Inorganic Polymers, Second Edition
... A polymer is a very-long-chain macromolecule in which hundreds or thousands of atoms are linked together to form a one-dimensional array. The skeletal atoms usually bear side groups, often two in number, which can be as small as hydrogen, chlorine, or fluorine atoms or as large as aryl or long-chain ...
... A polymer is a very-long-chain macromolecule in which hundreds or thousands of atoms are linked together to form a one-dimensional array. The skeletal atoms usually bear side groups, often two in number, which can be as small as hydrogen, chlorine, or fluorine atoms or as large as aryl or long-chain ...
Structure and packing of phosphatidylcholines in lamellar and
... than ionic detergents is that the biological function of solubilized membrane proteins is in many cases preserved. Moreover, a theoretical understanding of micellar and liquid-crystalline aggregates may be easier to achieve than with ionic detergents due to the absence of electrostatic head group in ...
... than ionic detergents is that the biological function of solubilized membrane proteins is in many cases preserved. Moreover, a theoretical understanding of micellar and liquid-crystalline aggregates may be easier to achieve than with ionic detergents due to the absence of electrostatic head group in ...
Alkyl Chain Length Dependence of the Dynamics and Structure in
... beam from the pulse shaper, which generated pulses 1 and 2 in the 2D IR experiments and the single pump pulse in the PSPP experiments, was crossed in the sample with the probe pulse. The probe pulse, which carried the signal in pump−probe and vibrational echo experiments, was sent to a spectrometer ...
... beam from the pulse shaper, which generated pulses 1 and 2 in the 2D IR experiments and the single pump pulse in the PSPP experiments, was crossed in the sample with the probe pulse. The probe pulse, which carried the signal in pump−probe and vibrational echo experiments, was sent to a spectrometer ...
Aalborg University 2010
... shape of the cavities, containing the binding sites, must not be altered considerably when pressure is applied. Silica is the most common packing material in HPLC. It can be made into uniformed and small particles and the mechanical durability is high. The sol-gel procedure is applicable process to ...
... shape of the cavities, containing the binding sites, must not be altered considerably when pressure is applied. Silica is the most common packing material in HPLC. It can be made into uniformed and small particles and the mechanical durability is high. The sol-gel procedure is applicable process to ...
III. Polyelectrolyte Phenomena (Dautzenberg et al., Polyelectrolytes
... where A and B are constants. The Fuoss-Strauss formula tracks only the downward shift in s/c for c above the maximum, not the lower c rise and maximum itself. Diluting a polyelectrolyte solution with solvent aliquots containing a low but constant value of cs reduces I because polyelectrolyte solut ...
... where A and B are constants. The Fuoss-Strauss formula tracks only the downward shift in s/c for c above the maximum, not the lower c rise and maximum itself. Diluting a polyelectrolyte solution with solvent aliquots containing a low but constant value of cs reduces I because polyelectrolyte solut ...
Design of Thermoresponsive Polymers with
... polymers that exhibit LCST and UCST behavior are attractive because they offer the potential to engineer smart materials that respond only within a specific range of an environmental variable rather than just beyond a critical value. Reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) techniques hav ...
... polymers that exhibit LCST and UCST behavior are attractive because they offer the potential to engineer smart materials that respond only within a specific range of an environmental variable rather than just beyond a critical value. Reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) techniques hav ...
Structure and Properties of Low-Molecular
... an AAM solution containing the dissolved target lowmolecular-mass component, provides the only necessary condition. In the first case, the low-molecularmass compound serves by itself as AAM at elevated temperatures (however, evidently, at temperatures below the glass transition temperature or the me ...
... an AAM solution containing the dissolved target lowmolecular-mass component, provides the only necessary condition. In the first case, the low-molecularmass compound serves by itself as AAM at elevated temperatures (however, evidently, at temperatures below the glass transition temperature or the me ...
Spring mechanics of α-helical polypeptide
... If the vertical and horizontal distances between the two cross-linking points when the tip is in contact with the substrate are v and h, the relationship between the actual length of a fully stretched peptide, L, and the observed stretch length in the F–E curve, S, is L2 ⫽ (S ⫹ v)2 ⫹ h2 Although it ...
... If the vertical and horizontal distances between the two cross-linking points when the tip is in contact with the substrate are v and h, the relationship between the actual length of a fully stretched peptide, L, and the observed stretch length in the F–E curve, S, is L2 ⫽ (S ⫹ v)2 ⫹ h2 Although it ...
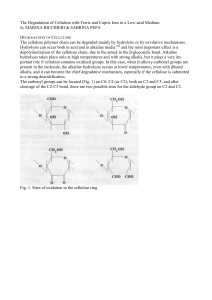
The Degradation of Cellulose with Ferric and Cupric Ions in a Low
... DEGRADATION OF CELLULOSE The cellulose polymer chain can be degraded mainly by hydrolytic or by oxi-dative mechanisms. Hydrolysis can occur both in acid and in alkaline media1"6 and the most important effect is a depolymerization of the cellulose chain, due to the attack to the β-glucosidic bond. Al ...
