IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... Abstract : The distribution transformer monitoring system is composed of Transformer Terminal Unit (TTU), GPRS wireless communication network and master station. TTU is installed in the transformer, which mainly accomplishes data collection, analysis and record, pops up alarm information in time whe ...
... Abstract : The distribution transformer monitoring system is composed of Transformer Terminal Unit (TTU), GPRS wireless communication network and master station. TTU is installed in the transformer, which mainly accomplishes data collection, analysis and record, pops up alarm information in time whe ...
Ohms Law Lab – Activity
... measured in Volts, or as Joules/Coulomb. Voltage provides the energy in the circuit needed to do work. Resistance is how much current is slowed by a device measured in Ohms. Electrical resistance is needed in a circuit. It allows the energy to be transformed into heat, light, motion, etc. Without re ...
... measured in Volts, or as Joules/Coulomb. Voltage provides the energy in the circuit needed to do work. Resistance is how much current is slowed by a device measured in Ohms. Electrical resistance is needed in a circuit. It allows the energy to be transformed into heat, light, motion, etc. Without re ...
Selecting Directional Elements for Impedance-Grounded
... No grounding method satisfies all these objectives. Utilities have to sacrifice some objectives in order to achieve those that they consider more important. For example, limiting ground fault current reduces equipment thermal stress and communications interference and also increases personnel safety ...
... No grounding method satisfies all these objectives. Utilities have to sacrifice some objectives in order to achieve those that they consider more important. For example, limiting ground fault current reduces equipment thermal stress and communications interference and also increases personnel safety ...
Lesson 3: [llel+llel] Parallel Circuits
... Coulombs have to fall this distance to return to the battery. 4) W hat does our m odel predict the voltage drop across the other light bulb will be? Explain. All model predicts that the voltage (potential) drop across the light bulb will be 1 Volt. The Coulom bs have to fall this distance to return ...
... Coulombs have to fall this distance to return to the battery. 4) W hat does our m odel predict the voltage drop across the other light bulb will be? Explain. All model predicts that the voltage (potential) drop across the light bulb will be 1 Volt. The Coulom bs have to fall this distance to return ...
HW-8-TR-V2
... output, the final tank circuit can affect the received signal. On the loading adjustment there is a large "dip" in receive strength just clockwise of where the transmitter is properly peaked. To avoid the dip, tune your transmitter first (into a dummary load!), then proceed to peaking the preselecto ...
... output, the final tank circuit can affect the received signal. On the loading adjustment there is a large "dip" in receive strength just clockwise of where the transmitter is properly peaked. To avoid the dip, tune your transmitter first (into a dummary load!), then proceed to peaking the preselecto ...
Homework 2
... (24 points) We’ve seen in class that the ideal voltmeter looks like an open circuit, and that the ideal ammeter looks like a short circuit, so as not to affect the circuit it’s measuring. However, in real life—the world in which engineers operate—voltmeters and ammeters aren’t ideal. Voltmeters take ...
... (24 points) We’ve seen in class that the ideal voltmeter looks like an open circuit, and that the ideal ammeter looks like a short circuit, so as not to affect the circuit it’s measuring. However, in real life—the world in which engineers operate—voltmeters and ammeters aren’t ideal. Voltmeters take ...
KNOWLEDGE BASE ARTICLE
... (A or Amps). Current measurements are common on batteries and power supplies (i.e. AA NiMH battery: 2600 mAh, DC power supply: 1.5 A). Current is also induced into targets by the electromagnetic field produced by metal detectors, these are called eddy currents. ...
... (A or Amps). Current measurements are common on batteries and power supplies (i.e. AA NiMH battery: 2600 mAh, DC power supply: 1.5 A). Current is also induced into targets by the electromagnetic field produced by metal detectors, these are called eddy currents. ...
READ THIS FIRST! - Millennia Media
... The HV-3C enclosure measures 19" wide x 1.75" high x 13" deep and is designed for mounting into a standard 1U, 19" equipment rack. If the HV-3C is mounted in a road case or other rack which is prone to strong vibration or shock, it is recommended that the rear of the HV-3C be supported or otherwise ...
... The HV-3C enclosure measures 19" wide x 1.75" high x 13" deep and is designed for mounting into a standard 1U, 19" equipment rack. If the HV-3C is mounted in a road case or other rack which is prone to strong vibration or shock, it is recommended that the rear of the HV-3C be supported or otherwise ...
Roger Stockton`s Notes on the EV
... alone, but on the other hand, it should be pretty simple to place a voltage divider between the cap terminal and pack negative (N) (T6 should you wish to implement the divider at the harness plug or socket) to drop the voltage appropriately. T10: this is the input used to sense the motor voltage. Th ...
