Analytical Solution of Time Periodic Electroosmotic Flows: Analogies
... extrema that are stronger than the Stokes layers. This have the potential to result in low Reynolds number flow instabilities. It is also shown that, unlike the steady pure electroosmotic flows, the bulk flow region of time periodic electroosmotic flows are rotational when the diffusion length scale ...
... extrema that are stronger than the Stokes layers. This have the potential to result in low Reynolds number flow instabilities. It is also shown that, unlike the steady pure electroosmotic flows, the bulk flow region of time periodic electroosmotic flows are rotational when the diffusion length scale ...
Infrared Spectroscopy
... of 2hν, 3hν, or higher are observed. These correspond to bands called overtones in an IR spectrum. They are of lower intensity than the fundamental vibration bands. A molecule is not just two atoms joined on a spring, of course. A bond can come apart, and it cannot be compressed beyond a certain poi ...
... of 2hν, 3hν, or higher are observed. These correspond to bands called overtones in an IR spectrum. They are of lower intensity than the fundamental vibration bands. A molecule is not just two atoms joined on a spring, of course. A bond can come apart, and it cannot be compressed beyond a certain poi ...
Chapter 13 - UniMAP Portal
... Henry (H) The unit of inductance. RL time A fixed time interval set by the L and R constant values, that determines the time response of a circuit. It equals the ratio of L/R. Inductive The opposition of an inductor to sinusoidal reactance current. The unit is the ohm. Quality factor The ratio of re ...
... Henry (H) The unit of inductance. RL time A fixed time interval set by the L and R constant values, that determines the time response of a circuit. It equals the ratio of L/R. Inductive The opposition of an inductor to sinusoidal reactance current. The unit is the ohm. Quality factor The ratio of re ...
Cost-effective-EMC-Design-by-Working-with-the-Laws-of
... – but if so, it was never properly explained to us how this related to circuit design, power supply decoupling, PCB layout, shielding, filtering, etc… – either to make circuits function well, or achieve EMC, to improve our employer’s financial performance o ...
... – but if so, it was never properly explained to us how this related to circuit design, power supply decoupling, PCB layout, shielding, filtering, etc… – either to make circuits function well, or achieve EMC, to improve our employer’s financial performance o ...
a single-phase cascaded multilevel inverter
... is comprised of a series connection of the proposed basic unit and is able to only generate positive levels at the output. Therefore, an H-bridge is added to the proposed inverter. This inverter is called the developed cascaded multilevel inverter. In order to generate all voltage levels (even and o ...
... is comprised of a series connection of the proposed basic unit and is able to only generate positive levels at the output. Therefore, an H-bridge is added to the proposed inverter. This inverter is called the developed cascaded multilevel inverter. In order to generate all voltage levels (even and o ...
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitors 2 ) Find the charge on 4uF
... c) In a certain region 0.1 m3 of space, electric potential is found to be 5V throughout. What is the electric field in this region? [1] d) Write down the dimensional formula of potential? [1] 13 Two charges 3C and - 3C are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart. a) Identify an equipotential surface ...
... c) In a certain region 0.1 m3 of space, electric potential is found to be 5V throughout. What is the electric field in this region? [1] d) Write down the dimensional formula of potential? [1] 13 Two charges 3C and - 3C are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart. a) Identify an equipotential surface ...
Components and Methods for Current Measurement
... A signal to indicate the “how much” condition and the “too much” condition is available in a variety of different measurement methods, as listed below: 1. Resistive (direct) a. Current sense resistors 2. Magnetic (indirect) a. Current transformer b. Rogowski coil c. Hall effect device 3. Transistor ...
... A signal to indicate the “how much” condition and the “too much” condition is available in a variety of different measurement methods, as listed below: 1. Resistive (direct) a. Current sense resistors 2. Magnetic (indirect) a. Current transformer b. Rogowski coil c. Hall effect device 3. Transistor ...