... DEGRADATION OF CELLULOSE The cellulose polymer chain can be degraded mainly by hydrolytic or by oxi-dative mechanisms. Hydrolysis can occur both in acid and in alkaline media1"6 and the most important effect is a depolymerization of the cellulose chain, due to the attack to the β-glucosidic bond. Al ...
Controlling monomer-sequence using supramolecular
... monomers and/or the growing polymer are required for a template to exert control over any property of the polymer. In literature, the term templating is occasionally also used for systems where covalent bonds are used to influence the properties of polymers (in an intramolecular polymerisation), but ...
... monomers and/or the growing polymer are required for a template to exert control over any property of the polymer. In literature, the term templating is occasionally also used for systems where covalent bonds are used to influence the properties of polymers (in an intramolecular polymerisation), but ...
Controlling monomer-sequence using
... monomers and/or the growing polymer are required for a template to exert control over any property of the polymer. In literature, the term templating is occasionally also used for systems where covalent bonds are used to influence the properties of polymers (in an intramolecular polymerisation), but ...
... monomers and/or the growing polymer are required for a template to exert control over any property of the polymer. In literature, the term templating is occasionally also used for systems where covalent bonds are used to influence the properties of polymers (in an intramolecular polymerisation), but ...
Microporous polymer beads for chemical
... method where the monomer(s) and initiator are completely soluble in the continuous phase, whereas the polymer is not. Polymers precipitate during polymerization, and further polymerization occurs in the precipitated particles by continuous absorption of monomers. Emulsion polymerization: Emulsion po ...
... method where the monomer(s) and initiator are completely soluble in the continuous phase, whereas the polymer is not. Polymers precipitate during polymerization, and further polymerization occurs in the precipitated particles by continuous absorption of monomers. Emulsion polymerization: Emulsion po ...
doc_296
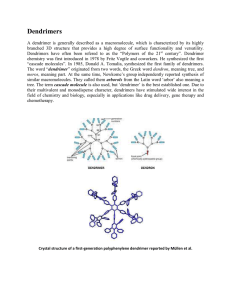
... the concept and implications of 'double exponential' growth. Double exponential growth, similar to a rapid growth technique for linear polymers, involves an AB2 monomer with orthogonal protecting groups for the A and B functionalities. This approach allows the preparation of monomers for both conver ...
... the concept and implications of 'double exponential' growth. Double exponential growth, similar to a rapid growth technique for linear polymers, involves an AB2 monomer with orthogonal protecting groups for the A and B functionalities. This approach allows the preparation of monomers for both conver ...
Photo cross-linkable poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymers III: micro-fabricated temperature responsive hydrogels
... swollen state containing more than 95 wt% of water. Above q Part II: [1]. * Corresponding author. Tel.: þ 49-351-463-337-88; fax: þ 49-351-463371-22. E-mail address: [email protected] (D. Kuckling). ...
... swollen state containing more than 95 wt% of water. Above q Part II: [1]. * Corresponding author. Tel.: þ 49-351-463-337-88; fax: þ 49-351-463371-22. E-mail address: [email protected] (D. Kuckling). ...
Side Chain Chemistry Mediates Backbone Fragmentation in
... rich peptide radicals generated by electron capture methods. In fact, it is shown that side chain chemistry dictates both the occurrence and relative abundance of backbone fragments that are observed. Fragmentation at aromatic residues occurs preferentially over most other amino acids. The origin of ...
... rich peptide radicals generated by electron capture methods. In fact, it is shown that side chain chemistry dictates both the occurrence and relative abundance of backbone fragments that are observed. Fragmentation at aromatic residues occurs preferentially over most other amino acids. The origin of ...
Thermal Decomposition of Polymers - Marcelo Hirschler
... flammable liquids, the gasification process is simply evaporation. The liquid evaporates at a rate required to maintain the equilibrium vapor pressure above the liquid. In the case of polymeric materials, the original material itself is essentially involatile, and the quite large molecules must be b ...
... flammable liquids, the gasification process is simply evaporation. The liquid evaporates at a rate required to maintain the equilibrium vapor pressure above the liquid. In the case of polymeric materials, the original material itself is essentially involatile, and the quite large molecules must be b ...
Hydrogen bond strength and [beta]-sheet propensities: The role of a
... 3). In the p model of Kim and Berg considered here (Fig. 2b), the fact that the peptide group of the experimentally varied residue bonds to water in both the unfolded and the structured states helps to ensure that context-dependent effects due to the neighboring polypeptide chain are absent. Also th ...
