Metformin overdose in dogs and cats
... to treat the acidosis and reduce the toxic concentrations of metformin.12 Left untreated, lactic acidosis can result in confusion, hypotension, coma, collapse, and death.8 In a pediatric study, doses of up to 196 mg/kg of metformin produced no signs of lactic acidosis or hypoglycemia. Most of the ch ...
... to treat the acidosis and reduce the toxic concentrations of metformin.12 Left untreated, lactic acidosis can result in confusion, hypotension, coma, collapse, and death.8 In a pediatric study, doses of up to 196 mg/kg of metformin produced no signs of lactic acidosis or hypoglycemia. Most of the ch ...
Introduction to anesthesiology
... quickly i.e. if over dosage occurred, it cannot be reversed rapidly. ...
... quickly i.e. if over dosage occurred, it cannot be reversed rapidly. ...
data sheet
... ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS Lignocaine should be used with caution in patients receiving other local anaesthetics or agents structurally related to amide-type local anaesthetics, e.g. antiarrhythmic drugs such as mexiletine, since the toxic effects are additive. Specific interaction studies with lignocaine ...
... ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS Lignocaine should be used with caution in patients receiving other local anaesthetics or agents structurally related to amide-type local anaesthetics, e.g. antiarrhythmic drugs such as mexiletine, since the toxic effects are additive. Specific interaction studies with lignocaine ...
Xylocaine 2% Viscous
... Cimetidine or betablockers have been shown to cause potentially toxic plasma concentrations when lignocaine is given in repeated high doses over a long period of time. Therefore, caution should be taken if lignocaine was administered at higher than recommended doses over extended period of time. Phe ...
... Cimetidine or betablockers have been shown to cause potentially toxic plasma concentrations when lignocaine is given in repeated high doses over a long period of time. Therefore, caution should be taken if lignocaine was administered at higher than recommended doses over extended period of time. Phe ...
Sodium Bicarbonate - use in critical care
... Headache / nausea / vomiting Blindness (optic nerve damage) Drowsiness / coma Seizures Raised anion/osmolar gap acidosis ...
... Headache / nausea / vomiting Blindness (optic nerve damage) Drowsiness / coma Seizures Raised anion/osmolar gap acidosis ...
Carboxyhemoglobinemia in Acute Care
... may prove to be a valuable marker of disease severity. There are also reports of CO poisoning by the Monday Morning Phenomena where carboxyhemoglobinemia is induced within the closed circuit anesthesia system during surgery, inhaled nitric oxide therapy, and anti-hypertension treatment with sodium n ...
... may prove to be a valuable marker of disease severity. There are also reports of CO poisoning by the Monday Morning Phenomena where carboxyhemoglobinemia is induced within the closed circuit anesthesia system during surgery, inhaled nitric oxide therapy, and anti-hypertension treatment with sodium n ...
Treatment
... Though anxiety is often seen as a minor side-effect of MDMA use, there have been a number of reports of more severe reaction with an acute panic disorder. This has been reported in subjects without prior personal or family history of an anxiety disorder and where a modest dose of Ecstasy was taken ...
... Though anxiety is often seen as a minor side-effect of MDMA use, there have been a number of reports of more severe reaction with an acute panic disorder. This has been reported in subjects without prior personal or family history of an anxiety disorder and where a modest dose of Ecstasy was taken ...
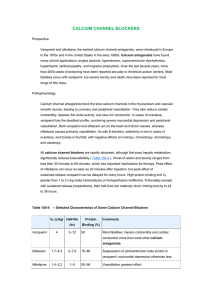
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
... nifedipine causes primarily vasodilation. As with β-blockers, selectivity is lost in cases of overdose, and toxicity is fourfold, with negative effects on inotropy, chronotropy, dromotropy, and vasotropy. All calcium channel blockers are rapidly absorbed, although first-pass hepatic metabolism signi ...
... nifedipine causes primarily vasodilation. As with β-blockers, selectivity is lost in cases of overdose, and toxicity is fourfold, with negative effects on inotropy, chronotropy, dromotropy, and vasotropy. All calcium channel blockers are rapidly absorbed, although first-pass hepatic metabolism signi ...
The effects of arsenic on the two major fibre types in the chelae of
... Arsenic is a proven carcinogen found in the soil in gold mining regions at concentrations that can be thousands of times greater than gold. During mining arsenic is released into the environment, easily entering surrounding water bodies. The main chemical forms of arsenic found in the environment ar ...
... Arsenic is a proven carcinogen found in the soil in gold mining regions at concentrations that can be thousands of times greater than gold. During mining arsenic is released into the environment, easily entering surrounding water bodies. The main chemical forms of arsenic found in the environment ar ...
Elephant Ear - UNM Biology
... Wagner, W. L., D. R. Herbst, and S. H. Sohmer. 1999. Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawai‘i. Revised edition. Vol. 2. University of Hawaii ...
... Wagner, W. L., D. R. Herbst, and S. H. Sohmer. 1999. Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawai‘i. Revised edition. Vol. 2. University of Hawaii ...
