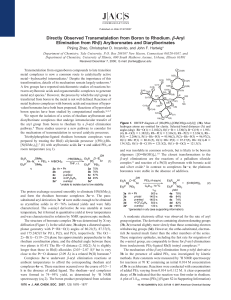
A Tungsten(VI) Nitride Having a W ( Core µ
... for [W(µ-N)(CH2-t-Bu)(OAr)2]2 and [W(µ-15N)(CH2-tBu)(OAr)2]2, respectively. The 507 cm-1 absorption is at considerably lower energy than either 836 or 651 cm-1 and would suggest that the bonding within the W2(µ-N)2 core of the anion is significantly weaker, consistent with addition of the electron t ...
... for [W(µ-N)(CH2-t-Bu)(OAr)2]2 and [W(µ-15N)(CH2-tBu)(OAr)2]2, respectively. The 507 cm-1 absorption is at considerably lower energy than either 836 or 651 cm-1 and would suggest that the bonding within the W2(µ-N)2 core of the anion is significantly weaker, consistent with addition of the electron t ...
Functional group migrations between boron and
... cobalt complex) to 0.463 Å greater than the sum of the covalent radii of transition metal and boron (in a gold complex).29 Furthermore, the nature of the interaction can vary from direct Z1-B interaction with the metal centre to Z7-BC6 interactions in which the boron atom and all six carbon atoms of ...
... cobalt complex) to 0.463 Å greater than the sum of the covalent radii of transition metal and boron (in a gold complex).29 Furthermore, the nature of the interaction can vary from direct Z1-B interaction with the metal centre to Z7-BC6 interactions in which the boron atom and all six carbon atoms of ...
BARIUM NITRATE
... nitrite, Ba(NO2)2. Reactions with soluble metal sulfates or sulfuric acid yield barium sulfate. Many insoluble barium salts, such as the carbonate, oxalate and phosphate of the metal, are precipitated by similar double decomposition reactions. Ba(NO3)2 is an oxidizer and reacts vigorously with commo ...
... nitrite, Ba(NO2)2. Reactions with soluble metal sulfates or sulfuric acid yield barium sulfate. Many insoluble barium salts, such as the carbonate, oxalate and phosphate of the metal, are precipitated by similar double decomposition reactions. Ba(NO3)2 is an oxidizer and reacts vigorously with commo ...
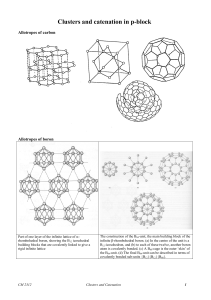
Clusters and Polynuclear Compounds
... fascinating chemical oddities. The exponential growth of their chemistry has been made possible by the advent of X-ray crystallography and many other spectroscopic techniques. The term “metal atom cluster” was introduced in 1964 by F. A. Cotton to designate a finite group of metal atoms held togethe ...
... fascinating chemical oddities. The exponential growth of their chemistry has been made possible by the advent of X-ray crystallography and many other spectroscopic techniques. The term “metal atom cluster” was introduced in 1964 by F. A. Cotton to designate a finite group of metal atoms held togethe ...
Arylboronates and Diarylborinates
... The proton exchange occurred smoothly to eliminate HN(SiMe3)2 and form the rhodium boronate complexes 3a-e. The parasubstituted aryl derivatives 3a-d were stable enough to be obtained as crystalline solids in 45-76% isolated yields and were fully characterized. The o-anisyl derivative 3e was unstabl ...
... The proton exchange occurred smoothly to eliminate HN(SiMe3)2 and form the rhodium boronate complexes 3a-e. The parasubstituted aryl derivatives 3a-d were stable enough to be obtained as crystalline solids in 45-76% isolated yields and were fully characterized. The o-anisyl derivative 3e was unstabl ...
Document
... There is no combination of ligand σ orbitals with the symmetry of the metal T2g orbitals, so these do not participate in σ bonding. ...
... There is no combination of ligand σ orbitals with the symmetry of the metal T2g orbitals, so these do not participate in σ bonding. ...
