Foreign Direct Investment in the Republic of Ireland (FDI)
... investment was encouraged by the strength of the US economy and the global demand for high-tech products. Finally, and by no means least important, have been demographic factors. Until recently, exceptionally high birth rates have made Ireland one of the youngest countries in the OECD while emigrati ...
... investment was encouraged by the strength of the US economy and the global demand for high-tech products. Finally, and by no means least important, have been demographic factors. Until recently, exceptionally high birth rates have made Ireland one of the youngest countries in the OECD while emigrati ...
UNITED STATES`.`
... L2mong the various classes of physical features in the Northeastern United States, streams appear to be the most often nanied.8 Since a generic term is inI arialdy appended when these riallies are formally recorded on maps,g a large niass of stream terms await the attention oi place-name geographers ...
... L2mong the various classes of physical features in the Northeastern United States, streams appear to be the most often nanied.8 Since a generic term is inI arialdy appended when these riallies are formally recorded on maps,g a large niass of stream terms await the attention oi place-name geographers ...
The Kingdom - Seomra Ranga
... The Islands • The Blasket Islands, Valentia and the Skelligs are a few of the islands off the coast of Kerry. • The Blasket Islands are famous for their poets and writers. • No one lives on the Blasket Islands today • The last family left the great Blasket in ...
... The Islands • The Blasket Islands, Valentia and the Skelligs are a few of the islands off the coast of Kerry. • The Blasket Islands are famous for their poets and writers. • No one lives on the Blasket Islands today • The last family left the great Blasket in ...
World Geography - Net Start Class
... Today, the countries of Scandinavia have much in common – Similar political views, languages, and religion – Large, wealthy cities, strong economies, and well-educated workers – High standards of living – Sweden, Denmark, Greenland, Finland, Norway, and Iceland are among the world’s most peaceful, s ...
... Today, the countries of Scandinavia have much in common – Similar political views, languages, and religion – Large, wealthy cities, strong economies, and well-educated workers – High standards of living – Sweden, Denmark, Greenland, Finland, Norway, and Iceland are among the world’s most peaceful, s ...
KS2 History / Geography Planning Revised April 2016 Year A 2015
... Spring / Summer term History – The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain Julius Caesar’s attempted invasion in 55-54BC The roman Army by AD 42 and the power of its army Successful invasion by Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall British resistance, for example Boudica ...
... Spring / Summer term History – The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain Julius Caesar’s attempted invasion in 55-54BC The roman Army by AD 42 and the power of its army Successful invasion by Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall British resistance, for example Boudica ...
Northern Ireland
... Northern Ireland as Ulster. Catholics seldom use this name. For most Catholics the term Ulster is used only to refer to the historic Irish province of Ulster, which consisted of the current six counties and three other counties that are now in the Republic of Ireland. Catholics tend to refer to the ...
... Northern Ireland as Ulster. Catholics seldom use this name. For most Catholics the term Ulster is used only to refer to the historic Irish province of Ulster, which consisted of the current six counties and three other counties that are now in the Republic of Ireland. Catholics tend to refer to the ...
CLIL LESSON (Grade 7th, level A1)
... In the centre of Northern England there are hills called the Pennines. In the South-West of England there are gently rolling hills (Dartmoor) and in the Northern Ireland there are the Mourne Mountains. In the East and South-East of England the land is flat . In the East there is a very low and wet a ...
... In the centre of Northern England there are hills called the Pennines. In the South-West of England there are gently rolling hills (Dartmoor) and in the Northern Ireland there are the Mourne Mountains. In the East and South-East of England the land is flat . In the East there is a very low and wet a ...
Northern Europe
... – England joined with Wales and Scotland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain – Launched overseas empire and had colonies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Australia by the late 1800s – Economy soared with the industrial revolution in the 1700s and 1800s – At its height the British Empire ...
... – England joined with Wales and Scotland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain – Launched overseas empire and had colonies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Australia by the late 1800s – Economy soared with the industrial revolution in the 1700s and 1800s – At its height the British Empire ...
Page 6
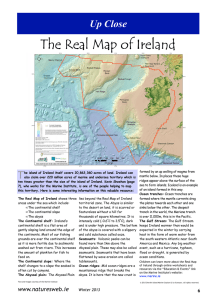
... formed by an up welling of magma from mantle below. In places these huge ridges appear above the surface of the sea to form islands. Iceland is an example of an island formed in this way. Ocean trenches: Ocean trenches are The Real Map of Ireland shows three lies beyond the Real Map of Ireland forme ...
... formed by an up welling of magma from mantle below. In places these huge ridges appear above the surface of the sea to form islands. Iceland is an example of an island formed in this way. Ocean trenches: Ocean trenches are The Real Map of Ireland shows three lies beyond the Real Map of Ireland forme ...
Chapter 10 Section 1 The United Kingdom
... • The Celts settled in Ireland during 300 B.C. • The official language is Gaelic and English. • Most people speak English • 57% of people live in cities ...
... • The Celts settled in Ireland during 300 B.C. • The official language is Gaelic and English. • Most people speak English • 57% of people live in cities ...
