3.1 How does the body heal?
... commonly used antiseptics and cleansing agents. Use of these agents is often responsible for delayed healing, since they are non-selective in their activity and will kill healthy cells as well as bacteria. It is preferable to avoid the prolonged use of these products on a granulating wound. Their us ...
... commonly used antiseptics and cleansing agents. Use of these agents is often responsible for delayed healing, since they are non-selective in their activity and will kill healthy cells as well as bacteria. It is preferable to avoid the prolonged use of these products on a granulating wound. Their us ...
NASHA™ – the MONOGRAPH
... and tissue reorganization. That is, when cells need space for motility and separation these functions are performed in a hyaluronic acid medium. The hyaluronic acid network assists in cell differentiation, cell migration, tissue morphogenesis, embryogenesis and wound repair. Tissues involved in move ...
... and tissue reorganization. That is, when cells need space for motility and separation these functions are performed in a hyaluronic acid medium. The hyaluronic acid network assists in cell differentiation, cell migration, tissue morphogenesis, embryogenesis and wound repair. Tissues involved in move ...
Slide 1
... The clinical features of inflammation have been recognized since ancient times as swelling, redness, pain, and heat. The underlying mechanisms which produce these symptoms are complex, involving many different cells and cell products. A normal inflammatory response is essential to fight infections ...
... The clinical features of inflammation have been recognized since ancient times as swelling, redness, pain, and heat. The underlying mechanisms which produce these symptoms are complex, involving many different cells and cell products. A normal inflammatory response is essential to fight infections ...
PART 1 B - Veterinary Medicines Directorate
... action appears to be mediated by the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis via the inhibition of the cylo-oxygenase enzyme. Sulphur is a non-metallic element, used for topical dermatologic therapy, possessing antiseptic, antifungal, antiparasitic, anti-acne, anti-pruritic, antiseborrhoeic and kerato ...
... action appears to be mediated by the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis via the inhibition of the cylo-oxygenase enzyme. Sulphur is a non-metallic element, used for topical dermatologic therapy, possessing antiseptic, antifungal, antiparasitic, anti-acne, anti-pruritic, antiseborrhoeic and kerato ...
Cell-wall Constituents of Rickettsiae and Psittacosis
... Morgan-Elson reaction for N-acetylhexosamines was obtained. Although bacterial cell-wall mucopeptides containing muramic acid are not the only polymers hydrolysed by lysozyme (for instance chitin, a p( 1-4)-linked poly N-acetylglucosamine, is attacked to some extent as Berger & Weiser (1957) showed) ...
... Morgan-Elson reaction for N-acetylhexosamines was obtained. Although bacterial cell-wall mucopeptides containing muramic acid are not the only polymers hydrolysed by lysozyme (for instance chitin, a p( 1-4)-linked poly N-acetylglucosamine, is attacked to some extent as Berger & Weiser (1957) showed) ...
Modeling Barrier Tissues In Vitro: Methods, Achievements, and
... The skin is commonly referred to as our “largest organ”, serving as a protective barrier between the human body and surrounding environment. Understanding skin physiology is necessary in the development of safe topical products like transdermal drugs and cosmetics, but also in wound healing, skin di ...
... The skin is commonly referred to as our “largest organ”, serving as a protective barrier between the human body and surrounding environment. Understanding skin physiology is necessary in the development of safe topical products like transdermal drugs and cosmetics, but also in wound healing, skin di ...
Comparison of cytotoxicity and wound healing effect of
... promotes epithelial healing[3,4]. Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide, is one of the most common viscous polymers used in artificial tears to achieve their prolonged residence efficacious in the treatment of aqueous tear-deficient dry eye symptoms and ocular surface ...
... promotes epithelial healing[3,4]. Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide, is one of the most common viscous polymers used in artificial tears to achieve their prolonged residence efficacious in the treatment of aqueous tear-deficient dry eye symptoms and ocular surface ...
KSVDL Clinical Pathology Submission Form
... Renal Profile (Urea N, Creatinine, Pi, Na, K, Cl)(red top) Electrolyte Panel (Na, K, Cl)(red top) Avian/Reptile Chemistry Panel (heparin, green top) Dairy Metabolic Profile (Ca, Mg, P, NEFA) ...
... Renal Profile (Urea N, Creatinine, Pi, Na, K, Cl)(red top) Electrolyte Panel (Na, K, Cl)(red top) Avian/Reptile Chemistry Panel (heparin, green top) Dairy Metabolic Profile (Ca, Mg, P, NEFA) ...
