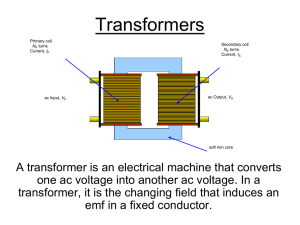
Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories
... recognized hazards that can cause death or serious physical harm to employees – Suitability for installation – Mechanical strength and durability – Electrical insulation – Heating effects under condition of use – Arcing effects – Classification by type, size, voltage, 1926.403(b)(1) current capacity ...
... recognized hazards that can cause death or serious physical harm to employees – Suitability for installation – Mechanical strength and durability – Electrical insulation – Heating effects under condition of use – Arcing effects – Classification by type, size, voltage, 1926.403(b)(1) current capacity ...
Datasheet - Littelfuse
... The NSA5.0AFT3G is designed to protect voltage sensitive components from high voltage, high energy transients. It has excellent clamping capability, high surge capability, low zener impedance and a fast response time. The NSA5.0AFT3G is ideally suited for use in communication systems, automotive, nu ...
... The NSA5.0AFT3G is designed to protect voltage sensitive components from high voltage, high energy transients. It has excellent clamping capability, high surge capability, low zener impedance and a fast response time. The NSA5.0AFT3G is ideally suited for use in communication systems, automotive, nu ...
Additional Protection for Electronic Control Gears for Luminaires
... SP 230/10K Protection Classes I and II When operating electronic components for lighting systems, there is often a need to provide additional protection against voltage surges. These voltage surges, also known as mains transients, can have very different causes. They can be created when switching in ...
... SP 230/10K Protection Classes I and II When operating electronic components for lighting systems, there is often a need to provide additional protection against voltage surges. These voltage surges, also known as mains transients, can have very different causes. They can be created when switching in ...
Digital Rotor Telemetry Short Form Catalog
... Environmentally rugged transmitter — mud/ice/splash resistant Excellent rotor-to-pickup-coil movement tolerance High data integrity and noise immunity ...
... Environmentally rugged transmitter — mud/ice/splash resistant Excellent rotor-to-pickup-coil movement tolerance High data integrity and noise immunity ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #5
... This circuit can be modeled using SPICE in the following way: • vin (t) represents a 60 Hz, 110 VAC (RMS) power source, modeled using: VIN 1 0 0 AC SIN(0 160V 60Hz 0 0) • R1 is a small resistance (eg, R1 ∼ 0.1 Ω), intended only to ensure numerical stability of the simulation. However, it could also ...
... This circuit can be modeled using SPICE in the following way: • vin (t) represents a 60 Hz, 110 VAC (RMS) power source, modeled using: VIN 1 0 0 AC SIN(0 160V 60Hz 0 0) • R1 is a small resistance (eg, R1 ∼ 0.1 Ω), intended only to ensure numerical stability of the simulation. However, it could also ...
DE-ACCM6G - Dimension Engineering
... It is important to note that the X and Y outputs remain unclamped, i.e. 0g still corresponds to Vcc/2 . So if one accidentally powers a DE-ACCM5G with 14V, the outputs would read 7v or more, which might be enough to damage an external device connected at the time. Reverse voltage Even the best engin ...
... It is important to note that the X and Y outputs remain unclamped, i.e. 0g still corresponds to Vcc/2 . So if one accidentally powers a DE-ACCM5G with 14V, the outputs would read 7v or more, which might be enough to damage an external device connected at the time. Reverse voltage Even the best engin ...
CH 13.2 Notes
... current you must force it to pass through the meter. Electrical meters called ammeters, are designed specifically to measure only current. ...
... current you must force it to pass through the meter. Electrical meters called ammeters, are designed specifically to measure only current. ...
Circuit Design - BDJ Engineering
... 2. Engineers use circuit diagrams to communicate components and functions of electrical circuits. ...
... 2. Engineers use circuit diagrams to communicate components and functions of electrical circuits. ...
document
... be impaired. See section 4.11 for additional information on electronic components. Water may affect the filler material of fuses and will degrade the insulation and interruption capabilities. Low voltage power circuit breakers and medium voltage breakers are designed to be maintainable with the poss ...
... be impaired. See section 4.11 for additional information on electronic components. Water may affect the filler material of fuses and will degrade the insulation and interruption capabilities. Low voltage power circuit breakers and medium voltage breakers are designed to be maintainable with the poss ...
NEMA Evaluating Water damaged Electrical Equipment
... be impaired. See section 4.11 for additional information on electronic components. Water may affect the filler material of fuses and will degrade the insulation and interruption capabilities. Low voltage power circuit breakers and medium voltage breakers are designed to be maintainable with the poss ...
