ELEC34 - aes journals
... types of induction motor faults, their causes and detection techniques. It is found that the detection techniques which evaluate the dynamic behaviour of the signal (such as Wavelet Transform analysis) are best suited for the purpose. Keywords— Fault detection and identification (FDI), Mechanical an ...
... types of induction motor faults, their causes and detection techniques. It is found that the detection techniques which evaluate the dynamic behaviour of the signal (such as Wavelet Transform analysis) are best suited for the purpose. Keywords— Fault detection and identification (FDI), Mechanical an ...
SED2 Variable Frequency Drives
... can lead to problems and increased installation costs. In addition, building design specifications often require compliance with IEEE 519 standard which limits the amount of harmonic current and voltage distortion allowed on the power system. Other products solve the problem by adding more equipment ...
... can lead to problems and increased installation costs. In addition, building design specifications often require compliance with IEEE 519 standard which limits the amount of harmonic current and voltage distortion allowed on the power system. Other products solve the problem by adding more equipment ...
RF Performance Test Guidelines White Paper
... To compensate for this loss, measure the insertion loss from the DUT to the spectrum analyzer. You can do this by replacing the DUT with a calibrated RF generator sending a carrier wave with a known output power of, for instance, 0 dBm (Figure 3.). The power level you now measure on the spectrum ana ...
... To compensate for this loss, measure the insertion loss from the DUT to the spectrum analyzer. You can do this by replacing the DUT with a calibrated RF generator sending a carrier wave with a known output power of, for instance, 0 dBm (Figure 3.). The power level you now measure on the spectrum ana ...
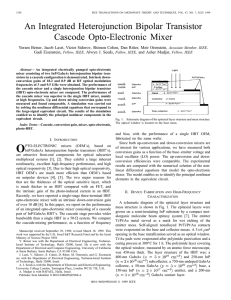
General Description Features
... The architecture of the MAX1846/MAX1847 current-mode PWM controller is a BiCMOS multi-input system that simultaneously processes the output-error signal, the current-sense signal, and a slope-compensation ramp (Functional Diagram). Slope compensation prevents subharmonic oscillation, a potential res ...
... The architecture of the MAX1846/MAX1847 current-mode PWM controller is a BiCMOS multi-input system that simultaneously processes the output-error signal, the current-sense signal, and a slope-compensation ramp (Functional Diagram). Slope compensation prevents subharmonic oscillation, a potential res ...
analysis of the parallel resonance circuit with supercapacitor
... It can be noticed from Fig. 4b, that the imaginary part of the admittance reaches zero value for a given phase resonance radial frequency. Designation of a specified value of resonance radial frequency is possible by solving equation (7) numerically. Fig. 6 presents a graphical way of finding the so ...
... It can be noticed from Fig. 4b, that the imaginary part of the admittance reaches zero value for a given phase resonance radial frequency. Designation of a specified value of resonance radial frequency is possible by solving equation (7) numerically. Fig. 6 presents a graphical way of finding the so ...
How RF transformers work and how they are measured
... Amplitude balance, sometimes called “unbalance”, is the absolute value of the difference in signal amplitude, in dB, between the two outputs of a center-tapped transformer using the center tap as a ground reference. Phase balance, sometimes called “unbalance”, is the absolute value of the difference ...
... Amplitude balance, sometimes called “unbalance”, is the absolute value of the difference in signal amplitude, in dB, between the two outputs of a center-tapped transformer using the center tap as a ground reference. Phase balance, sometimes called “unbalance”, is the absolute value of the difference ...
Low-Cost Grid Connected Photovoltaic System Mahdi Salimi
... proposed which is capable of local load compensation. Usage of high-efficiency DC-DC converters has been investigated in [9] to improve efficiency. In 1994 instantaneous reactive power theory has been proposed by H.Akagi for controlling of Active Power Filters(APF)[10], and in reference [11] such a ...
... proposed which is capable of local load compensation. Usage of high-efficiency DC-DC converters has been investigated in [9] to improve efficiency. In 1994 instantaneous reactive power theory has been proposed by H.Akagi for controlling of Active Power Filters(APF)[10], and in reference [11] such a ...
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation
... 1. Set logic gate and switch Vdd = +3V to +5V and use HCT series logic to provide a TTL driver interface. 2. Control inputs A/B can be driven directly with CMOS logic (HC) with Vdd of +3 to +8 Volts applied to the CMOS logic gates. 3. DC Blocking capacitors are required for each RF port as shown. Ca ...
... 1. Set logic gate and switch Vdd = +3V to +5V and use HCT series logic to provide a TTL driver interface. 2. Control inputs A/B can be driven directly with CMOS logic (HC) with Vdd of +3 to +8 Volts applied to the CMOS logic gates. 3. DC Blocking capacitors are required for each RF port as shown. Ca ...
MAX44264 Ultra-Low Power Op Amp in a Tiny 6-Bump WLP General Description
... The common-mode input range of the MAX44264 extends down to ground, and offers excellent commonmode rejection. These devices are guaranteed not to undergo phase reversal when the input is overdriven. ...
... The common-mode input range of the MAX44264 extends down to ground, and offers excellent commonmode rejection. These devices are guaranteed not to undergo phase reversal when the input is overdriven. ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.