The Field Effect Transistor
... This lab begins with some experiments on a junction field effect transistor (JFET), type 2N5458 and then continues with op amps using the TL082/084 dual/quad op amp chips. Details of these devices, including pin-out, can be found on the data sheets in the supplementary reading section on your web pa ...
... This lab begins with some experiments on a junction field effect transistor (JFET), type 2N5458 and then continues with op amps using the TL082/084 dual/quad op amp chips. Details of these devices, including pin-out, can be found on the data sheets in the supplementary reading section on your web pa ...
EXPERIMENT #2: DC Circuits and Tools
... Figure 2: Circuit symbols (a) and physical symbols (b) of the digital multimeter used in three modes: voltmeter, ammeter, ohmmeter, respectively. Measurement devices are not considered essential elements in most final circuit designs. Except in the academic setting, a circuit schematic rarely expres ...
... Figure 2: Circuit symbols (a) and physical symbols (b) of the digital multimeter used in three modes: voltmeter, ammeter, ohmmeter, respectively. Measurement devices are not considered essential elements in most final circuit designs. Except in the academic setting, a circuit schematic rarely expres ...
Current - 7th and 8th Grade Science
... 2. 4.0A of current flow through a circuit with 30.0 of resistance. What is the voltage of the power source? 3. A battery provides 1.5V of potential to a circuit with a motor. If the circuit draws 0.55A of current, what resistance does the motor provide? ...
... 2. 4.0A of current flow through a circuit with 30.0 of resistance. What is the voltage of the power source? 3. A battery provides 1.5V of potential to a circuit with a motor. If the circuit draws 0.55A of current, what resistance does the motor provide? ...
Fluxmeter Measuring Procedures
... then separated by this exact same radius, then the magnetic field inside the 2/3 of the coils radius there was a perfect homogeneous magnetic field. Now for measuring a magnet, we do the exact opposite. We place the magnet on a flat plane inside this homogeneous area, and then we remove the magnet a ...
... then separated by this exact same radius, then the magnetic field inside the 2/3 of the coils radius there was a perfect homogeneous magnetic field. Now for measuring a magnet, we do the exact opposite. We place the magnet on a flat plane inside this homogeneous area, and then we remove the magnet a ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to make it an open circuit here so the current is 0. To turn off the voltage source, we need to make it a short circuit. Look at the two 10 kΩ resistors. They are in parallel because they share the same pair of nodes. The two 10 ...
... To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to make it an open circuit here so the current is 0. To turn off the voltage source, we need to make it a short circuit. Look at the two 10 kΩ resistors. They are in parallel because they share the same pair of nodes. The two 10 ...
S1SD-1TI-1U Temperature Converter Connection
... devices: - resistance thermometers - thermocouples - PTC thermistors - potentiometers - voltage sources - field device with its own characteristic ...
... devices: - resistance thermometers - thermocouples - PTC thermistors - potentiometers - voltage sources - field device with its own characteristic ...
Chapter 36: Principles of Electrical Systems
... ► Semiconductor materials include silicon, germanium, gallium-arsenide, and silicon carbide. ► Electrical circuits contain a power supply, a current flow on/off switch, a functional component, a conductive pathway, and a protection device (e.g., a fuse). ► Voltage is the electrical pressure differen ...
... ► Semiconductor materials include silicon, germanium, gallium-arsenide, and silicon carbide. ► Electrical circuits contain a power supply, a current flow on/off switch, a functional component, a conductive pathway, and a protection device (e.g., a fuse). ► Voltage is the electrical pressure differen ...
Parallel and Series Circuits
... b. Are all the connections good or is one loose? c. Is the potentiometer turned all the way to one side or another (if connected)? If so this may be adding too much resistance to the circuit so try turning it the other way. d. Is there enough light? Solar panels are very picky about the amount of li ...
... b. Are all the connections good or is one loose? c. Is the potentiometer turned all the way to one side or another (if connected)? If so this may be adding too much resistance to the circuit so try turning it the other way. d. Is there enough light? Solar panels are very picky about the amount of li ...
INTERMEDIATE/SECONDARY ARTICLE: Measuring Electricity
... mysterious force to most of us. Understanding electricity and how it is measured is confusing because we cannot see it. We are familiar with terms such as watt, volt, and amp, but most of us do not have a clear understanding of these terms. We buy a 60-watt lightbulb, a tool that requires 120 volts, ...