What Roles Do Carbohydrates Play In Vivo
... O-Linked: Extracellular Rigidity and Cell Signaling Cell surface glycoproteins • Protect cell from unwanted interactions • Extracellular interactions/ signal transduction ...
... O-Linked: Extracellular Rigidity and Cell Signaling Cell surface glycoproteins • Protect cell from unwanted interactions • Extracellular interactions/ signal transduction ...
Inflammations and Their Therapy by Means of Isopathy
... are also induced by further damages, can be of influence herein. Therefore, an inflammation is always the result of an overstrain of the storage capacity of the basic substance, in which, according to the present knowledge, two fundamental noxas take part: infections and the endobiosis resp. latenti ...
... are also induced by further damages, can be of influence herein. Therefore, an inflammation is always the result of an overstrain of the storage capacity of the basic substance, in which, according to the present knowledge, two fundamental noxas take part: infections and the endobiosis resp. latenti ...
Combining Kinetic Ligand Binding and 3D Tumor Invasion
... However, when the competitor dissociates slower (larger R value), the association curve of the ligand consists of two phases, starting with a typical “overshoot” and then a decline until a new equilibrium is reached. Competitors whose residence times are greater than that of the SDF1-α-d2 ligand, su ...
... However, when the competitor dissociates slower (larger R value), the association curve of the ligand consists of two phases, starting with a typical “overshoot” and then a decline until a new equilibrium is reached. Competitors whose residence times are greater than that of the SDF1-α-d2 ligand, su ...
点击下载观看
... kinds of animals,and partly exist in the the human oral cavity and vagina. At present it is believed that the bifidobacterium does not have the pathogenicity, is beneficial to the human. ...
... kinds of animals,and partly exist in the the human oral cavity and vagina. At present it is believed that the bifidobacterium does not have the pathogenicity, is beneficial to the human. ...
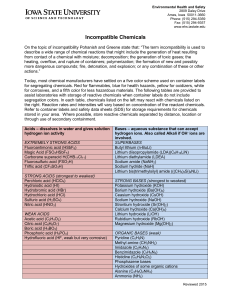
Incompatible Chemicals
... describe a wide range of chemical reactions that might include the generation of heat resulting from contact of a chemical with moisture; decomposition; the generation of toxic gases; the heating, overflow, and rupture of containers; polymerization; the formation of new and possibly more dangerous c ...
... describe a wide range of chemical reactions that might include the generation of heat resulting from contact of a chemical with moisture; decomposition; the generation of toxic gases; the heating, overflow, and rupture of containers; polymerization; the formation of new and possibly more dangerous c ...
View PPT slides - Digital Pathology Association
... PTEN expression by IHC (advantages over sequencing) Other Biomarkers KRAS and/or BRAF mutation (depending on tumor type) EGFR, HER2, c-Met amplification (depending on tumor type) IGF-1R, p-EGFR, p-HER2, p-HER3 Biomarkers for PD/Target Modulation p-S6, p-4EBP1, p-mTOR, Cleaved Caspase 3, Ki ...
... PTEN expression by IHC (advantages over sequencing) Other Biomarkers KRAS and/or BRAF mutation (depending on tumor type) EGFR, HER2, c-Met amplification (depending on tumor type) IGF-1R, p-EGFR, p-HER2, p-HER3 Biomarkers for PD/Target Modulation p-S6, p-4EBP1, p-mTOR, Cleaved Caspase 3, Ki ...
1 - Yimg
... hormones localized to tissues where they are produced. prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes. derived from arachidonic acid arachidonic acid from linoleic acid an essential fatty acid Table 1. Physiological functions of eicosanoids. ...
... hormones localized to tissues where they are produced. prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes. derived from arachidonic acid arachidonic acid from linoleic acid an essential fatty acid Table 1. Physiological functions of eicosanoids. ...
Antifungal
... and a cell membrane composed of ergosterol. While bacterial cells are prokaryotic. So, antibacterial agents can exhibit ...
... and a cell membrane composed of ergosterol. While bacterial cells are prokaryotic. So, antibacterial agents can exhibit ...
Introduction to histopathology
... proportion to the damage caused by the antigen or pathogen and does more harm than good. Autoimmune diseases are by their very nature a type of hypersensitivity reaction; however, there are many instances where the immune reaction against an antigen or a pathogen is out of proportion to the damage t ...
... proportion to the damage caused by the antigen or pathogen and does more harm than good. Autoimmune diseases are by their very nature a type of hypersensitivity reaction; however, there are many instances where the immune reaction against an antigen or a pathogen is out of proportion to the damage t ...
