MFJ-259B HF/VHF SWR Analyzer
... Narrowband detectors are expensive, since narrowband detector systems must have at least one selective gainstabilized receiver. Narrowband detectors would price antenna and impedance analyzers far outside the price range of most hobbyists. Broadband detectors are sensitive to out-of-band external vo ...
... Narrowband detectors are expensive, since narrowband detector systems must have at least one selective gainstabilized receiver. Narrowband detectors would price antenna and impedance analyzers far outside the price range of most hobbyists. Broadband detectors are sensitive to out-of-band external vo ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon
... With the advancement in miniaturization of semiconductor structures, ESD handling capability of the devices is becoming a concern. Increasing ESD handling capability of the I/O ports costs additional chip size and affects the I/O capacitance significantly. This is very important for high frequency d ...
... With the advancement in miniaturization of semiconductor structures, ESD handling capability of the devices is becoming a concern. Increasing ESD handling capability of the I/O ports costs additional chip size and affects the I/O capacitance significantly. This is very important for high frequency d ...
A Low-Loss VHF/UHF Diplexer
... are necessary before using the diplexer. The high performance of the diplexer, which compares with similar professional products on the market, cannot be realized without sophisticated measurement equipment. When operating at higher power levels (up to 100 W for VHF or UHF input), perfect adjustment ...
... are necessary before using the diplexer. The high performance of the diplexer, which compares with similar professional products on the market, cannot be realized without sophisticated measurement equipment. When operating at higher power levels (up to 100 W for VHF or UHF input), perfect adjustment ...
Comparison of Transverter vs. Tranceiver Performance (K2DH)
... VHF/UHF- more than enough for most weak-signal operation. So, what are the disadvantages? First, generally, transceivers cost quite a bit of money. Newer all-mode transceivers can easily run $1-2k, more in some cases. For someone starting out on these bands, this kind of expense may be out of range. ...
... VHF/UHF- more than enough for most weak-signal operation. So, what are the disadvantages? First, generally, transceivers cost quite a bit of money. Newer all-mode transceivers can easily run $1-2k, more in some cases. For someone starting out on these bands, this kind of expense may be out of range. ...
WM-UR800 8 Channel UHF Wireless Microphone
... The Wireless Microphone System is a professional and commercial grade UHF system. It supports up to 1600 individual channels to be used simultaneously (multiple receivers required, 200 point x 8 band =1600 channels). This is perfect for any situation where multiple microphones are required. This sys ...
... The Wireless Microphone System is a professional and commercial grade UHF system. It supports up to 1600 individual channels to be used simultaneously (multiple receivers required, 200 point x 8 band =1600 channels). This is perfect for any situation where multiple microphones are required. This sys ...
Terms
... inside buildings than VHF signals? = The shorter wavelength allows them to more easily penetrate the structure of buildings What antenna polarization is normally used for longdistance weak-signal CW and SSB contacts using the VHF and UHF bands? = Horizontal What can happen if the antennas at opposit ...
... inside buildings than VHF signals? = The shorter wavelength allows them to more easily penetrate the structure of buildings What antenna polarization is normally used for longdistance weak-signal CW and SSB contacts using the VHF and UHF bands? = Horizontal What can happen if the antennas at opposit ...
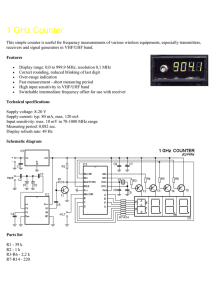
1 GHz Counter
... D1, D2 - BAT41 (BAR19) - may be ommited D3 - HD-M514RD (red) or HD-M512RD (green), 4-digits multiplex driven LED display from HP, or four standard 1-digit LED displays X1 - 4.000 MHz crystal BNC input connector To use with a receiver as a digital scale, close the -10,7 pins. IC3 program download: co ...
... D1, D2 - BAT41 (BAR19) - may be ommited D3 - HD-M514RD (red) or HD-M512RD (green), 4-digits multiplex driven LED display from HP, or four standard 1-digit LED displays X1 - 4.000 MHz crystal BNC input connector To use with a receiver as a digital scale, close the -10,7 pins. IC3 program download: co ...
WM-UR802 8 Channel UHF Wireless Microphone
... 8 Channel UHF Wireless Microphone System WM-UR802 Applications: Board room, conference hall, class room, conventional center and religious gathering. ...
... 8 Channel UHF Wireless Microphone System WM-UR802 Applications: Board room, conference hall, class room, conventional center and religious gathering. ...
UHF television broadcasting
UHF television broadcasting is the use of ultra high frequency (UHF) radio for over the air transmission of television signals. UHF frequencies are used for both analog and digital television broadcasts. UHF channels are typically given higher channel numbers like the US arrangement with channels numbered 14 to 83.UHF broadcasting became possible due to the introduction of new high-frequency vacuum tubes developed by Philips immediately prior to the opening of World War II. These were used in experimental television receivers in the UK in the 1930s, and became widely used during the war as radar receivers. These tubes flooded the market in the post-war era. At the same time, the development of color television was taking its first steps, initially based on different transmission systems. The US FCC set aside a block of the then-unused and now-practical UHF frequencies for color television use. The introduction of the backward compatible NTSC standard led to these channels being released for any television use in 1952.Early receivers were generally less efficient at UHF band reception, and the signals are also subject to more environmental interference. Additionally, the signals are less susceptible to diffraction effects, which can improve reception at long range. UHF therefore has to be broadcast at much higher powers to provide the same reception as VHF. UHF generally had less clear signals, and for some markets, became the home of smaller broadcasters who were not willing to bid on the more coveted VHF allocations. These issues are greatly reduced with digital television, and today most over-the-air broadcasts take place on UHF, while VHF channels are being retired. To avoid the appearance of disappearing channels, digital broadcast systems have a virtual channel concept, allowing stations to keep their original VHF channel number while actually broadcasting on a UHF frequency.Over time a number of former television channels in the upper UHF band have been re-designated for other uses. Channel 37 was not used in the US and some other countries in order to prevent interference with radio astronomy. In 1983, the US FCC removed channels 70 through 83 and reassigned them to Land Mobile Radio System. In 2009, with the move to digital television complete in the US, channels 52 through 69 were reallocated as the 700 MHz band for cellular telephone service. In 2011, Channel 51 was removed to prevent interference with the 700 MHz band. The US UHF channel map now includes channels 14 through 36 and 38 through 50.