Verb, Adverbs, Conjunctions, Interjections Practice sheets
... behind the tree. In, under, near, and behind are prepositions. Examples I will gladly lend that book to you. The red house on the corner is ours. The dog hid underneath the porch. He ran after the bus. The following is a list of the most commonly used PREPOSITIONS about ...
... behind the tree. In, under, near, and behind are prepositions. Examples I will gladly lend that book to you. The red house on the corner is ours. The dog hid underneath the porch. He ran after the bus. The following is a list of the most commonly used PREPOSITIONS about ...
Name Date Period ______ DGP Review Match each part of speech
... Identify the complete subject(s) and simple subject(s) in each sentence by underlining the complete subject once and writing an “S” above the simple subject. Identify the complete predicate(s) by underlining them twice, and put a P above the simple predicate. 21. He himself was a very old man with s ...
... Identify the complete subject(s) and simple subject(s) in each sentence by underlining the complete subject once and writing an “S” above the simple subject. Identify the complete predicate(s) by underlining them twice, and put a P above the simple predicate. 21. He himself was a very old man with s ...
Parts of Speech
... Hooking up words, phrases, clauses, and complex sentences. Conjunction examples-and, or, but, nor Conjunction example in a sentence- In the mornings, when I am usually wide awake, I love to take a walk through the gardens and down by the lake, where I often see a duck and a drake, and I wonder a ...
... Hooking up words, phrases, clauses, and complex sentences. Conjunction examples-and, or, but, nor Conjunction example in a sentence- In the mornings, when I am usually wide awake, I love to take a walk through the gardens and down by the lake, where I often see a duck and a drake, and I wonder a ...
English Class 2-22-08
... Sometimes there can be more than two objects. That’s called Compound Object Nouns ...
... Sometimes there can be more than two objects. That’s called Compound Object Nouns ...
GLOSARIO DE INGLÉS (Educación Media) Adjective: A word that
... Statement: An affirmative or negative sentence that is not a question or command. Structure: The way that words or part of speech are arranged or put together. Subject: The person or thing which performs the action described by the verb. Support: To help to show something to be true. Synonym: A word ...
... Statement: An affirmative or negative sentence that is not a question or command. Structure: The way that words or part of speech are arranged or put together. Subject: The person or thing which performs the action described by the verb. Support: To help to show something to be true. Synonym: A word ...
Subject-verb agreement
... Collective nouns are especially tricky because they can be singular or plural, depending on the context. Collective nouns are followed by singular verbs when the members of the group are functioning as a single entity, and by plural verbs when they are functioning as individuals within the group. e. ...
... Collective nouns are especially tricky because they can be singular or plural, depending on the context. Collective nouns are followed by singular verbs when the members of the group are functioning as a single entity, and by plural verbs when they are functioning as individuals within the group. e. ...
The Parts of Speech
... than one part of speech – it can change roles depending on the situation and on how you use it. For example, if you play golf, you might use a 9 iron. Iron is a noun here; it is part of the name of an object. If you say the club is made of iron, it is still a noun. But if you say that you plan to ir ...
... than one part of speech – it can change roles depending on the situation and on how you use it. For example, if you play golf, you might use a 9 iron. Iron is a noun here; it is part of the name of an object. If you say the club is made of iron, it is still a noun. But if you say that you plan to ir ...
Transitive Vs. Intransitive Verbs
... Transitive Verbs Q: What are transitive verbs? A: Transitive verbs are action verbs that have an object (person, place, thing) to receive that action. In the first sentence (from the previous slide), the direct object, ball, received the action of the verb, hit. ...
... Transitive Verbs Q: What are transitive verbs? A: Transitive verbs are action verbs that have an object (person, place, thing) to receive that action. In the first sentence (from the previous slide), the direct object, ball, received the action of the verb, hit. ...
Transitive Vs. Intransitive Verbs
... Transitive Verbs Q: What are transitive verbs? A: Transitive verbs are action verbs that have an object (person, place, thing) to receive that action. In the first sentence (from the previous slide), the direct object, ball, received the action of the verb, hit. ...
... Transitive Verbs Q: What are transitive verbs? A: Transitive verbs are action verbs that have an object (person, place, thing) to receive that action. In the first sentence (from the previous slide), the direct object, ball, received the action of the verb, hit. ...
1st handout
... Grammarians must also understand the function of words (and groups of words) at the sentence level. You must be able to identify parts of a sentence: subjects, predicates, objects, complements, phrases, independent clauses, and dependent clauses. A Subject is a noun, pronoun, or noun group about whi ...
... Grammarians must also understand the function of words (and groups of words) at the sentence level. You must be able to identify parts of a sentence: subjects, predicates, objects, complements, phrases, independent clauses, and dependent clauses. A Subject is a noun, pronoun, or noun group about whi ...
