Optical Atomic Clocks
... As Maxwell realized, an atom can be an ideal frequency standard because, as far as we know, one atom is exactly identical to another atom of the same species. Therefore, if we build a device that registers the frequency of a natural oscillation of an atom, say the mechanical oscillations of an elect ...
... As Maxwell realized, an atom can be an ideal frequency standard because, as far as we know, one atom is exactly identical to another atom of the same species. Therefore, if we build a device that registers the frequency of a natural oscillation of an atom, say the mechanical oscillations of an elect ...
Optical atomic clocks
... The degree to which we can synchronize a local oscillator’s frequency to the atoms’ natural oscillations is always limited by noise in the measurement protocol we use to establish this synchronization. In addition, although isolated atoms are in a sense perfect, their natural frequencies can be shif ...
... The degree to which we can synchronize a local oscillator’s frequency to the atoms’ natural oscillations is always limited by noise in the measurement protocol we use to establish this synchronization. In addition, although isolated atoms are in a sense perfect, their natural frequencies can be shif ...
Optical Atomic Clocks for Space
... theory and hence fundamentally incomplete because it does not include quantum effects. An extremely important goal in fundamental physics is therefore the development of a quantum theory of gravity that describes all particle interactions in a unified way (Figure 1). A new theory of quantum gravity ...
... theory and hence fundamentally incomplete because it does not include quantum effects. An extremely important goal in fundamental physics is therefore the development of a quantum theory of gravity that describes all particle interactions in a unified way (Figure 1). A new theory of quantum gravity ...
Einstein_Discover (Chicago refs)
... We have learned that the work that led up to Einstein’s great discoveries was long and complicated, typically spanning years. There is no easy synopsis that does not mislead in some aspects. Much of the work was devoted to lengthy, mundane investigations. They brought moments of disappointment, fru ...
... We have learned that the work that led up to Einstein’s great discoveries was long and complicated, typically spanning years. There is no easy synopsis that does not mislead in some aspects. Much of the work was devoted to lengthy, mundane investigations. They brought moments of disappointment, fru ...
Optical atomic clocks
... of optical frequency standards and clocks was how to measure optical frequencies. The oscillations of the electric field for visible frequencies are too fast (∼ 1015 per second) to detect directly, so there was no way to measure the absolute frequency of the optical clocks (i.e., relative to the SI ...
... of optical frequency standards and clocks was how to measure optical frequencies. The oscillations of the electric field for visible frequencies are too fast (∼ 1015 per second) to detect directly, so there was no way to measure the absolute frequency of the optical clocks (i.e., relative to the SI ...
Time Travel and Warp Drives
... some particular technological advance might be achieved. Scientists and engineers by contrast work to answer “how,” attempting to extend our knowledge of the laws of nature and to apply this knowledge creatively in new situations. The fact that science, in due course, frequently has provided answers ...
... some particular technological advance might be achieved. Scientists and engineers by contrast work to answer “how,” attempting to extend our knowledge of the laws of nature and to apply this knowledge creatively in new situations. The fact that science, in due course, frequently has provided answers ...
Vibrating Rays Theory arXiv:1407.5001v8
... show that the above mentioned anomalies exhibit a signature of VRT. The third reason is related to the time definition in a rotating frame. According to Special Relativity (SRT) there is not a unique way to assign a time, whereas under VRT no contradictions are present. And finally, that VRT is comp ...
... show that the above mentioned anomalies exhibit a signature of VRT. The third reason is related to the time definition in a rotating frame. According to Special Relativity (SRT) there is not a unique way to assign a time, whereas under VRT no contradictions are present. And finally, that VRT is comp ...
$doc.title
... Ross, Dept. of Mathematics, The Ohio State University2 ). He used this for his number theory course, but it applies at least as well to relativity. After all, what will do is to spend the whole semester thinking about space and time. What could be simpler and more familiar? We will have to work hard ...
... Ross, Dept. of Mathematics, The Ohio State University2 ). He used this for his number theory course, but it applies at least as well to relativity. After all, what will do is to spend the whole semester thinking about space and time. What could be simpler and more familiar? We will have to work hard ...