Ohdo Syndrome - UK Genetic Testing Network
... Utility of a negative test result: will allow prioritisation of mutation negative cases for additional aetiological investigations including CGH array, other single gene analyses and research / exome studies aimed at identifying other genes causing Ohdo syndrome. 29. How will the availability of thi ...
... Utility of a negative test result: will allow prioritisation of mutation negative cases for additional aetiological investigations including CGH array, other single gene analyses and research / exome studies aimed at identifying other genes causing Ohdo syndrome. 29. How will the availability of thi ...
Hanson RR. Congenital and inherited anomalies of the
... Affected species include cattle, sheep, dogs, cats, horses, ~ & k e s equail, rats; and W e II glycogenosis in Shorthorn and Brahman cattle has been well documented and i s i&erite;i-as &I autosomal recessive disorder. Affected cattle develop muscular weakness and die at 9-16 mo of age, often with a ...
... Affected species include cattle, sheep, dogs, cats, horses, ~ & k e s equail, rats; and W e II glycogenosis in Shorthorn and Brahman cattle has been well documented and i s i&erite;i-as &I autosomal recessive disorder. Affected cattle develop muscular weakness and die at 9-16 mo of age, often with a ...
Myopathies
... • The dystrophin gene (Xp21) spans (∼1% of the total X chromosome), making it one of the largest in the human genome; its enormous size is a probable explanation for its particular vulnerability to mutation • Deletions appear to represent a large proportion of the genetic abnormalities, with framesh ...
... • The dystrophin gene (Xp21) spans (∼1% of the total X chromosome), making it one of the largest in the human genome; its enormous size is a probable explanation for its particular vulnerability to mutation • Deletions appear to represent a large proportion of the genetic abnormalities, with framesh ...
Crush Syndrome - UNM Emergency Department
... But wait! • What about chronic renal patients? • How many patients per machine? • Where do you get supplies? • How do you organize your response? • Who get to decide who receives dialysis? • Who operates the machinery? • How do you monitor progress? • Where can you get laboratory support? ...
... But wait! • What about chronic renal patients? • How many patients per machine? • Where do you get supplies? • How do you organize your response? • Who get to decide who receives dialysis? • Who operates the machinery? • How do you monitor progress? • Where can you get laboratory support? ...
Enzyme levels
... mg on a monthly basis until the lowest dose that controls the disease is reached. ...
... mg on a monthly basis until the lowest dose that controls the disease is reached. ...
Temperature management in critically ill patients
... Initially simple methods can be instituted, such as uncovering the patient whilst preserving their dignity and using cold towels placed across the patient or in the axillae. If ice packs are used, care must be taken to ensure that the ice does not come into direct contact with the patient’s skin and ...
... Initially simple methods can be instituted, such as uncovering the patient whilst preserving their dignity and using cold towels placed across the patient or in the axillae. If ice packs are used, care must be taken to ensure that the ice does not come into direct contact with the patient’s skin and ...
Clinical Anesthesia - Shantou University
... – Elimination of rebreathing, high fresh gas flows, low anesthetic-circuit volume, low absorption by anesthetic circuit, decreased solubility, high cerebral blood flow, increased ventilation, length of time ...
... – Elimination of rebreathing, high fresh gas flows, low anesthetic-circuit volume, low absorption by anesthetic circuit, decreased solubility, high cerebral blood flow, increased ventilation, length of time ...
Toxicology learning objectives File
... 2) Understand additional treatment options are available for some drugs including decontamination options; enhanced elimination and the use of antidotes 3) Be able to recognise and manage acute toxidromes 4) Review ECG changes associated with some toxicological agents 5) Be aware of specific drugs t ...
... 2) Understand additional treatment options are available for some drugs including decontamination options; enhanced elimination and the use of antidotes 3) Be able to recognise and manage acute toxidromes 4) Review ECG changes associated with some toxicological agents 5) Be aware of specific drugs t ...
Malignant hyperthermia

Malignant hyperthermia (MH) or malignant hyperpyrexia is a rare life-threatening condition that is usually triggered by exposure to certain drugs used for general anesthesia — specifically the volatile anesthetic agents and succinylcholine, a neuromuscular blocking agent. In susceptible individuals, these drugs can induce a drastic and uncontrolled increase in oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle, which overwhelms the body's capacity to supply oxygen, remove carbon dioxide, and regulate body temperature, eventually leading to circulatory collapse and death if not immediately treated.Susceptibility to MH is often inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder, for which there are at least 6 genetic loci of interest, most prominently the ryanodine receptor gene (RYR1). MH susceptibility is phenotypically and genetically related to central core disease (CCD), an autosomal dominant disorder characterized both by MH signs and myopathy. MH is usually revealed upon or shortly after exposure to certain general anesthetic agents. There is no simple, straightforward test to diagnose the condition. Treatment with dantrolene and other drugs is usually initiated when MH is strongly suspected. Dantrolene and the avoidance of triggering agents in susceptible people have markedly reduced the mortality from this condition.