Histamine, Serotonin and Bradykinin
... B2 = mediate contraction of venous smooth muscle (Bradykinin induces profound vasodilation) Overall: produce marked vasodilation in heart, kidney, intestine, skeletal muscle and liver. 10x more potent than histamine in relaxing vascular smooth muscle. In veins, primary effect is contraction. Are als ...
... B2 = mediate contraction of venous smooth muscle (Bradykinin induces profound vasodilation) Overall: produce marked vasodilation in heart, kidney, intestine, skeletal muscle and liver. 10x more potent than histamine in relaxing vascular smooth muscle. In veins, primary effect is contraction. Are als ...
G-Protein Coupled Receptors Past, Present, Future Outline and
... chief substance in action. Further, that nicotine, curari, atropine, pilocarpine, strychnine, and most other alkaloids, as well as the effective material of internal secretions produce their effects by combining with the receptive substance, and not by an action on axon-endings if these are present, ...
... chief substance in action. Further, that nicotine, curari, atropine, pilocarpine, strychnine, and most other alkaloids, as well as the effective material of internal secretions produce their effects by combining with the receptive substance, and not by an action on axon-endings if these are present, ...
PPT
... Importance of graded dose-response curves 1.Calculation of the ED50 (The dose that produces 50% of the maximum response in one animal Comparing ED50 of different drugs on the same animal gives an idea about the equieffective doses i.e the doses that produce the same effect. Comparing ED50 of th ...
... Importance of graded dose-response curves 1.Calculation of the ED50 (The dose that produces 50% of the maximum response in one animal Comparing ED50 of different drugs on the same animal gives an idea about the equieffective doses i.e the doses that produce the same effect. Comparing ED50 of th ...
Cell to cell communication, homeostasis and control pathways
... _ Drug A and B act through different receptors and signal pathways. _ Drugs A and B are agonists for the same receptor. _ Drugs A and B will compete for the same receptor. _ The receptor from drug A is coupled to a G protein. _ If drug A is present, stomach acid will increase even if drug B is also ...
... _ Drug A and B act through different receptors and signal pathways. _ Drugs A and B are agonists for the same receptor. _ Drugs A and B will compete for the same receptor. _ The receptor from drug A is coupled to a G protein. _ If drug A is present, stomach acid will increase even if drug B is also ...
β 3 - Faculty
... Brunton L L, Blumenthal D K, Murri N, Dandan R H, Knollmann B C. Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 11th ed. New York: McGrawHill, 2005. Carpéné, C., Galitzky, J., Fontana, E., Atgié, C., Lafontan, M., & Berlan, M. (1999). Selective activation of β3-adrenoceptors by octopa ...
... Brunton L L, Blumenthal D K, Murri N, Dandan R H, Knollmann B C. Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 11th ed. New York: McGrawHill, 2005. Carpéné, C., Galitzky, J., Fontana, E., Atgié, C., Lafontan, M., & Berlan, M. (1999). Selective activation of β3-adrenoceptors by octopa ...
1-alpha adrenergic blockers 2017-03-15 05:542.2 MB
... Fall in arterial pressure with less tachycardia than with non-selective - blockers. because 2 isn’t blocked here ...
... Fall in arterial pressure with less tachycardia than with non-selective - blockers. because 2 isn’t blocked here ...
felix may 2nd year neuroscience Neuroreceptor characterisation by
... IC50 is the more effective the drug is per mole. These values are used by pharmacologists extensively as a guidline for effective dosing regimes. Similarly the Kd value is of great interest in pharmacodynamics as it indicates the affinity of a ligand for a receptor type or group of receptors. A low ...
... IC50 is the more effective the drug is per mole. These values are used by pharmacologists extensively as a guidline for effective dosing regimes. Similarly the Kd value is of great interest in pharmacodynamics as it indicates the affinity of a ligand for a receptor type or group of receptors. A low ...
Medicinal Chemistry (MDCH) 5220
... NOTE: this study guide is not inclusive and is only intended as a guide; in addition to using this guide, please look over the notes… Well known and Top200 drugs are worthwhile to recognize (and name). The WWW page has old exams that have questions on basic principles (and also show the general form ...
... NOTE: this study guide is not inclusive and is only intended as a guide; in addition to using this guide, please look over the notes… Well known and Top200 drugs are worthwhile to recognize (and name). The WWW page has old exams that have questions on basic principles (and also show the general form ...
Metrifonate
... biotransformation of mertifonate occurs independently of the hepatic cytochrome P450 It is slowly and non-enzymatically transformed to DDVP which is PH dependent Serum t½ is 2 hours ...
... biotransformation of mertifonate occurs independently of the hepatic cytochrome P450 It is slowly and non-enzymatically transformed to DDVP which is PH dependent Serum t½ is 2 hours ...
2nd Lecture 1433
... It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must change its function upon binding in such a way that the function of the biologic system (cell, tissue, etc) is altered This is necessar ...
... It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must change its function upon binding in such a way that the function of the biologic system (cell, tissue, etc) is altered This is necessar ...
Receptors & Transmitters
... disease (epilepsy, ALS, Parkinson’s) drug abuse (cocaine, amphetamine) treatment (depression, OCD) ...
... disease (epilepsy, ALS, Parkinson’s) drug abuse (cocaine, amphetamine) treatment (depression, OCD) ...
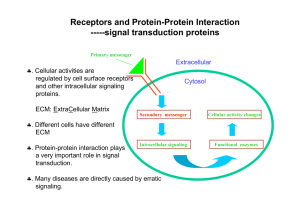
Receptors and Protein-Protein Interaction ----
... ♣. Different cells have different ECM ♣. Protein-protein interaction plays a very important role in signal transduction. ...
... ♣. Different cells have different ECM ♣. Protein-protein interaction plays a very important role in signal transduction. ...
Abstract
... receptor antagonists that block both AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes (eg saralasin). AT1-selective antagonists have also been studied in this model, at pharmacologically relevant doses. The AT1 blocker eprosartan reduced sympathetically-stimulated increases in blood pressure to a greater extent than c ...
... receptor antagonists that block both AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes (eg saralasin). AT1-selective antagonists have also been studied in this model, at pharmacologically relevant doses. The AT1 blocker eprosartan reduced sympathetically-stimulated increases in blood pressure to a greater extent than c ...
Effects of the histamine H3 receptor antagonist ABT
... to learning and memory function using a modified elevated plus-maze test in mice. In this test, the latency for mice to move from the open arm to the enclosed arm (i.e., transfer latency) was used as an index of memory. We tested whether ABT-239 (4-(2-{2-[(2R)-2methylpyrrolidinyl]ethyl}-benzofuran-5 ...
... to learning and memory function using a modified elevated plus-maze test in mice. In this test, the latency for mice to move from the open arm to the enclosed arm (i.e., transfer latency) was used as an index of memory. We tested whether ABT-239 (4-(2-{2-[(2R)-2methylpyrrolidinyl]ethyl}-benzofuran-5 ...
Population responses
... Mixed antagonist: binds to separate site but modulates the ability of agonist to bind Physiological antagonist: a drug (or endogenous mediator) that antagonizes the effect of another drug (or endogenous mediator) by producing an opposing physiological response, typically by a different type of recep ...
... Mixed antagonist: binds to separate site but modulates the ability of agonist to bind Physiological antagonist: a drug (or endogenous mediator) that antagonizes the effect of another drug (or endogenous mediator) by producing an opposing physiological response, typically by a different type of recep ...