... 3). In the p model of Kim and Berg considered here (Fig. 2b), the fact that the peptide group of the experimentally varied residue bonds to water in both the unfolded and the structured states helps to ensure that context-dependent effects due to the neighboring polypeptide chain are absent. Also th ...
Defined megadalton hyaluronan polymer standards. Anal
... but the lines formed by the 0.5- to 1.5-MDa linear standards extrapolate very well to the higher molecular weight data. Overall, the correlation was very good for all of the complexes in a given series as measured by the R values (range 0.987–0.992, n = 6). However, if one compares complexes with id ...
... but the lines formed by the 0.5- to 1.5-MDa linear standards extrapolate very well to the higher molecular weight data. Overall, the correlation was very good for all of the complexes in a given series as measured by the R values (range 0.987–0.992, n = 6). However, if one compares complexes with id ...
Physical Properties of Macromolecules Glass Transitions in Amorphous Polymers
... Conformational entropy of mixing, ΔSmixing Interaction free energy of mixing and the Flory-Huggins thermodynamic χ parameter Energetic interactions within the pure solvent Energetic interactions within the undiluted polymer Energetic interactions within the polymer-solvent mixture Complete expressio ...
... Conformational entropy of mixing, ΔSmixing Interaction free energy of mixing and the Flory-Huggins thermodynamic χ parameter Energetic interactions within the pure solvent Energetic interactions within the undiluted polymer Energetic interactions within the polymer-solvent mixture Complete expressio ...
33 POLYMERS I OPTIONAL MODULE - 2
... like fibres and therefore can be woven into fabrics. The common examples are nylon66, dacron, silk, etc. 3. Thermoplastics : These are linear polymers with very few cross linkages or no cross linkages at all. The polymeric chains are held by weak VANDER WAAL forces and slide over one another. Due to ...
... like fibres and therefore can be woven into fabrics. The common examples are nylon66, dacron, silk, etc. 3. Thermoplastics : These are linear polymers with very few cross linkages or no cross linkages at all. The polymeric chains are held by weak VANDER WAAL forces and slide over one another. Due to ...
THE ROLE OF FeSO4 IN THE OBTAINING OF
... Table 2 that copolymer composition depends on the ratio between initial components of the blend. The increase in PVP amount decreases the grafting efficiency f and increases the grafting degree p. Moreover these values are higher for the copolymers obtained via solution polymerization compared with ...
... Table 2 that copolymer composition depends on the ratio between initial components of the blend. The increase in PVP amount decreases the grafting efficiency f and increases the grafting degree p. Moreover these values are higher for the copolymers obtained via solution polymerization compared with ...
METO 637
... Photochemical chain initiation • In the troposphere several species are present that absorb solar ultraviolet radiation and can initiate radicalchain reactions. • Ozone is phololyzed at wavelengths less than 310 nm and the following reactions occur: O3 + hν → O1(D) + O2(1Δg) O1(D) + H2O → OH + OH • ...
... Photochemical chain initiation • In the troposphere several species are present that absorb solar ultraviolet radiation and can initiate radicalchain reactions. • Ozone is phololyzed at wavelengths less than 310 nm and the following reactions occur: O3 + hν → O1(D) + O2(1Δg) O1(D) + H2O → OH + OH • ...
Tuning the Molecular Properties of Polybenzimidazole by
... groups which are far apart in the benzene ring because acid groups are probably unable to form the internal dimmers through hydrogen bonding interaction between carboxylic groups of the same acids or coming from two different molecules of the acid.35,36 Thus TPA (1,4-) has lower solubility than IPA ...
... groups which are far apart in the benzene ring because acid groups are probably unable to form the internal dimmers through hydrogen bonding interaction between carboxylic groups of the same acids or coming from two different molecules of the acid.35,36 Thus TPA (1,4-) has lower solubility than IPA ...
Problem 14. MAGNESIUM DETERMINATION
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, G. This is the universal principle. If G < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, G. This is the universal principle. If G < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, DG. This is the universal principle. If DG < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
Radical polymerization

Free radical polymerization is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free radical building blocks. Free radicals can be formed via a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules. Following its generation, the initiating free radical adds (nonradical) monomer units, thereby growing the polymer chain.Free radical polymerization is a key synthesis route for obtaining a wide variety of different polymers and material composites. The relatively non-specific nature of free radical chemical interactions makes this one of the most versatile forms of polymerization available and allows facile reactions of polymeric free radical chain ends and other chemicals or substrates. In 2001, 40 billion of the 110 billion pounds of polymers produced in the United States were produced by free radical polymerization.Free radical polymerization is a type of chain growth polymerization, along with anionic, cationic and coordination polymerization.









![Hydrogen bond strength and [beta]-sheet propensities: The role of a](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001016933_1-f0906f8b94f5874649a4b4bfebaa6ef4-300x300.png)