Parts of Speech
... – Adverbs may also modify adjectives. – Many, though not all, adverbs end in -ly. – He waved wildly to get her attention. – The shirt he wore to the party was extremely bright. • While nouns answer the questions who and what, adverbs answer the questions how, when, why, and where. • Remember: Adverb ...
... – Adverbs may also modify adjectives. – Many, though not all, adverbs end in -ly. – He waved wildly to get her attention. – The shirt he wore to the party was extremely bright. • While nouns answer the questions who and what, adverbs answer the questions how, when, why, and where. • Remember: Adverb ...
Chapter 11 - EduVenture
... A prepositional phrase is introduced by a preposition and modifies a noun/pronoun or verb A participle phrase modifies a noun A gerund phrase acts as a noun An infinitive phrase can act as a noun or modify a noun or verb ...
... A prepositional phrase is introduced by a preposition and modifies a noun/pronoun or verb A participle phrase modifies a noun A gerund phrase acts as a noun An infinitive phrase can act as a noun or modify a noun or verb ...
ADJECTIVES Adjectives- modify nouns and pronouns by telling
... ADJECTIVES Adjectives- modify nouns and pronouns by telling which one, what kind, how many, or how much. WHICH ONE: this, that, these, those EXAMPLE: This poem moves along quickly. WHAT KIND: square, dirty, fast, regular EXAMPLE: Fast runners make baseball exciting. HOW MANY: some, few, both, thousa ...
... ADJECTIVES Adjectives- modify nouns and pronouns by telling which one, what kind, how many, or how much. WHICH ONE: this, that, these, those EXAMPLE: This poem moves along quickly. WHAT KIND: square, dirty, fast, regular EXAMPLE: Fast runners make baseball exciting. HOW MANY: some, few, both, thousa ...
notes as word document
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
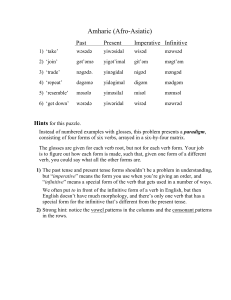
Amharic (Afro
... The glosses are given for each verb root, but not for each verb form. Your job is to figure out how each form is made, such that, given one form of a different verb, you could say what all the other forms are. 1) The past tense and present tense forms shouldn’t be a problem in understanding, but “im ...
... The glosses are given for each verb root, but not for each verb form. Your job is to figure out how each form is made, such that, given one form of a different verb, you could say what all the other forms are. 1) The past tense and present tense forms shouldn’t be a problem in understanding, but “im ...
Basic structure
... of the sentence is predicated. It is typically – but not always – a noun phrase. In traditional grammar it is said to be the „doer'' of the verbal action. A subject is essential in English sentence structure – so much so that a dummy subject (usually „it'') must sometimes be introduced (e.g. It is r ...
... of the sentence is predicated. It is typically – but not always – a noun phrase. In traditional grammar it is said to be the „doer'' of the verbal action. A subject is essential in English sentence structure – so much so that a dummy subject (usually „it'') must sometimes be introduced (e.g. It is r ...
Diagramming Sentences
... The boys are becoming angry. She must be exhausted. Your parents will be proud. ...
... The boys are becoming angry. She must be exhausted. Your parents will be proud. ...
can never oe ma prepOSltlOnalpnrase There and here are never the
... can never oe m a prepOSltlOnalpnrase There and here are never the subject of a sentence. The subject can be an "understood you": Bring me the remote control, please. (You bring it.) ...
... can never oe m a prepOSltlOnalpnrase There and here are never the subject of a sentence. The subject can be an "understood you": Bring me the remote control, please. (You bring it.) ...
Slide 1
... An absolute phrase is usually--but not always--a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun and a participle as well as any related modifiers. An absolute phrase is not a clause because it does not have a true verb. Absolute phrases do not directly connect to or modify any specific word in the s ...
... An absolute phrase is usually--but not always--a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun and a participle as well as any related modifiers. An absolute phrase is not a clause because it does not have a true verb. Absolute phrases do not directly connect to or modify any specific word in the s ...
p28 Ir + A + Infinitive.ppsx
... Verbs that do not follow certain patterns are called IRREGULAR verbs. ...
... Verbs that do not follow certain patterns are called IRREGULAR verbs. ...
Introduction to Grammar
... Rs/E3.1 Recognise and understand the organisational features and typical language of instructional texts (c) Know and use the term verb and understand its importance as an essential feature of a sentence which conveys the action Rs/E3.2 (E3.1b) Use implicit and explicit knowledge of different types ...
... Rs/E3.1 Recognise and understand the organisational features and typical language of instructional texts (c) Know and use the term verb and understand its importance as an essential feature of a sentence which conveys the action Rs/E3.2 (E3.1b) Use implicit and explicit knowledge of different types ...