... be impaired. See section 4.11 for additional information on electronic components. Water may affect the filler material of fuses and will degrade the insulation and interruption capabilities. Low voltage power circuit breakers and medium voltage breakers are designed to be maintainable with the poss ...
VI. Wye-Broken-Delta Vt, Ground Overvoltage Protection
... straightforward and dependable. However, these relays would typically provide sensitive protection for only about 95% of the stator winding. This is because the fault in the remaining 5% of the winding, near the neutral, does not cause sufficient 60 Hz residual voltage and residual current to operat ...
... straightforward and dependable. However, these relays would typically provide sensitive protection for only about 95% of the stator winding. This is because the fault in the remaining 5% of the winding, near the neutral, does not cause sufficient 60 Hz residual voltage and residual current to operat ...
The World`s Smallest Code-Practice Oscillator
... Secondly, the circuit works over a wide voltage and power range with no modifications. Figure 3 shows a test setup I built using a common 5-W speaker and four AA NiCd batteries. You might have to look twice to see the oscillator circuit because it’s so small, yet this setup produces a loud tone. The ...
... Secondly, the circuit works over a wide voltage and power range with no modifications. Figure 3 shows a test setup I built using a common 5-W speaker and four AA NiCd batteries. You might have to look twice to see the oscillator circuit because it’s so small, yet this setup produces a loud tone. The ...
testing grounding systems - Wyoming Department of Workforce
... cables, power cables, and cords that supply power to tools and portable or mobile equipment must be tested as prescribed in the regulation. This requirement does not apply to double insulated tools or circuits protected by ground-fault-circuit interrupters that trip at 5 milli-amperes or less. ...
... cables, power cables, and cords that supply power to tools and portable or mobile equipment must be tested as prescribed in the regulation. This requirement does not apply to double insulated tools or circuits protected by ground-fault-circuit interrupters that trip at 5 milli-amperes or less. ...
Code 42 Chart Wiring Diagram For EST
... 2. Checks for a normal EST ground path through the ignition module. An EST circuit 423 shorted to ground will also read less than 500 ohms. This will be checked later. 3. As the test light voltage touches circuit 424, the module should switch. 4. The module did not switch. This step checks for: ...
... 2. Checks for a normal EST ground path through the ignition module. An EST circuit 423 shorted to ground will also read less than 500 ohms. This will be checked later. 3. As the test light voltage touches circuit 424, the module should switch. 4. The module did not switch. This step checks for: ...
LTSR 15-NP
... Notes: 1) Only in refOUT mode or with external REF less than 2.525 V and greater than 2.475 V. For external REF out of these limits see leaflet. 2) VOUT is linked to VREF, by conception the difference between these two nodes for IP = 0 is maximum ± 25 mV, 2.475 V < VOUT < 2.525 V. 3) In Re ...
... Notes: 1) Only in refOUT mode or with external REF less than 2.525 V and greater than 2.475 V. For external REF out of these limits see leaflet. 2) VOUT is linked to VREF, by conception the difference between these two nodes for IP = 0 is maximum ± 25 mV, 2.475 V < VOUT < 2.525 V. 3) In Re ...
testing grounding systems
... cables, power cables, and cords that supply power to tools and portable or mobile equipment must be tested as prescribed in the regulation. This requirement does not apply to double insulated tools or circuits protected by ground-fault-circuit interrupters that trip at 5 milli-amperes or less. ...
... cables, power cables, and cords that supply power to tools and portable or mobile equipment must be tested as prescribed in the regulation. This requirement does not apply to double insulated tools or circuits protected by ground-fault-circuit interrupters that trip at 5 milli-amperes or less. ...
Electric Current
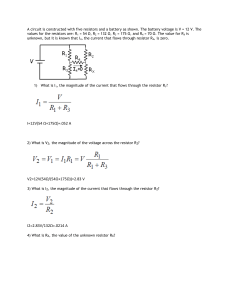
... A circuit is constructed with five resistors and a battery as shown. The battery voltage is V = 12 V. The values for the resistors are: R1 = 54 Ω, R2 = 132 Ω, R3 = 175 Ω, and R4 = 70 Ω. The value for RX is unknown, but it is known that I4, the current that flows through resistor R4, is zero. ...
... A circuit is constructed with five resistors and a battery as shown. The battery voltage is V = 12 V. The values for the resistors are: R1 = 54 Ω, R2 = 132 Ω, R3 = 175 Ω, and R4 = 70 Ω. The value for RX is unknown, but it is known that I4, the current that flows through resistor R4, is zero. ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.