... mysterious force to most of us. Understanding electricity and how it is measured is confusing because we cannot see it. We are familiar with terms such as watt, volt, and amp, but most of us do not have a clear understanding of these terms. We buy a 60-watt lightbulb, a tool that requires 120 volts, ...
Electical Safety Presentation
... Nominal: is the term used for the stated voltage for a given line. Example a 115 volt circuit may actually be 120 volts, but is called 115 volts nominal. ...
... Nominal: is the term used for the stated voltage for a given line. Example a 115 volt circuit may actually be 120 volts, but is called 115 volts nominal. ...
Grade 9 Academic Science – Electricity
... 5, we see that doubling of the total resistance while maintaining a constant voltage serves to halve the current in the circuit. Questions – CHOOSE THE MOST CORRECT ANSWER(S) and EXPLAIN YOUR CHOICE(S) 1. Which of the following will cause the current through an electrical circuit to decrease? Choose ...
... 5, we see that doubling of the total resistance while maintaining a constant voltage serves to halve the current in the circuit. Questions – CHOOSE THE MOST CORRECT ANSWER(S) and EXPLAIN YOUR CHOICE(S) 1. Which of the following will cause the current through an electrical circuit to decrease? Choose ...
Automatic Street Light
... L.D.R: (Light Depending Resistance) it is a special type of resistance whose value depends on the brightness of light which is falling on it. It has resistance of about 1mega ohm when in total darkness, but a resistance of only about 5k ohms when brightness illuminated. It responds to a large part o ...
... L.D.R: (Light Depending Resistance) it is a special type of resistance whose value depends on the brightness of light which is falling on it. It has resistance of about 1mega ohm when in total darkness, but a resistance of only about 5k ohms when brightness illuminated. It responds to a large part o ...
Transient currents and voltages
... Build a RC circuit according to Figure 1, using C = 1.0μF and the Rvar (Potentiometer 5‐25kΩ). Open the Desktop folder: 2nd Yr Lab Files and select Charge and Discharge of a Capacitor (Lab View Application). The Analog Output works as a function generator. Use the Square Wave form and vary the ...
... Build a RC circuit according to Figure 1, using C = 1.0μF and the Rvar (Potentiometer 5‐25kΩ). Open the Desktop folder: 2nd Yr Lab Files and select Charge and Discharge of a Capacitor (Lab View Application). The Analog Output works as a function generator. Use the Square Wave form and vary the ...
Ohm`s Law relates the voltage, current and resistance of a circuit. It
... When beginning to explore the world of electricity and electronics, it is vital to start by understanding the basics of voltage, current, and resistance. These are the three basic building blocks required to manipulate and utilize electricity. At first, these concepts can be difficult to understand ...
... When beginning to explore the world of electricity and electronics, it is vital to start by understanding the basics of voltage, current, and resistance. These are the three basic building blocks required to manipulate and utilize electricity. At first, these concepts can be difficult to understand ...
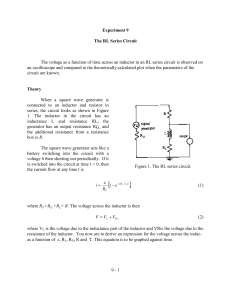
Theory
... 6) Now adjust the sweep speed on the oscilloscope (also the horizontal. magnification, if necessary) until only the first half of the trace shown in Figure 2 fills the screen. The horizontal adjustments, except for calibration, can be changed at will; however, do not change the vertical settings. 7 ...
... 6) Now adjust the sweep speed on the oscilloscope (also the horizontal. magnification, if necessary) until only the first half of the trace shown in Figure 2 fills the screen. The horizontal adjustments, except for calibration, can be changed at will; however, do not change the vertical settings. 7 ...
ECE320-HW4
... Figures (a) and (b) show two possible connections for a 20 kVA, 2300/230V transformer to be used as an autotransformer. With a source voltage of 2300 V, calculate the kVA rating and the power output at full load of unity power factor (p.f=1) of the autotransformer for both the connections. ...
... Figures (a) and (b) show two possible connections for a 20 kVA, 2300/230V transformer to be used as an autotransformer. With a source voltage of 2300 V, calculate the kVA rating and the power output at full load of unity power factor (p.f=1) of the autotransformer for both the connections. ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.