Human Tissues III
... through adenylyl cyclase that will increase the level of cAMP, which increases calcium, allowing fusion of the vesicles to release their molecules. This is mediated by antibody binding and antigen binding. As soon as antigen is there, it triggers secretion of factors to recruit and stimulate a respo ...
... through adenylyl cyclase that will increase the level of cAMP, which increases calcium, allowing fusion of the vesicles to release their molecules. This is mediated by antibody binding and antigen binding. As soon as antigen is there, it triggers secretion of factors to recruit and stimulate a respo ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... c. Reticular fibers are fine, collagenous fibers that form networks where connective tissue contacts other types of tissues. 3. Each major class of connective tissue has a fundamental cell type that exists in immature and mature forms. D. Types of Connective Tissue (pp. 129–137; Fig. 4.8; Table 4.1) ...
... c. Reticular fibers are fine, collagenous fibers that form networks where connective tissue contacts other types of tissues. 3. Each major class of connective tissue has a fundamental cell type that exists in immature and mature forms. D. Types of Connective Tissue (pp. 129–137; Fig. 4.8; Table 4.1) ...
Hyaluronidase enhances the activity of Adriamycin in breast cancer
... Prehm (1990) discussed the observation that high-molecular-mass hyaluronate inhibits cell growth, whereas small fragments are stimulatory. In addition, it is known that hyaluronidase treatment of living cells stimulates the synthesis of hyaluronic acid (Philipson et al. 1985; Larnier et al. 1989), w ...
... Prehm (1990) discussed the observation that high-molecular-mass hyaluronate inhibits cell growth, whereas small fragments are stimulatory. In addition, it is known that hyaluronidase treatment of living cells stimulates the synthesis of hyaluronic acid (Philipson et al. 1985; Larnier et al. 1989), w ...
Wound assessment and documentation
... BACTERIA are inevitably present in most wounds, often without detrimental effect. The presence of bacteria in a wound may result in: CONTAMINATION – the bacteria do not increase in number or cause clinical problems. COLONISATION – the bacteria multiply but wound tissues are not damaged. INFECTION – ...
... BACTERIA are inevitably present in most wounds, often without detrimental effect. The presence of bacteria in a wound may result in: CONTAMINATION – the bacteria do not increase in number or cause clinical problems. COLONISATION – the bacteria multiply but wound tissues are not damaged. INFECTION – ...
20101-viscera
... D. folic acid plus Vit B12 E. Vit B12 plus ferrous sulfate 9. Among the following anti-inflammatory mechanisms of glucocorticoids, which one can commonly be observed ? A. Increased influx of leukocytes to the site of inflammation B. Reduced expression of ACEI C. Reduced capillary permeability and e ...
... D. folic acid plus Vit B12 E. Vit B12 plus ferrous sulfate 9. Among the following anti-inflammatory mechanisms of glucocorticoids, which one can commonly be observed ? A. Increased influx of leukocytes to the site of inflammation B. Reduced expression of ACEI C. Reduced capillary permeability and e ...
lecture 2 - carbohydrates
... long unbranched molecules containing a repeating disaccharide unit. Usually one sugar is an uronic acid (either D-glucuronic or L-iduronic) and the other is either GlcNAc or GalNAc. One or both sugars contain sulfate groups (the only exception is hyaluronic acid). GAGs are highly negatively charged ...
... long unbranched molecules containing a repeating disaccharide unit. Usually one sugar is an uronic acid (either D-glucuronic or L-iduronic) and the other is either GlcNAc or GalNAc. One or both sugars contain sulfate groups (the only exception is hyaluronic acid). GAGs are highly negatively charged ...
Hyaluronic acid

Hyaluronic acid (HA) /ˌhaɪəl.jʊˈrɒnɨk/ (also called hyaluronan /haɪˈæljʊrənən/, hyaluronate /ˌhaɪəlˈjʊərəneɪt/ or /ˌhaɪəˈlʊərəneɪt/,) is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans in that it is nonsulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi, and can be very large, with its molecular weight often reaching the millions.One of the chief components of the extracellular matrix, hyaluronan contributes significantly to cell proliferation and migration, and may also be involved in the progression of some malignant tumors.The average 70 kg (154 lb) person has roughly 15 grams of hyaluronan in the body, one-third of which is turned over (degraded and synthesized) every day. Hyaluronic acid is also a component of the group A streptococcal extracellular capsule, and is believed to play a role in virulence.