The United Kingdom
... The United Kingdom. Geographical Features The official name of the UK is the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is made up of four countries, each with a distinct culture: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. London is the capital of England and the UK. The capital of ...
... The United Kingdom. Geographical Features The official name of the UK is the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is made up of four countries, each with a distinct culture: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. London is the capital of England and the UK. The capital of ...
The United Kingdom of Great Britain And Northern Ireland
... Cambridge is one of the best-known towns in the world, and the principal reason for its fame is its University. ...
... Cambridge is one of the best-known towns in the world, and the principal reason for its fame is its University. ...
Karta pracy kl.IIc Northern Ireland
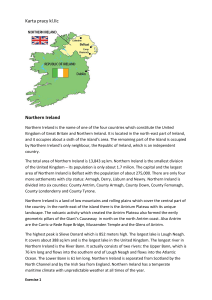
... Northern Ireland is a land of low mountains and rolling plains which cover the central part of the country. In the north-east of the island there is the Antrium Plateau with its unique landscape. The volcanic activity which created the Antrim Plateau also formed the eerily geometric pillars of the G ...
... Northern Ireland is a land of low mountains and rolling plains which cover the central part of the country. In the north-east of the island there is the Antrium Plateau with its unique landscape. The volcanic activity which created the Antrim Plateau also formed the eerily geometric pillars of the G ...
LearnEnglish elementary podcast support materials
... To give it its full title it’s ‘The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland’. You might hear it referred to as Britain, Great Britain or more often, simply as ‘The UK’. Four countries make up the UK – England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. It consists of a group of islands - 2 l ...
... To give it its full title it’s ‘The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland’. You might hear it referred to as Britain, Great Britain or more often, simply as ‘The UK’. Four countries make up the UK – England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. It consists of a group of islands - 2 l ...
A tourist guide round Britain Students: Viktoria Belogubtseva Tat
... The prevailing winds blow from the south-west. As these winds blow from the ocean, they are mild in winter and cool in summer, and are heavily charged with moisture at all times. As they approach the mountainous areas near the west coasts, they rise up the mountain slopes. Their temperature drops, w ...
... The prevailing winds blow from the south-west. As these winds blow from the ocean, they are mild in winter and cool in summer, and are heavily charged with moisture at all times. As they approach the mountainous areas near the west coasts, they rise up the mountain slopes. Their temperature drops, w ...
Great Britain
... the formal name of Britain was made by Aristotle (c. 384–322 BC), in his text [On The Universe], Vol. III. To quote his works, “...in the ocean however, are two islands, and those very large, called Bretannic, Albion and Ierna....” The archipelago has been referred to by a single name for over two t ...
... the formal name of Britain was made by Aristotle (c. 384–322 BC), in his text [On The Universe], Vol. III. To quote his works, “...in the ocean however, are two islands, and those very large, called Bretannic, Albion and Ierna....” The archipelago has been referred to by a single name for over two t ...
Diapositiva 1 - Colegio El Atabal
... cultural life of the island since ancient times. The missions, spread the Irish vision of Christianity to pagan England and the Frankish Empire. These missions brought written language to an illiterate population of Europe during the Dark Ages that followed the fall of Rome. ...
... cultural life of the island since ancient times. The missions, spread the Irish vision of Christianity to pagan England and the Frankish Empire. These missions brought written language to an illiterate population of Europe during the Dark Ages that followed the fall of Rome. ...
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern
... United States and a close partnership with France, "Heart's agreement", and has a total nuclear weapons program with the two countries. Other close allies include other members of the EU and NATO and the countries of the Commonwealth, as well as Japan. Global presence and influence of Britain are al ...
... United States and a close partnership with France, "Heart's agreement", and has a total nuclear weapons program with the two countries. Other close allies include other members of the EU and NATO and the countries of the Commonwealth, as well as Japan. Global presence and influence of Britain are al ...
Facts: The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
... Church was founded and the reign of his daughter Elizabeth I was marked by overseas expansion as well as great cultural development. In 1536, Wales was joined to England by the Act of Union. The power of the Parliament gradually grew and during the English Revolution (1649 1660) the monarchy was tem ...
... Church was founded and the reign of his daughter Elizabeth I was marked by overseas expansion as well as great cultural development. In 1536, Wales was joined to England by the Act of Union. The power of the Parliament gradually grew and during the English Revolution (1649 1660) the monarchy was tem ...
Geographical position of the British Isles
... They occupy the total area of 244000 square km. The British Isles consist of 2 large islands – Great Britain and Ireland , and a lot of small islands, the main of which are the Isle of Whight, Anglesey, the Isle of Scilly, the Isle of Man, the Hebrides, the Orkney Islands and the Shetland Islands. T ...
... They occupy the total area of 244000 square km. The British Isles consist of 2 large islands – Great Britain and Ireland , and a lot of small islands, the main of which are the Isle of Whight, Anglesey, the Isle of Scilly, the Isle of Man, the Hebrides, the Orkney Islands and the Shetland Islands. T ...