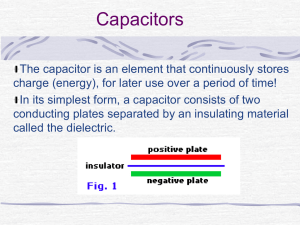
Capacitors
... The difference between a capacitor and a battery is that a capacitor can dump its entire charge in a tiny fraction of a second, where a battery would take minutes to completely discharge itself. That's why the electronic flash on a camera uses a capacitor -- the battery charges up the flash's capaci ...
... The difference between a capacitor and a battery is that a capacitor can dump its entire charge in a tiny fraction of a second, where a battery would take minutes to completely discharge itself. That's why the electronic flash on a camera uses a capacitor -- the battery charges up the flash's capaci ...
electric current - iGCSE Science Courses
... State that current is related to the flow of charge • Use and describe the use of an ammeter, both analogue and digital • State that current in metals is due to a flow of electrons ...
... State that current is related to the flow of charge • Use and describe the use of an ammeter, both analogue and digital • State that current in metals is due to a flow of electrons ...
Chapter 13
... Physical parameters affecting inductance The inductance given by the equation in the previous slide is for the ideal case. In practice, inductors have winding resistance (RW) and winding capacitance (CW). An equivalent circuit for a practical inductor including these effects is: CW ...
... Physical parameters affecting inductance The inductance given by the equation in the previous slide is for the ideal case. In practice, inductors have winding resistance (RW) and winding capacitance (CW). An equivalent circuit for a practical inductor including these effects is: CW ...
Capacitors/Capacitance
... The basic capacitor is composed of two parallel metallic plates separated by a non-conducting material called a dielectric. You will construct one for your crystal radio. The dielectric material can be a vacuum, air, paper, polystyrene, mica, or glass. Capacitors can be fixed (non-adjustable) or var ...
... The basic capacitor is composed of two parallel metallic plates separated by a non-conducting material called a dielectric. You will construct one for your crystal radio. The dielectric material can be a vacuum, air, paper, polystyrene, mica, or glass. Capacitors can be fixed (non-adjustable) or var ...
Measuring and Using Electricity tg.qxd
... There are two types of current. One is called alternating current, or ac, for short. The other is direct current, or dc. Direct current is the kind of current we get from batteries. This kind of current always travels in the same direction. Alternating current is the kind used in homes, businesses, ...
... There are two types of current. One is called alternating current, or ac, for short. The other is direct current, or dc. Direct current is the kind of current we get from batteries. This kind of current always travels in the same direction. Alternating current is the kind used in homes, businesses, ...
Constructing the dual graph from the original graph
... • Characterizing and finding dead center positions of mechanisms and the stability of determinate trusses. • Correlation between Instant Centers and Equimomental Lines. • Graph theory duality principal and the dual of linkages – trusses. • Detailed example of the face force and the procedure for der ...
... • Characterizing and finding dead center positions of mechanisms and the stability of determinate trusses. • Correlation between Instant Centers and Equimomental Lines. • Graph theory duality principal and the dual of linkages – trusses. • Detailed example of the face force and the procedure for der ...
capacitance
... Does changing the voltage supplied increase the capacity of the capacitor? Does changing the supply voltage change the amount of energy that can be stored? This is similar to the circuit found in the electronic flash in a camera. ...
... Does changing the voltage supplied increase the capacity of the capacitor? Does changing the supply voltage change the amount of energy that can be stored? This is similar to the circuit found in the electronic flash in a camera. ...
Displacement Current Does Not Exist
... matter! To illustrate this, if we integrate equation 5 from another starting point to the same end point, r, we will end up with an entirely different value for the magnetic field, H! Obviously, there is something wrong! Any one of these flaws would be sufficient to cast doubt on this and all of the ...
... matter! To illustrate this, if we integrate equation 5 from another starting point to the same end point, r, we will end up with an entirely different value for the magnetic field, H! Obviously, there is something wrong! Any one of these flaws would be sufficient to cast doubt on this and all of the ...
