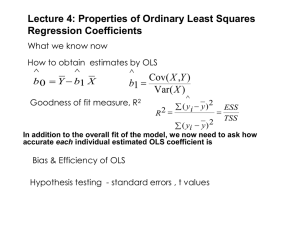
Properties of Least Squares Regression Coefficients: Lecture Slides
... • So this result means that if OLS done on a 100 different (random) samples would not expect to get same result every time – but the average of those estimates would equal the true value • Given 2 (unbiased) estimates will prefer the one whose range of estimates are more concentrated around the true ...
... • So this result means that if OLS done on a 100 different (random) samples would not expect to get same result every time – but the average of those estimates would equal the true value • Given 2 (unbiased) estimates will prefer the one whose range of estimates are more concentrated around the true ...
A Comparative Study of Issues in Big Data Clustering Algorithm with
... agglomerative or divisive. Given n objects to be clustered, agglomerative methods begin with n clusters. In each step, two clusters are chosen and merged. This process continuous until n clusters is generated. While hierarchical methods have been successfully applied to many biological applications, ...
... agglomerative or divisive. Given n objects to be clustered, agglomerative methods begin with n clusters. In each step, two clusters are chosen and merged. This process continuous until n clusters is generated. While hierarchical methods have been successfully applied to many biological applications, ...
Instrumental Variables
... • 3 reasons why this assumption might be violated: – Omitted variable bias: When an unobservable variable is capturing some of the dependent variable and this unobservable variable is not in your model. Instead, the variables you have included are picking up some of the unobserved and the unobserved ...
... • 3 reasons why this assumption might be violated: – Omitted variable bias: When an unobservable variable is capturing some of the dependent variable and this unobservable variable is not in your model. Instead, the variables you have included are picking up some of the unobserved and the unobserved ...
Semi-supervised Clustering with Partial Background Information,
... where Z is a normalization factor so that j=1 fij = 1. To incorporate fij into the objective function Q, we need to identify the class label associated with each cluster j. If k = q, the one-to-one correspondence between the classes and clusters is established during cluster initialization. The clus ...
... where Z is a normalization factor so that j=1 fij = 1. To incorporate fij into the objective function Q, we need to identify the class label associated with each cluster j. If k = q, the one-to-one correspondence between the classes and clusters is established during cluster initialization. The clus ...
Algorithm for Discovering Patterns in Sequences
... ^.{46}[bcx]{1}.{1}[ABx]{1}[aA*x]{1}[AB*]{1}[abx]{1}[aA*x]{1}.{1}[abcx]{1}[ABx]{1}.{1} [ABCx]{1}[ab*x]{1}[ABx]{1}.{1}[ABCx]{1}.{15}$ ...
... ^.{46}[bcx]{1}.{1}[ABx]{1}[aA*x]{1}[AB*]{1}[abx]{1}[aA*x]{1}.{1}[abcx]{1}[ABx]{1}.{1} [ABCx]{1}[ab*x]{1}[ABx]{1}.{1}[ABCx]{1}.{15}$ ...
A Review of Population-based Meta-Heuristic
... elements of a powerful meta-heuristic. Memory-less algorithms carry out a Markov process, as the information which is used to determine the next action is the current state of the search process. There are several ways of using memory. Also, the use of short term usually is different from long term ...
... elements of a powerful meta-heuristic. Memory-less algorithms carry out a Markov process, as the information which is used to determine the next action is the current state of the search process. There are several ways of using memory. Also, the use of short term usually is different from long term ...
2004MinnP6.1
... Synthetic estimators assume a model that describes the relationship between the target variable y and set of ancillary data X. Through this modelled relationship, the ancillary data can be used to predict the mean of y for all target areas. The estimator and its variance are developed on the assumpt ...
... Synthetic estimators assume a model that describes the relationship between the target variable y and set of ancillary data X. Through this modelled relationship, the ancillary data can be used to predict the mean of y for all target areas. The estimator and its variance are developed on the assumpt ...
SOL 5.2a Converting decimals into fractions or fractions into
... How to do it: (converting a decimal number into a fraction) Step 1: Read the decimal number. Step 2: Find the place value where the number ends, This is the bottom number (denominator) Step 3: The decimal number itself is the top number Step 4: Write out the top and bottom number Examples of conver ...
... How to do it: (converting a decimal number into a fraction) Step 1: Read the decimal number. Step 2: Find the place value where the number ends, This is the bottom number (denominator) Step 3: The decimal number itself is the top number Step 4: Write out the top and bottom number Examples of conver ...
proposal document
... Matrix factorization methods have been shown to be a useful decomposition for multivariate data as low dimensional data representations are cruical to numerous applications in statistics, signal processing and machine learning. With the library of factorization methods in Orange we will provide an e ...
... Matrix factorization methods have been shown to be a useful decomposition for multivariate data as low dimensional data representations are cruical to numerous applications in statistics, signal processing and machine learning. With the library of factorization methods in Orange we will provide an e ...
Expectation–maximization algorithm

In statistics, an expectation–maximization (EM) algorithm is an iterative method for finding maximum likelihood or maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimates of parameters in statistical models, where the model depends on unobserved latent variables. The EM iteration alternates between performing an expectation (E) step, which creates a function for the expectation of the log-likelihood evaluated using the current estimate for the parameters, and a maximization (M) step, which computes parameters maximizing the expected log-likelihood found on the E step. These parameter-estimates are then used to determine the distribution of the latent variables in the next E step.