Embedded Generation - Technical Access Standards
... ii) if breaker fail protection system is not installed, the greater of 500 milliseconds and the longest time expected to be taken for all relevant primary protection systems to clear the fault. The above requirements exclude faults that disconnect the generating unit from the power system by removin ...
... ii) if breaker fail protection system is not installed, the greater of 500 milliseconds and the longest time expected to be taken for all relevant primary protection systems to clear the fault. The above requirements exclude faults that disconnect the generating unit from the power system by removin ...
national Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA
... Abstract:-Low frequency oscillations, high torque pulsation are a major disadvantage of three phase permanent-magnet motor configurations. Choosing the proper number of stator slots and winding distribution as well as increasing number of phases are among the possible solutions for reducing torque p ...
... Abstract:-Low frequency oscillations, high torque pulsation are a major disadvantage of three phase permanent-magnet motor configurations. Choosing the proper number of stator slots and winding distribution as well as increasing number of phases are among the possible solutions for reducing torque p ...
pin diode - UniMAP Portal
... If large values of RF current are being switched, the reverse bias voltage must be large enough that the RF voltage during its forward excursion does not induce the flow of RF current through the PIN diode. If the PIN diode becomes warm when operating as a high power switch, the reverse bias voltage ...
... If large values of RF current are being switched, the reverse bias voltage must be large enough that the RF voltage during its forward excursion does not induce the flow of RF current through the PIN diode. If the PIN diode becomes warm when operating as a high power switch, the reverse bias voltage ...
Residential Load Models for Network Planning Purposes
... Other appliances are often used but have low power consumption. They can be combined as base load. The refrigerator is not shown in fig. 2, but its impact on the energy consumption of a household is significant and the peak power is between 80 W to 150 W. C. Classification of Residential Customers ...
... Other appliances are often used but have low power consumption. They can be combined as base load. The refrigerator is not shown in fig. 2, but its impact on the energy consumption of a household is significant and the peak power is between 80 W to 150 W. C. Classification of Residential Customers ...
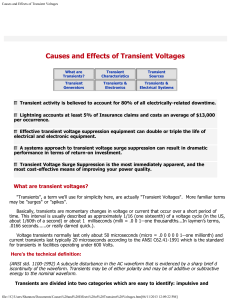
Causes and Effects of Transient Voltages
... file:///C|/Users/Shannon/Documents/Causes%20and%20Effects%20of%20Transient%20Voltages.htm[06/11/2013 12:09:22 PM] ...
... file:///C|/Users/Shannon/Documents/Causes%20and%20Effects%20of%20Transient%20Voltages.htm[06/11/2013 12:09:22 PM] ...
CISPR Guide
... minimum set of essential EMC requirements and test procedures, applicable to all the products or systems intended for operation in this environment, provided there do not exist any specific EMC Standards for a particular product family, product, system or installation. Limits are included, and refer ...
... minimum set of essential EMC requirements and test procedures, applicable to all the products or systems intended for operation in this environment, provided there do not exist any specific EMC Standards for a particular product family, product, system or installation. Limits are included, and refer ...
requirements for grid interconnection of renewable generation systems
... PRG - power produced by renewable generating system PRG = PL + Pout1 - Pin1 Pin – power received from the grid for critical and non critical loads Pout – excess power from renewable generating system to grid Pin1 – power received from the grid for critical loads Pout1 – power from renewable generati ...
... PRG - power produced by renewable generating system PRG = PL + Pout1 - Pin1 Pin – power received from the grid for critical and non critical loads Pout – excess power from renewable generating system to grid Pin1 – power received from the grid for critical loads Pout1 – power from renewable generati ...
Aalborg Universitet High-Performance Control of Paralleled Three-Phase Inverters for Residential
... (CAN bus), a central controller is used to derive compensated voltage references, which will be used by local controller, and exchange with DC/AC modules. This paper is organized as follows. Section II discusses the UPS topologies that are being used and presents the proposed control structure. In o ...
... (CAN bus), a central controller is used to derive compensated voltage references, which will be used by local controller, and exchange with DC/AC modules. This paper is organized as follows. Section II discusses the UPS topologies that are being used and presents the proposed control structure. In o ...
ECEN5817L28
... 5. Full-wave versions of the quasi-resonant switches exhibit very simple control characteristics: the conversion ratio µ is essentially independent of load current. However, these converters exhibit reduced efficiency at light load, due to the large circulating currents. In addition, significant swi ...
... 5. Full-wave versions of the quasi-resonant switches exhibit very simple control characteristics: the conversion ratio µ is essentially independent of load current. However, these converters exhibit reduced efficiency at light load, due to the large circulating currents. In addition, significant swi ...
1.3 Historical View of Microwave Transistors
... • The advances in CMOS processing, continuous scaling of gate length, progress in SOI (silicon on insulator) technology, and development of Si LDMOSFETs (laterally diffused MOSFET) suitability of MOSFETs and CMOS for microwave applications • The SOI concept seems to be more promising because of th ...
... • The advances in CMOS processing, continuous scaling of gate length, progress in SOI (silicon on insulator) technology, and development of Si LDMOSFETs (laterally diffused MOSFET) suitability of MOSFETs and CMOS for microwave applications • The SOI concept seems to be more promising because of th ...
Aalborg Universitet
... Notice that in islanded microgrids, there is no load-side ac voltage available for reference. The inverters themselves produce the ac system voltage. Actually by using the proposed control strategy of microgrids, the load-side ac voltage E is controlled indirectly because ψE is already regulated due ...
... Notice that in islanded microgrids, there is no load-side ac voltage available for reference. The inverters themselves produce the ac system voltage. Actually by using the proposed control strategy of microgrids, the load-side ac voltage E is controlled indirectly because ψE is already regulated due ...
``The use of electric motors for the propulsion of seagoing vessels
... This project concerns the acquisition of technical knowledge regarding the discipline Electrical Engineering. Within this discipline we decided to investigate the use of electric motors for the propulsion of seagoing vessels. The main question of the project, which will be answered in this report, i ...
... This project concerns the acquisition of technical knowledge regarding the discipline Electrical Engineering. Within this discipline we decided to investigate the use of electric motors for the propulsion of seagoing vessels. The main question of the project, which will be answered in this report, i ...
Development of a 60 kHz, 180 kW, Over 85% Efficiency Inductive
... Abstract: Conventional contact-based train power transfer systems have high maintenance costs and safety issues and cause noise and additional aerodynamic drag. Instead of the conventional system, a loosely coupled online wireless power transfer (WPT) system for a train is proposed in this paper. Th ...
... Abstract: Conventional contact-based train power transfer systems have high maintenance costs and safety issues and cause noise and additional aerodynamic drag. Instead of the conventional system, a loosely coupled online wireless power transfer (WPT) system for a train is proposed in this paper. Th ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.