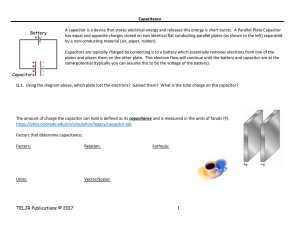
Capacitance
... by a non-conducting material (air, paper, rubber). Capacitors are typically charged by connecting it to a battery which essentially removes electrons from one of the plates and places them on the other plate. This electron flow will continue until the battery and capacitor are at the same potential ...
... by a non-conducting material (air, paper, rubber). Capacitors are typically charged by connecting it to a battery which essentially removes electrons from one of the plates and places them on the other plate. This electron flow will continue until the battery and capacitor are at the same potential ...
JA3116861689
... Basically MHD equation is the combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. Now a day’s MHD is very vastly growing branch whose principle can be applied to physical science and also fundamental ...
... Basically MHD equation is the combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. Now a day’s MHD is very vastly growing branch whose principle can be applied to physical science and also fundamental ...
Generation of electricity
... where a smooth and wide range of speed control is required. It is generally more economical to transmit and distribute electricity in alternating current (AC) form, therefore all electricity generated at is AC.
The exception is for very long transmission lines connecting two
network ...
... where a smooth and wide range of speed control is required. It is generally more economical to transmit and distribute electricity in alternating current (AC) form, therefore all electricity generated at
semiconductor
... component, a device that can amplify, producing an output signal with more power in it than the input signal. ...
... component, a device that can amplify, producing an output signal with more power in it than the input signal. ...
Electricity_and_Magnetism_Unit_STUDY_GUIDE_KEY
... What is the difference between an open In an open circuit, the path is not circuit and a closed circuit? In which type complete and electricity will not of circuit can electrons flow? flow. In a closed circuit, the path is ...
... What is the difference between an open In an open circuit, the path is not circuit and a closed circuit? In which type complete and electricity will not of circuit can electrons flow? flow. In a closed circuit, the path is ...
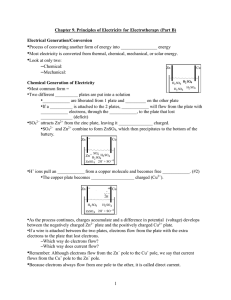
Chapter 9 (Part B)
... ____________________, electricity flows in the wire. •An electrical generator consists of: –A bar _________________ mounted on a rotating pedestal –Two ____________ plates positioned at the end of the magnet and connected with a large loop of wire (or a metal core with a coil of wire around) –Source ...
... ____________________, electricity flows in the wire. •An electrical generator consists of: –A bar _________________ mounted on a rotating pedestal –Two ____________ plates positioned at the end of the magnet and connected with a large loop of wire (or a metal core with a coil of wire around) –Source ...
Capacitors - Honors Physics Website (Blue 5)
... Capacitors store electric charge and decay through exponential means. They are made out of two parallel plates with a material (typically waxed paper) between them. This material is called a dielectric. ...
... Capacitors store electric charge and decay through exponential means. They are made out of two parallel plates with a material (typically waxed paper) between them. This material is called a dielectric. ...
Lecture 07: Current Flow - Purdue Physics
... Current – Orders of Magnitude • 1 x 10-12 A = 1 pA (about 107 e-/s) •10 x 10-9 A = 10 nA (leakage current in transistors) • 1 x 10-6 A = 1 A (typical input current to IC) • 1 x 10-3 A =1 mA (humans can feel this) ...
... Current – Orders of Magnitude • 1 x 10-12 A = 1 pA (about 107 e-/s) •10 x 10-9 A = 10 nA (leakage current in transistors) • 1 x 10-6 A = 1 A (typical input current to IC) • 1 x 10-3 A =1 mA (humans can feel this) ...
Lecture 23 - UConn Physics
... electric and magnetic fields into four equations, all of which you now know. • However, he realized that the equations of electricity & magnetism as then known (and now known by you) have an inconsistency related to the conservation of charge! Gauss’ Law ...
... electric and magnetic fields into four equations, all of which you now know. • However, he realized that the equations of electricity & magnetism as then known (and now known by you) have an inconsistency related to the conservation of charge! Gauss’ Law ...