Atomic Clocks - FNWI (Science) Education Service Centre
... development. To measure time, a reference oscillator is needed. It is impossible to measure time itself. It is only possible to measure a frequency or duration. In time measurement, it is assumed that two identical phenomena acquire the same time to be produced, the socalled reproducibility postulat ...
... development. To measure time, a reference oscillator is needed. It is impossible to measure time itself. It is only possible to measure a frequency or duration. In time measurement, it is assumed that two identical phenomena acquire the same time to be produced, the socalled reproducibility postulat ...
OCR GCSE Science Physics A and B PAG 3: Motion
... calculate the acceleration using acceleration (m/s2) = change in speed (m/s) ÷ time (s) 3. Start with a force of 1 N (100 g) and record the acceleration in the table below. 4. Increase the force by 1 N each time and record the accelerations in the table below. 5. Repeat this 2 more times and calcula ...
... calculate the acceleration using acceleration (m/s2) = change in speed (m/s) ÷ time (s) 3. Start with a force of 1 N (100 g) and record the acceleration in the table below. 4. Increase the force by 1 N each time and record the accelerations in the table below. 5. Repeat this 2 more times and calcula ...
Begin Adventure / How to Break the Light Barrier by A.D. 2079 (third
... This edition, the third, has undergone a subtle name change, going from "A.D. 2070" in the title to A.D. 2079 as the timeline is fine-tuned. Because of the almost universal failure to recognize the distinction between physical (reality-based, dynamical) and visual (appearance-based, kinematical) var ...
... This edition, the third, has undergone a subtle name change, going from "A.D. 2070" in the title to A.D. 2079 as the timeline is fine-tuned. Because of the almost universal failure to recognize the distinction between physical (reality-based, dynamical) and visual (appearance-based, kinematical) var ...
Physics 252: Frames of Reference and Newton`s Laws
... earth, but Aristotle himself apparently disagrees, and even Descartes thought that light traveled instantaneously. Galileo, unfairly as usual, in Two New Sciences (page 42) has Simplicio stating the Aristotelian position, SIMP. Everyday experience shows that the propagation of light is instantaneous ...
... earth, but Aristotle himself apparently disagrees, and even Descartes thought that light traveled instantaneously. Galileo, unfairly as usual, in Two New Sciences (page 42) has Simplicio stating the Aristotelian position, SIMP. Everyday experience shows that the propagation of light is instantaneous ...
Relativity
... motion of the reference frame. He examined Maxwell’s ideas as applied to a frame-ofreference experiment that required only a magnet and a closed coil of wire. Einstein used a method called a thought experiment, which is an experiment carried out in the imagination but not actually performed. A thoug ...
... motion of the reference frame. He examined Maxwell’s ideas as applied to a frame-ofreference experiment that required only a magnet and a closed coil of wire. Einstein used a method called a thought experiment, which is an experiment carried out in the imagination but not actually performed. A thoug ...
Acceleration Analysi..
... to be able to withstand such high levels of acceleration. Since much machinery is designed for human use, these acceleration tolerance data should be of great interest and value to the machine designer. Several references dealing with these human factors data are provided in the bibliography to Chap ...
... to be able to withstand such high levels of acceleration. Since much machinery is designed for human use, these acceleration tolerance data should be of great interest and value to the machine designer. Several references dealing with these human factors data are provided in the bibliography to Chap ...
Relativity Presentation
... was a problem with ‘simultaneity’ if all observers saw light with the same speed... Ana and Ben see the light hit the ends at the same time... ...
... was a problem with ‘simultaneity’ if all observers saw light with the same speed... Ana and Ben see the light hit the ends at the same time... ...
2 Spacetime and General - Farmingdale State College
... occurs almost instantaneously at the point B.) Hence the lapse of proper time for an accelerated observer is less than the proper time for an observer at rest. Thus, time must slow down during an acceleration, a result that we will confirm in our study of general relativity. In chapter 1 we discusse ...
... occurs almost instantaneously at the point B.) Hence the lapse of proper time for an accelerated observer is less than the proper time for an observer at rest. Thus, time must slow down during an acceleration, a result that we will confirm in our study of general relativity. In chapter 1 we discusse ...
Section 4.3 - CPO Science
... down, the speed decreases so the car covers less distance each second. The position vs. time graph gets shallower with time. ...
