Full text
... tasks that can be performed using machine learning or data mining techniques. Hence a lot of research has been carried out in this area. Chen et al. [7] use a two-stage approach composed of k-means clustering and support vector machines (SVM) classification together with computation of feature impor ...
... tasks that can be performed using machine learning or data mining techniques. Hence a lot of research has been carried out in this area. Chen et al. [7] use a two-stage approach composed of k-means clustering and support vector machines (SVM) classification together with computation of feature impor ...
Slide 1
... We have data on 224 first-year computer science majors at a large university in a given year. The data for each student include: * Cumulative GPA after 2 semesters at the university (y, response variable) * SAT math score (SATM, x1, explanatory variable) * SAT verbal score (SATV, x2, explanatory va ...
... We have data on 224 first-year computer science majors at a large university in a given year. The data for each student include: * Cumulative GPA after 2 semesters at the university (y, response variable) * SAT math score (SATM, x1, explanatory variable) * SAT verbal score (SATV, x2, explanatory va ...
A Comparative Analysis of Various Clustering Techniques
... successively distributes into smaller clusters, until each object is in one cluster. Hierarchical clustering techniques use various criteria to decide at each step which clusters should be joined as well as where the cluster should be partitioned into different clusters. It is based on measure of cl ...
... successively distributes into smaller clusters, until each object is in one cluster. Hierarchical clustering techniques use various criteria to decide at each step which clusters should be joined as well as where the cluster should be partitioned into different clusters. It is based on measure of cl ...
lab7 - faculty.ucr.edu
... One of the possible ways, a reasonable and cheap one, to resolve the problem is to use the stepwise selection method with SLE and SLS close to ...
... One of the possible ways, a reasonable and cheap one, to resolve the problem is to use the stepwise selection method with SLE and SLS close to ...
A clustering algorithm using the tabu search approach
... each pattern, a random number, 0 < R < 1, is generated. If R > Pt then this pattern is assigned to cluster 2, where i is randomly generated but not the same cluster as in the current solution, 0 < i < TV, and Pt is the predefined probability threshold; otherwise it is partitioned to the same cluster ...
... each pattern, a random number, 0 < R < 1, is generated. If R > Pt then this pattern is assigned to cluster 2, where i is randomly generated but not the same cluster as in the current solution, 0 < i < TV, and Pt is the predefined probability threshold; otherwise it is partitioned to the same cluster ...
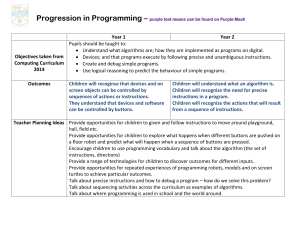
Outcomes Children will recoginse that devices and on screen
... Progression in Programming – purple text means can be found on Purple Mash confidence and understanding with this resource before moving to FSW logo which is a free download. 2DIY could be used to allow children to create games linked to all areas of the curriculum, extending their skills in planni ...
... Progression in Programming – purple text means can be found on Purple Mash confidence and understanding with this resource before moving to FSW logo which is a free download. 2DIY could be used to allow children to create games linked to all areas of the curriculum, extending their skills in planni ...
Round to - Ohio State Computer Science and Engineering
... when copying the formula (Signified by $ in front of column and row) ...
... when copying the formula (Signified by $ in front of column and row) ...
Expectation–maximization algorithm

In statistics, an expectation–maximization (EM) algorithm is an iterative method for finding maximum likelihood or maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimates of parameters in statistical models, where the model depends on unobserved latent variables. The EM iteration alternates between performing an expectation (E) step, which creates a function for the expectation of the log-likelihood evaluated using the current estimate for the parameters, and a maximization (M) step, which computes parameters maximizing the expected log-likelihood found on the E step. These parameter-estimates are then used to determine the distribution of the latent variables in the next E step.