In this lesson, we review the parts of speech. Chances are you have
... Persons, places, or things ...
... Persons, places, or things ...
AWIV 3A - Austin Casey
... Take out a piece of paper and make your own sentences #1-6. Make one sentence for each noun type. Underline the noun. Label them A-F Ex: A. The bear caught salmon from the river. A ...
... Take out a piece of paper and make your own sentences #1-6. Make one sentence for each noun type. Underline the noun. Label them A-F Ex: A. The bear caught salmon from the river. A ...
Unit Five Summary -
... Adjectives that directly modify a noun are called “attributive” because they attribute a certain characteristic to a noun. Attributive adjectives have the following properties: 1. They follow the noun they modify 2. They agree with the noun they modify in: ...
... Adjectives that directly modify a noun are called “attributive” because they attribute a certain characteristic to a noun. Attributive adjectives have the following properties: 1. They follow the noun they modify 2. They agree with the noun they modify in: ...
File
... I give the backpack to Rosa. Who is receiving the backpack? ROSA The Indirect Object(IO) is the ROSA. ...
... I give the backpack to Rosa. Who is receiving the backpack? ROSA The Indirect Object(IO) is the ROSA. ...
Verbs TBH 18
... Linking verbs may deal with the senses look, feel, taste, and sound that describe the subject. These verbs will not indicate an action. (Fish tastes good) Linking verbs convey a sense of existing or change. Examples include appear, seem, get, turn, and remain. (Spock grew old.) ...
... Linking verbs may deal with the senses look, feel, taste, and sound that describe the subject. These verbs will not indicate an action. (Fish tastes good) Linking verbs convey a sense of existing or change. Examples include appear, seem, get, turn, and remain. (Spock grew old.) ...
Everything you need to know about the
... Everything you need to know about the Irregular French verb avoir Avoir is one of the most common French verbs. It is irregular in conjugation and literally means "to have." However, it is also used in numerous idiomatic expressions and as an auxiliary verb. To Have Avoir means "to have" in most sen ...
... Everything you need to know about the Irregular French verb avoir Avoir is one of the most common French verbs. It is irregular in conjugation and literally means "to have." However, it is also used in numerous idiomatic expressions and as an auxiliary verb. To Have Avoir means "to have" in most sen ...
Present participles
... Remember: participles are verbs transformed into adjectives. As adjectives, they follow the same rules as other Latin adjectives. That means they have to agree with the nouns they modify in Case, Number, and Gender. ...
... Remember: participles are verbs transformed into adjectives. As adjectives, they follow the same rules as other Latin adjectives. That means they have to agree with the nouns they modify in Case, Number, and Gender. ...
grammatik-kanon - TEP
... 8. Adjectives and adverbs The adjective qualifies a noun or a pronoun: A beautiful girl. The girl is beautiful. She is beautiful. The adverb qualifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or a whole sentence. She sings beautifully. She is remarkably pretty. She sings extremely well. Unfortunately I ...
... 8. Adjectives and adverbs The adjective qualifies a noun or a pronoun: A beautiful girl. The girl is beautiful. She is beautiful. The adverb qualifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or a whole sentence. She sings beautifully. She is remarkably pretty. She sings extremely well. Unfortunately I ...
actionverbs
... • Circle the action verb in each sentence below. • Sal listens to his favorite song. • Craig hits the baseball over the fence. • The little pig grunts. ...
... • Circle the action verb in each sentence below. • Sal listens to his favorite song. • Craig hits the baseball over the fence. • The little pig grunts. ...
Verbs
... - The subject is not doing anything. Instead it is or is like something else in the sentence. - Linking verbs tell us that the subject has a word in the predicate that renames it (a noun) or describes it ( an adjective) - In other words, they are equal. ...
... - The subject is not doing anything. Instead it is or is like something else in the sentence. - Linking verbs tell us that the subject has a word in the predicate that renames it (a noun) or describes it ( an adjective) - In other words, they are equal. ...
Studies of particular languages
... meaning depends on the infinitive: thus it can mean' to have good cause to' or it may even have an imperative sense. The haben+zu+infinitive construction has more nuances than the modal verbs; it expresses its modal value less definitely and this lexical indefiniteness allows free play to subjective ...
... meaning depends on the infinitive: thus it can mean' to have good cause to' or it may even have an imperative sense. The haben+zu+infinitive construction has more nuances than the modal verbs; it expresses its modal value less definitely and this lexical indefiniteness allows free play to subjective ...
SAT Writing Workshop - Leuzinger High School
... all, most, some, more, any, less, none • If the noun can be counted (books, cars, people, etc.) then the pronoun is plural. • If the noun cannot be counted (air, water, time, etc.) then the pronoun is singular. Examples: • Most of the pie is gone. • Most of the cookies are gone. • All of the student ...
... all, most, some, more, any, less, none • If the noun can be counted (books, cars, people, etc.) then the pronoun is plural. • If the noun cannot be counted (air, water, time, etc.) then the pronoun is singular. Examples: • Most of the pie is gone. • Most of the cookies are gone. • All of the student ...