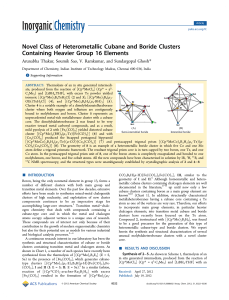
Novel Class of Heterometallic Cubane and Boride Clusters
... accomplishing large-core structures.1 Transition metal−chalcogen chemistry that deals with compounds containing a cubane-type core and in which the metal and chalcogen atoms occupy adjacent vertices is a unique area of research. These compounds are of interest not only because of their contribution ...
... accomplishing large-core structures.1 Transition metal−chalcogen chemistry that deals with compounds containing a cubane-type core and in which the metal and chalcogen atoms occupy adjacent vertices is a unique area of research. These compounds are of interest not only because of their contribution ...
THE p -BLOCK ELEMENTS
... Boron is non-metallic in nature. It is extremely hard and black coloured solid. It exists in many allotropic forms. Due to very strong crystalline lattice, boron has unusually high melting point. Rest of the members are soft metals with low melting point and high electrical conductivity. It is worth ...
... Boron is non-metallic in nature. It is extremely hard and black coloured solid. It exists in many allotropic forms. Due to very strong crystalline lattice, boron has unusually high melting point. Rest of the members are soft metals with low melting point and high electrical conductivity. It is worth ...
Electronic and chemical interactions between boron and carbon
... Figure 9 shows FT-IRAS spectra acquired after dosing different amounts of CO to a surface with 0.26 ML of B at 220 K. For all CO coverages the IR absorption band shows two peaks. Both features shift to higher frequency when the CO coverage increases, probably as a consequence of an enhancement in di ...
... Figure 9 shows FT-IRAS spectra acquired after dosing different amounts of CO to a surface with 0.26 ML of B at 220 K. For all CO coverages the IR absorption band shows two peaks. Both features shift to higher frequency when the CO coverage increases, probably as a consequence of an enhancement in di ...
Multiwalled Boron Nitride Nanotubes: Growth, Properties, and
... CNTs [22], ball-milling [23], chemical vapor deposition (CVD) [24], boron oxide CVD (BOCVD)/floating zone method [25, 26], etc. These BNNTs contain impurities including amorphous boron nitride (a-BN) powders and other solid-state by-products. It is also challenging to use these techniques to directl ...
... CNTs [22], ball-milling [23], chemical vapor deposition (CVD) [24], boron oxide CVD (BOCVD)/floating zone method [25, 26], etc. These BNNTs contain impurities including amorphous boron nitride (a-BN) powders and other solid-state by-products. It is also challenging to use these techniques to directl ...
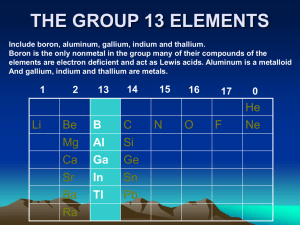
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... Note that in this process, molten Bauxite (Al2O3.nH2O) is the electrolyte. The melting point of Bauxite is high above 2000°C. This mean that large amount of energy is needed. To minimize the energy operational cost, some cryolite (Na3AlF6 ) reduces the melting point to about 1000°C. The aluminium m ...
... Note that in this process, molten Bauxite (Al2O3.nH2O) is the electrolyte. The melting point of Bauxite is high above 2000°C. This mean that large amount of energy is needed. To minimize the energy operational cost, some cryolite (Na3AlF6 ) reduces the melting point to about 1000°C. The aluminium m ...
Class 11 Class 12 The p- Block Element • Group13 (B to Tl
... iii) Boranes react with alkali metal hydrides in diethyl ether to form borohydride complexes. B2H6 + 2MH →2M+[BH4 ]- (M= Li or Na) Metal borohydride (iv) Diborane reacts with ammonia to give borazine at 450 K. B 2 H 6 + 6 NH 3 → 3B 3 N 3 H 6 + 12H 2 • Borazine has a cyclic structure ...