Презентация на тему Великобритания
... of the United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the island of Ireland and many small islands. Northern Ireland - the only part of the UK with a land border with another sovereign country the Republic of Ireland. All other boundaries are water: UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
... of the United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the island of Ireland and many small islands. Northern Ireland - the only part of the UK with a land border with another sovereign country the Republic of Ireland. All other boundaries are water: UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the ...
THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN
... England, Scotland and Wales (Great Britain) together with Northern Ireland from the country officially known as “The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland” simply the United Kingdom. Its area is of about 245,000 square miles. The island of Great Britain can be divided into two main re ...
... England, Scotland and Wales (Great Britain) together with Northern Ireland from the country officially known as “The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland” simply the United Kingdom. Its area is of about 245,000 square miles. The island of Great Britain can be divided into two main re ...
Terminology of the British Isles
Various terms are used to describe the different (and sometimes overlapping) geographical and political areas of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, and the smaller islands which surround them. The terminology is often a source of confusion, partly owing to the similarity between some of the actual words used, but also because they are often used loosely. In addition, many of the words carry both geographical and political connotations which are affected by the history of the islands. The purpose of this article is to explain the meanings of and relationships among the terms in use. However many of these classifications are contentious and have resulted in the British Isles naming dispute.In brief, the main terms and their simple explanations are as follows. Geographical terms:The British Isles is a group of islands in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Continental Europe. It includes Ireland, Great Britain, the Isle of Man, Shetland, Orkney, and thousands of smaller islands. Traditionally the Channel Islands are included, though these specific islands are geographically closer to mainland continental Europe, being positioned off the French coast of Normandy. This, in part, has resulted in the term being disputed. Great Britain is the largest island of the archipelago.Ireland is the second largest island of the archipelago and lies directly to the west of Great Britain. The island of Ireland itself has its own list of Irish Isles.The full list of islands in the British Isles includes over 6,000 islands, of which 51 have an area larger than 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi). Political terms: The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the constitutional monarchy occupying the island of Great Britain, the small nearby islands (but not the Isle of Man or the Channel Islands), and the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland. Usually, it is shortened to United Kingdom or the UK, though Britain is also an officially recognised short form. ""Great Britain"" is sometimes used as a short form, and is the name used by the UK in some international organisations. The abbreviation GB is frequently used for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in international agreements, e.g. Universal Postal Union and Road Traffic Convention, as well as in the ISO 3166 country codes (GB and GBR). ""England"" was also formerly used synecdochically to refer to the whole United Kingdom, but this usage became rare early in the 20th century. Ireland is the sovereign republic occupying the larger portion of the island of Ireland. However, to distinguish the state from the island, or to distinguish either of these from Northern Ireland, it is also called ""the Republic of Ireland"" or simply ""the Republic"". Occasionally, its Irish-language name, Éire (or Eire without the diacritic), will be used in an English-language context to distinguish it from ""Northern Ireland"", even though the word Éire directly translates as ""Ireland"".England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are the four countries of the United Kingdom though they are also referred to as the constituent countries or, especially in sporting contexts, home nations of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.England and Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland are legal jurisdictions within the United Kingdom.Great Britain means the countries of England, Wales and Scotland considered as a unit.British Islands consists of the United Kingdom, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. These are the states within the British Isles that have the British monarch as head of state.Linguistic terms:The two sovereign states in the region, the United Kingdom and Ireland, are frequently referred to as countries. So too are England, Wales, Scotland and, to a lesser extent, Northern Ireland (as is the whole island of Ireland).British is an adjective pertaining to the United Kingdom; for example, a citizen of the UK is called a British citizen—but for citizenship purposes ""British"" includes the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man.Anglo- is often used as an adjectival prefix referring to the United Kingdom (notwithstanding that its original meaning is ""English"") particularly in the field of diplomatic relations. It can also refer to the English language, to anglophone peoples and can have a variety of other shades of meaning.Wales is sometimes called the Principality of Wales, although this has no modern constitutional basis.Northern Ireland is often referred to as a province or called Ulster, after the traditional Irish province of Ulster in which it is located.SportForms of national representation vary from sport to sport. England, Scotland and Wales often compete separately as nations. In some sports—such as rugby and cricket—the island of Ireland competes as a nation; in others, most notably association football, Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland field separate teams. In these contexts England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland/Northern Ireland are sometimes described as the home nations.Rugby union players from both Ireland and Great Britain play for British and Irish Lions representing the four ""Home Unions"" of England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales.Great Britain is sometimes used to mean United Kingdom. For example, at the Olympic Games, the team called ""Great Britain"" represents Great Britain and Northern Ireland. However, athletes from Northern Ireland have, by virtue of their entitlement to dual nationality, the choice of participating in either the Great Britain team or the Republic of Ireland team.In the majority of individual sports (e.g. tennis and athletics), at international level competitors are identified as GB if they are from Great Britain or Northern Ireland. A small number of sports (e.g. golf, darts, snooker) identify participants as representing their constituent country. In the Commonwealth Games, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each compete as separate nations, as do each of the three Crown Dependencies (Ireland is not part of the Commonwealth and is not eligible to participate).↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ 13.0 13.1