means we now have the 40-kohm resistor in series with a parallel combination of the 60-kohm resisto ...
... Chapter 5, Solution 48. We can break this problem up into parts. The 5 mV source separates the lower circuit from the upper. In addition, there is no current flowing into the input of the op amp which means we now have the 40-kohm resistor in series with a parallel combination of the 60-kohm resisto ...
Systems Repair Worksheet
... 20. Circuits must have consumers or _________, power ____________, & ____________ providing paths along with controllers & protection devices properly located to perform desired operations. 21. In a ___________ circuit, the voltage __________ at each load, the __________ is the same throughout the c ...
... 20. Circuits must have consumers or _________, power ____________, & ____________ providing paths along with controllers & protection devices properly located to perform desired operations. 21. In a ___________ circuit, the voltage __________ at each load, the __________ is the same throughout the c ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.