... iii) Boranes react with alkali metal hydrides in diethyl ether to form borohydride complexes. B2H6 + 2MH →2M+[BH4 ]- (M= Li or Na) Metal borohydride (iv) Diborane reacts with ammonia to give borazine at 450 K. B 2 H 6 + 6 NH 3 → 3B 3 N 3 H 6 + 12H 2 • Borazine has a cyclic structure ...
Paper
... research is mostly limited to the nitrides of boron, aluminum and silicon and to a smaller extent to the preparation of nitrides of transition metals. It should be emphasized that most precursors for nitride preparation are air and/or moisture-sensetive compounds. Nevertheless, many ...
... research is mostly limited to the nitrides of boron, aluminum and silicon and to a smaller extent to the preparation of nitrides of transition metals. It should be emphasized that most precursors for nitride preparation are air and/or moisture-sensetive compounds. Nevertheless, many ...
New perspectives in boron-nitrogen chemistry
... recent efforts of several groups to obtain well-defined mixed crystals of hexagonal boron nitride and graphite, BCxN, or also of cubic boron nitride and diamond will have brought more structural clarity than had been necessary for testing some refractory properties of such materials under the aspect ...
... recent efforts of several groups to obtain well-defined mixed crystals of hexagonal boron nitride and graphite, BCxN, or also of cubic boron nitride and diamond will have brought more structural clarity than had been necessary for testing some refractory properties of such materials under the aspect ...
CH 11 The p block element
... Dimeric structure of aluminium chloride – Boron halides do not form dimers because the size of boron is so small that it is unable to coordinate four large-sized halide ions. ...
... Dimeric structure of aluminium chloride – Boron halides do not form dimers because the size of boron is so small that it is unable to coordinate four large-sized halide ions. ...
THE GROUP 13 ELEMENTS - University of the Witwatersrand
... refractory material. In mineral form called corundum and as a gemstone is called sapphire, ruby, emerald or amethyst depending o the amount of metal ion impurities. Dehydration of Al(OH)3 at temperatures below 900 °C result in the formation of γ-alumina, which is metastable polycrystalline form with ...
... refractory material. In mineral form called corundum and as a gemstone is called sapphire, ruby, emerald or amethyst depending o the amount of metal ion impurities. Dehydration of Al(OH)3 at temperatures below 900 °C result in the formation of γ-alumina, which is metastable polycrystalline form with ...
ques for JACS 2008, 130, 16729
... HOMOs and LUMOs different for the group 11 complexes in Figure 11? 4. How would you rationalize the trends in MB interactions between and within group 10 and 11 boratranes metal complexes by appealing to Effective Nuclear Charge arguments? Are the experimental results consistent with what you expec ...
... HOMOs and LUMOs different for the group 11 complexes in Figure 11? 4. How would you rationalize the trends in MB interactions between and within group 10 and 11 boratranes metal complexes by appealing to Effective Nuclear Charge arguments? Are the experimental results consistent with what you expec ...
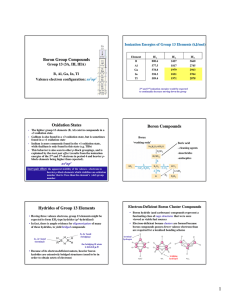
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • Hexagonal boron nitride exists as layers of fused rings, similar in structure to graphite • In these assemblies, boron atoms lie directly over nitrogen atoms ...
... • Hexagonal boron nitride exists as layers of fused rings, similar in structure to graphite • In these assemblies, boron atoms lie directly over nitrogen atoms ...
Boron nitride

Boron nitride is a chemical compound with chemical formula BN, consisting of equal numbers of boron and nitrogen atoms. BN is isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice and thus exists in various crystalline forms. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and softest among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic (sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN. Its hardness is inferior only to diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite and may even be harder than the cubic form.Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are traditionally used as parts of high-temperature equipment. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. Nanotubes of BN can be produced that have a structure similar to that of carbon nanotubes, i.e. graphene (or BN) sheets rolled on themselves, but the properties are very different.