Introduction to Linguistics I English Morphosyntax
... (1) the boy –– he (2) the girl –– she 3. Case In English, nouns distinguish only two cases: (i) common case, and (ii) genitive case. The genitive –s is a clitic. (1) the queen’s favorite game the queen of England’s favorite game ...
... (1) the boy –– he (2) the girl –– she 3. Case In English, nouns distinguish only two cases: (i) common case, and (ii) genitive case. The genitive –s is a clitic. (1) the queen’s favorite game the queen of England’s favorite game ...
The aims of the theoretical course of Grammar
... E.g.: We have arranged to meet in the usual place. Do you take these books? She will go there. They are reading a book. According to their morphological structure verbs are divided into: • simple verbs: write, known, love, live; • derived verbs, having affixes: organize, rewrite, magnify, decompose; ...
... E.g.: We have arranged to meet in the usual place. Do you take these books? She will go there. They are reading a book. According to their morphological structure verbs are divided into: • simple verbs: write, known, love, live; • derived verbs, having affixes: organize, rewrite, magnify, decompose; ...
Accents, Syllables and English Grammar
... Mastering NT Greek 2. Accents, Syllables, and English Grammar ...
... Mastering NT Greek 2. Accents, Syllables, and English Grammar ...
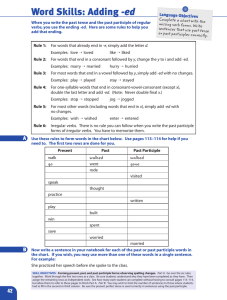
Word Skills: Adding -ed
... For example: She practiced her speech before she spoke to the class. SKILL OBJECTIVES: Forming present, past, and past participle forms; observing spelling changes. Part A: Go over the six rules together. Work through the first two rows as a class. Be sure students understand why they have been comp ...
... For example: She practiced her speech before she spoke to the class. SKILL OBJECTIVES: Forming present, past, and past participle forms; observing spelling changes. Part A: Go over the six rules together. Work through the first two rows as a class. Be sure students understand why they have been comp ...
CFG Phrases for English
... right place. It is in fact a long way from where it’s supposed to appear. • And note that it’s separated from its verb by 2 other verbs. • In Penn Treebank, these types of movement are annotated by have an empty Trace constituent appear in the right place. ...
... right place. It is in fact a long way from where it’s supposed to appear. • And note that it’s separated from its verb by 2 other verbs. • In Penn Treebank, these types of movement are annotated by have an empty Trace constituent appear in the right place. ...
INGLES V Actividad 1 A Actividad 1 A. How to form a phrasal verbs
... A phrasal verb is a combination of a verb and a preposition, a verb and an adverb, or a verb with both an adverb and a preposition, any of which are part of the syntax of the sentence, and so are a complete semantic unit. Sentences, however, may contain direct and indirect objects in addition to the ...
... A phrasal verb is a combination of a verb and a preposition, a verb and an adverb, or a verb with both an adverb and a preposition, any of which are part of the syntax of the sentence, and so are a complete semantic unit. Sentences, however, may contain direct and indirect objects in addition to the ...
Brain_Lexicon_Design..
... had a K-F written frequency of 10 or below. All verbs but one had only verb meanings (one had a secondary noun meaning). Design: This study was broken down into three phases. Phase One: Eight words (four nouns and four verbs) were chosen from the list of 24 words. They appeared on the screen for one ...
... had a K-F written frequency of 10 or below. All verbs but one had only verb meanings (one had a secondary noun meaning). Design: This study was broken down into three phases. Phase One: Eight words (four nouns and four verbs) were chosen from the list of 24 words. They appeared on the screen for one ...
A Remedial English Grammar
... E.g. The fruit is ripened by the sun. The sun has ripened the fruit. The past participle of most intransitive verbs can take only have. E.g. The girl has fainted. ...
... E.g. The fruit is ripened by the sun. The sun has ripened the fruit. The past participle of most intransitive verbs can take only have. E.g. The girl has fainted. ...
File - Renaissance middle school
... Subject and verb agreement and predicate. The subject identifies who or what is the focus with the verb showing its action. The predicate tells the reader what the subject is doing or what it is like. Punctuation (i.e. period (.), question mark (?), colon (:), semi-colon (;), Contraction means ...
... Subject and verb agreement and predicate. The subject identifies who or what is the focus with the verb showing its action. The predicate tells the reader what the subject is doing or what it is like. Punctuation (i.e. period (.), question mark (?), colon (:), semi-colon (;), Contraction means ...
Editing Out Subject-Verb Agreement Errors
... What They Are And How To Correct Them Situation #4 If the subject of the sentence is an indefinite pronoun, or a pronoun that “[does] not refer to specific persons or things,” one should consider the context in which the indefinite pronoun is used to figure out the number (Lunsford 640). Indefinite ...
... What They Are And How To Correct Them Situation #4 If the subject of the sentence is an indefinite pronoun, or a pronoun that “[does] not refer to specific persons or things,” one should consider the context in which the indefinite pronoun is used to figure out the number (Lunsford 640). Indefinite ...