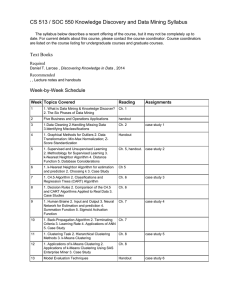
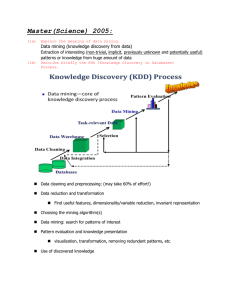
Monte Carlo Methods in Scientific Computing
... crystal is drastically softened in the porous glass and becomes continuous, an effect that was not attributed to finitesize effects but rather to the influence of ...
... crystal is drastically softened in the porous glass and becomes continuous, an effect that was not attributed to finitesize effects but rather to the influence of ...
A Bundle Method to Solve Multivalued Variational Inequalities
... di®erentiable and strongly convex and f¸k gk2IN be a sequence of positive numbers. The problem considered at iteration k is the following: k ...
... di®erentiable and strongly convex and f¸k gk2IN be a sequence of positive numbers. The problem considered at iteration k is the following: k ...
Parameter Estimation for Linear Gaussian Covariance Models
... Linear Gaussian covariance models are Gaussian models with linear constraints on the covariance matrix. Such models arise in many applications, such as stochastic processes from repeated time series data, Brownian motion tree models used for phylogenetic analyses, and network tomography models used ...
... Linear Gaussian covariance models are Gaussian models with linear constraints on the covariance matrix. Such models arise in many applications, such as stochastic processes from repeated time series data, Brownian motion tree models used for phylogenetic analyses, and network tomography models used ...
Title Methods for Constructing Statistical Model Associated with Movement and Neuron Data
... relationship between the arm movement of monkey and its neuron firing rate. This estimation statistical model could be a cornerstone for the neurologists and medical professionals research on how the human body movement could be determined by the neurons of brain. In this paper, I first derive the t ...
... relationship between the arm movement of monkey and its neuron firing rate. This estimation statistical model could be a cornerstone for the neurologists and medical professionals research on how the human body movement could be determined by the neurons of brain. In this paper, I first derive the t ...
Introduction to Statistical Inference and Learning
... Introduction to Statistical Inference and Learning Instructors: Roi Weiss, Boaz Nadler In this course we will cover the basic concepts underlying modern data analysis, machine learning and statistical inference. Subject to time constraints, topics covered will include 1. Basic probability, inequalit ...
... Introduction to Statistical Inference and Learning Instructors: Roi Weiss, Boaz Nadler In this course we will cover the basic concepts underlying modern data analysis, machine learning and statistical inference. Subject to time constraints, topics covered will include 1. Basic probability, inequalit ...
Expectation–maximization algorithm

In statistics, an expectation–maximization (EM) algorithm is an iterative method for finding maximum likelihood or maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimates of parameters in statistical models, where the model depends on unobserved latent variables. The EM iteration alternates between performing an expectation (E) step, which creates a function for the expectation of the log-likelihood evaluated using the current estimate for the parameters, and a maximization (M) step, which computes parameters maximizing the expected log-likelihood found on the E step. These parameter-estimates are then used to determine the distribution of the latent variables in the next E step.