... down, the speed decreases so the car covers less distance each second. The position vs. time graph gets shallower with time. ...
On the Experimental Proofs of Relativistic Length Contraction and
... as indicating that the rate of a moving clock, "when viewed from the stationary system," is slower by the factor 7 than the rate of the same clock at rest in the stationary system [4], Later he generalized this statement by declaring that "a living organism after any lengthy flight could be returned ...
... as indicating that the rate of a moving clock, "when viewed from the stationary system," is slower by the factor 7 than the rate of the same clock at rest in the stationary system [4], Later he generalized this statement by declaring that "a living organism after any lengthy flight could be returned ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter H1
... The observer moving along with the protons will measure an electric force F eE , where E is the electric field caused by one of the protons at the position of the other. The observer in the lab will measure an electric force Fe eE and a magnetic force Fm evB since the lab observer sees a mov ...
... The observer moving along with the protons will measure an electric force F eE , where E is the electric field caused by one of the protons at the position of the other. The observer in the lab will measure an electric force Fe eE and a magnetic force Fm evB since the lab observer sees a mov ...
Solved Problems in Special Relativity - UBC PHAS
... Eq. (4) indicates that the time interval ∆t measured by observers at rest in S is larger than the time interval ∆t0 measured by an observer at rest with respect to the clock. That is, “moving clocks run slow”. It is important to note that Eq. (4) relates clock readings on a single clock in S 0 with ...
... Eq. (4) indicates that the time interval ∆t measured by observers at rest in S is larger than the time interval ∆t0 measured by an observer at rest with respect to the clock. That is, “moving clocks run slow”. It is important to note that Eq. (4) relates clock readings on a single clock in S 0 with ...
Chapter 11 RELATIVITY
... of the theoretical mechanism that explained light's ability to travel through a vacuum--a step many physicists of the day were not willing to take. Einstein said enough. If ether cannot be experimentally observed, there is no reason to assume it exists at all. b.) The second assumption--that the law ...
... of the theoretical mechanism that explained light's ability to travel through a vacuum--a step many physicists of the day were not willing to take. Einstein said enough. If ether cannot be experimentally observed, there is no reason to assume it exists at all. b.) The second assumption--that the law ...
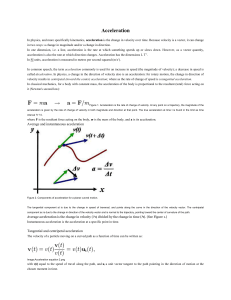
Acceleration
... Extension of this approach to three-dimensional space curves that cannot be contained on a planar surface leads to the Frenet-Serret formulas. ...
... Extension of this approach to three-dimensional space curves that cannot be contained on a planar surface leads to the Frenet-Serret formulas. ...
A moving clock ticks slower.
... The time interval between two events which occur at the same place in an observer’s frame of reference is called the proper time of the interval between the events. We use t0 to denote proper time. Suppose you are timing an event by clicking a stopwatch on at the start and off at the end. In order f ...
... The time interval between two events which occur at the same place in an observer’s frame of reference is called the proper time of the interval between the events. We use t0 to denote proper time. Suppose you are timing an event by clicking a stopwatch on at the start and off at the end. In order f ...
Learning material
... blue line. The green line represents the twin astronaut who travels out through space and back again. In the first figure the proper times measured along the green and blue lines are not the same. Time dilation means that the travelling astronaut returns home with less time elapsed than the stay-at- ...
... blue line. The green line represents the twin astronaut who travels out through space and back again. In the first figure the proper times measured along the green and blue lines are not the same. Time dilation means that the travelling astronaut returns home with less time elapsed than the stay-at- ...
Precise Measurement of Time
... nisms have been used over the cen- such as temperature (2). By the midturies as sources of periodicity for dle of the twentieth century, the stameasuring time. Many prehistoric bility of the best gravity pendulum monuments are oriented to detect clocks was approximately 2 x 10- 8 . the summer solsti ...
... nisms have been used over the cen- such as temperature (2). By the midturies as sources of periodicity for dle of the twentieth century, the stameasuring time. Many prehistoric bility of the best gravity pendulum monuments are oriented to detect clocks was approximately 2 x 10- 8 . the summer solsti ...