Clustering Sentence-Level Text Using a Novel Fuzzy Relational
... algorithm is capable of identifying overlapping clusters of semantically related sentences. Comparisons with the ARCA algorithm on each of these data sets suggest that FRECCA is capable of identifying softer clusters than ARCA, without sacrificing performance as evaluated by external measures. Altho ...
... algorithm is capable of identifying overlapping clusters of semantically related sentences. Comparisons with the ARCA algorithm on each of these data sets suggest that FRECCA is capable of identifying softer clusters than ARCA, without sacrificing performance as evaluated by external measures. Altho ...
Logistic Regression
... The LOGISTIC procedure continues in spite of the above warning. Results shown are based on the last maximum likelihood iteration. Validity of the model fit is questionable. ...
... The LOGISTIC procedure continues in spite of the above warning. Results shown are based on the last maximum likelihood iteration. Validity of the model fit is questionable. ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... the category of NP-complete problems. And a number of methods have been devised to solve them. Among them FCFS, SJF, Priority Scheduling and RR are of much importance and are widely used for scheduling of jobs in a processor. This study is an effort to develop a simple general algorithm (genetic alg ...
... the category of NP-complete problems. And a number of methods have been devised to solve them. Among them FCFS, SJF, Priority Scheduling and RR are of much importance and are widely used for scheduling of jobs in a processor. This study is an effort to develop a simple general algorithm (genetic alg ...
ERSA Slides - Craig Ulmer
... Pad FP units out to latency P Work on a P iterations at a time Sequentially issue strip of P iterations Thus: ignore FP latency in scheduling ...
... Pad FP units out to latency P Work on a P iterations at a time Sequentially issue strip of P iterations Thus: ignore FP latency in scheduling ...
6. Nitty gritty details on logistic regression
... The LOGISTIC procedure continues in spite of the above warning. Results shown are based on the last maximum likelihood iteration. Validity of the model fit is questionable. ...
... The LOGISTIC procedure continues in spite of the above warning. Results shown are based on the last maximum likelihood iteration. Validity of the model fit is questionable. ...
32. STATISTICS 32. Statistics 1
... Revised September 2009 by G. Cowan (RHUL). This chapter gives an overview of statistical methods used in high-energy physics. In statistics, we are interested in using a given sample of data to make inferences about a probabilistic model, e.g., to assess the model’s validity or to determine the valu ...
... Revised September 2009 by G. Cowan (RHUL). This chapter gives an overview of statistical methods used in high-energy physics. In statistics, we are interested in using a given sample of data to make inferences about a probabilistic model, e.g., to assess the model’s validity or to determine the valu ...
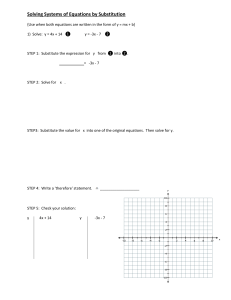
Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution {Use when both
... Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution {Use when both equations are written in the form of y = mx + b} 1) Solve: y = 4x + 14 ❶ ...
... Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution {Use when both equations are written in the form of y = mx + b} 1) Solve: y = 4x + 14 ❶ ...
Expectation–maximization algorithm

In statistics, an expectation–maximization (EM) algorithm is an iterative method for finding maximum likelihood or maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimates of parameters in statistical models, where the model depends on unobserved latent variables. The EM iteration alternates between performing an expectation (E) step, which creates a function for the expectation of the log-likelihood evaluated using the current estimate for the parameters, and a maximization (M) step, which computes parameters maximizing the expected log-likelihood found on the E step. These parameter-estimates are then used to determine the distribution of the latent variables in the next E step.