... alone, but on the other hand, it should be pretty simple to place a voltage divider between the cap terminal and pack negative (N) (T6 should you wish to implement the divider at the harness plug or socket) to drop the voltage appropriately. T10: this is the input used to sense the motor voltage. Th ...
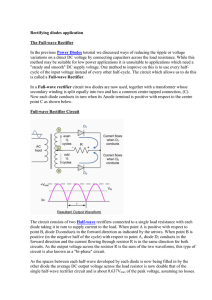
Rectifying diodes application
... different d.c. voltage output different transformer ratios can be used, but one main disadvantage of this type of rectifier is that having a larger transformer for a given power output with two separate windings makes this type of circuit costly compared to a "Bridge Rectifier" circuit equivalent. T ...
... different d.c. voltage output different transformer ratios can be used, but one main disadvantage of this type of rectifier is that having a larger transformer for a given power output with two separate windings makes this type of circuit costly compared to a "Bridge Rectifier" circuit equivalent. T ...
Models WA5A, WA5V Distributor (with Square Root
... ● Do not connect anything to the terminals that are not used in the wiring diagram. Otherwise it may cause the malfunction or damage. ● The power line and input/output signal lines should be installed away from noise-generating sources. Otherwise accuracy cannot be guaranteed. ● The grounding res ...
... ● Do not connect anything to the terminals that are not used in the wiring diagram. Otherwise it may cause the malfunction or damage. ● The power line and input/output signal lines should be installed away from noise-generating sources. Otherwise accuracy cannot be guaranteed. ● The grounding res ...
Model Y482A22/NP 4-channel, line-powered
... WARNING 2: This equipment is designed with user safety in mind; however, the protection provided by the equipment may be impaired if the equipment is used in a manner not specified by PCB Piezotronics, Inc. Caution 1: Cables can kill your equipment. High voltage electrostatic discharge can damage el ...
... WARNING 2: This equipment is designed with user safety in mind; however, the protection provided by the equipment may be impaired if the equipment is used in a manner not specified by PCB Piezotronics, Inc. Caution 1: Cables can kill your equipment. High voltage electrostatic discharge can damage el ...
Tariff Rule No. 2 Character of Servic
... interrupting devices to disconnect completely such motors from the line as a protection against damage due to overheating. It is recommended that such protection devices be installed in each conductor connected to three-phase motors to protect against overheating due to open phase or low voltage con ...
... interrupting devices to disconnect completely such motors from the line as a protection against damage due to overheating. It is recommended that such protection devices be installed in each conductor connected to three-phase motors to protect against overheating due to open phase or low voltage con ...
LM6172 - Brandeis
... Note 3: Continuous short circuit operation can result in exceeding the maximum allowed junction temperature of 150˚C. Note 4: The maximum power dissipation is a function of TJ(max), θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD = (TJ(max) − TA)/θJA. All number ...
... Note 3: Continuous short circuit operation can result in exceeding the maximum allowed junction temperature of 150˚C. Note 4: The maximum power dissipation is a function of TJ(max), θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD = (TJ(max) − TA)/θJA. All number ...
goettlicher_peter_20110509
... No other connection is allowed and all other should be kept galvanic isolated or the risk to introduce currents into the PE-system has to be managed. Within the layer: up to 60mV between GND-PE and local GND-electronics. ...
... No other connection is allowed and all other should be kept galvanic isolated or the risk to introduce currents into the PE-system has to be managed. Within the layer: up to 60mV between GND-PE and local GND-electronics. ...
lecture notes from ECS303
... The most important active elements are voltage and current sources: (a) Voltage source provides the circuit with a specified voltage (e.g. a 1.5V battery) (b) Current source provides the circuit with a specified current (e.g. a 1A current source). In addition, we may characterize the voltage or curr ...
... The most important active elements are voltage and current sources: (a) Voltage source provides the circuit with a specified voltage (e.g. a 1.5V battery) (b) Current source provides the circuit with a specified current (e.g. a 1A current source). In addition, we may characterize the voltage or curr ...
... designed for a maximum fault current of 31,5 kA at the 170 kV busbar. This designed maximum fault current, although relatively small for onshore installations, is a new phenomenon for offshore installations. In case of a short circuit also very high transient currents can be induced in earthing cond ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.



![Lesson 3: [llel+llel] Parallel Circuits](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014097890_1-3c36e45d3295a1e9d71d4d9b7f7bb136-300x300.png)